
If a circular race track is banked at angle $\theta $ ($\theta >$ angle of repose), radius of track is r and $\mu $ is coefficient of friction between car and road. Calculate minimum speed of car on inclined plane to avoid slipping.
$\begin{align}
& (a)v=\left[ rg\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta -\mu }{1+\mu \tan \theta } \right) \right] \\
& (b)v={{\left[ rg\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta +\mu }{1-\mu \tan \theta } \right) \right]}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \\
& (c)v={{\left[ rg\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta -\mu }{1+\mu \tan \theta } \right) \right]}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \\
& (d)v={{\left[ rg\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta +\mu }{1+\mu \tan \theta } \right) \right]}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: For the car to avoid slipping, the net force on the car should be balanced in the horizontal and vertical direction. Also, the direction of friction will be towards the banking of the curved road, that is downwards along the slope of the road.
Complete answer:
Let us first examine the case by drawing the free body diagram of the car. The free body diagram of the car is given below:
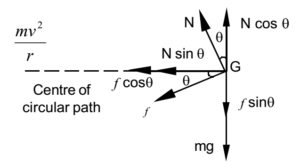
Now, we have to balance the net force on the car in horizontal and vertical direction.
In the vertical direction:
$N\cos \theta $ is the vertical component of the Normal reaction acting upwards.
$mg$ is the weight of the car acting downwards.
$f\sin \theta $ is the vertical component of the frictional force acting downwards.
Where, $f=\mu N$
Thus, balancing the forces in vertical direction, we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow N\cos \theta =mg+\mu N\sin \theta \\
& \Rightarrow mg=N\cos \theta -\mu N\sin \theta \\
\end{align}$ [Let this expression be equation number (1)]
In the horizontal direction:
$\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$ is the centrifugal force acting towards the right.
$N\sin \theta $ is the horizontal component of Normal reaction acting towards the left.
$f\cos \theta $ is the horizontal component of Frictional force acting towards the left.
Where, $f=\mu N$
Thus, balancing the forces in horizontal direction, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}=N\sin \theta +\mu N\cos \theta $ [Let this expression be equation number (2)]
Now, on dividing equation number (2) by equation number (1), we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{}^{m{{v}^{2}}}/{}_{r}}{mg}=\dfrac{N\sin \theta +\mu N\cos \theta }{N\cos \theta -\mu N\sin \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{rg}=\dfrac{\sin \theta +\mu \cos \theta }{\cos \theta -\mu \sin \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=rg\left( \dfrac{\sin \theta +\mu \cos \theta }{\cos \theta -\mu \sin \theta } \right) \\
\end{align}$
Dividing the numerator and denominator of the term inside the bracket by $\cos \theta $, we get:
$\Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=rg\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta +\mu }{1-\mu \tan \theta } \right)$
Now taking square roots both side, we get the velocity as:
$\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{rg\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta +\mu }{1-\mu \tan \theta } \right)}$
Thus, the minimum velocity of the car to avoid slipping should be equal to ${{\left[ rg\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta +\mu }{1-\mu \tan \theta } \right) \right]}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}$ .
Hence, option (b) is the correct option.
Note:
We should always be able to tell the direction of frictional force on a body especially when it is moving or rolling. As it was given to us that the banking angle of the road was greater than the angle of repose, it means that the car could no longer stay stationary on the surface of the road.
Complete answer:
Let us first examine the case by drawing the free body diagram of the car. The free body diagram of the car is given below:

Now, we have to balance the net force on the car in horizontal and vertical direction.
In the vertical direction:
$N\cos \theta $ is the vertical component of the Normal reaction acting upwards.
$mg$ is the weight of the car acting downwards.
$f\sin \theta $ is the vertical component of the frictional force acting downwards.
Where, $f=\mu N$
Thus, balancing the forces in vertical direction, we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow N\cos \theta =mg+\mu N\sin \theta \\
& \Rightarrow mg=N\cos \theta -\mu N\sin \theta \\
\end{align}$ [Let this expression be equation number (1)]
In the horizontal direction:
$\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$ is the centrifugal force acting towards the right.
$N\sin \theta $ is the horizontal component of Normal reaction acting towards the left.
$f\cos \theta $ is the horizontal component of Frictional force acting towards the left.
Where, $f=\mu N$
Thus, balancing the forces in horizontal direction, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}=N\sin \theta +\mu N\cos \theta $ [Let this expression be equation number (2)]
Now, on dividing equation number (2) by equation number (1), we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{}^{m{{v}^{2}}}/{}_{r}}{mg}=\dfrac{N\sin \theta +\mu N\cos \theta }{N\cos \theta -\mu N\sin \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{v}^{2}}}{rg}=\dfrac{\sin \theta +\mu \cos \theta }{\cos \theta -\mu \sin \theta } \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=rg\left( \dfrac{\sin \theta +\mu \cos \theta }{\cos \theta -\mu \sin \theta } \right) \\
\end{align}$
Dividing the numerator and denominator of the term inside the bracket by $\cos \theta $, we get:
$\Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=rg\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta +\mu }{1-\mu \tan \theta } \right)$
Now taking square roots both side, we get the velocity as:
$\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{rg\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta +\mu }{1-\mu \tan \theta } \right)}$
Thus, the minimum velocity of the car to avoid slipping should be equal to ${{\left[ rg\left( \dfrac{\tan \theta +\mu }{1-\mu \tan \theta } \right) \right]}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}$ .
Hence, option (b) is the correct option.
Note:
We should always be able to tell the direction of frictional force on a body especially when it is moving or rolling. As it was given to us that the banking angle of the road was greater than the angle of repose, it means that the car could no longer stay stationary on the surface of the road.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




