
If a circle passes through the point \[( - 1,0)\] touches y- axis at \[(0,2)\], then the chord of the length of the circle along the x-axis is
A. \[\dfrac{5}{2}\]
B. \[5\]
C. \[\dfrac{3}{2}\]
D. \[3\]
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: First use the given data and draw the diagram of the circle and allocate all the given points and then form the equation of circle using given conditions and let it passes through the given point and then calculate the length of chord using distance formula among given points as \[d = \sqrt {{{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2}} \]. The general equation of circle can be given as
\[{\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]where \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] are centres and r is the radius of circle.
Complete step by step Answer:
As the given information are as a circle passes through the point \[( - 1,0)\] touches y- axis at \[(0,2)\]
Diagram:
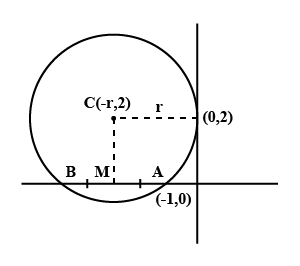
Hence, let the centre of the circle be \[\left( { - r,2} \right)\] and radius of the above circle be \[r\]. As the centre and the radius is known calculate the equation of circle as
\[{\left( {x + r} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 2} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
As point A \[( - 1,0)\] lies on the circle and so let satisfy the point in the equation of circle as
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[{\left( { - 1 + r} \right)^2} + {\left( {0 - 2} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
On expanding the bracket and simplifying the terms
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[{r^2} - 2r + 1 + 4 = {r^2}\]
Hence, the value of r can be given as
\[
\Rightarrow 2r = 5 \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{5}{2} \\
\]
So, the centre of circle is given as \[C\left( { - \dfrac{5}{2},2} \right)\]
The general coordinate of the point M on the x axis can be given as \[M\left( { - \dfrac{5}{2},0} \right)\] and it is quite clear through the diagram.
As the length of chord is \[AB\]
It can be given as \[AB = AM + BM\]
And \[AM\] can be calculated using the distance formula \[d = \sqrt {{{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2}} \] as both points coordinates are known,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[AM = \sqrt {{{\left( {0 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 1 - \left( { - \dfrac{5}{2}} \right)} \right)}^2}} \]
On simplifying further we cans see that,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[AM = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^2}} \]
Hence, on squaring and taking square root we can say that,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[AM = \dfrac{3}{2}\]
As \[AM = BM\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[AB = 2AM\]
Hence, \[AB = 2 \times \dfrac{3}{2} = 3\]
Therefore, the length of chord is \[3\].
Hence, option (D) is our correct answer.
Note: The chord is a line segment that joins 2 points on the circumference of the circle. A chord only covers the part inside the circle. A chord of a circle is a straight line segment whose endpoints both lie on the circle. The infinite line extension of a chord is a secant line or just secant. More generally, a chord is a line segment joining two points on any curve, for instance, an ellipse.
\[{\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]where \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] are centres and r is the radius of circle.
Complete step by step Answer:
As the given information are as a circle passes through the point \[( - 1,0)\] touches y- axis at \[(0,2)\]
Diagram:

Hence, let the centre of the circle be \[\left( { - r,2} \right)\] and radius of the above circle be \[r\]. As the centre and the radius is known calculate the equation of circle as
\[{\left( {x + r} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 2} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
As point A \[( - 1,0)\] lies on the circle and so let satisfy the point in the equation of circle as
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[{\left( { - 1 + r} \right)^2} + {\left( {0 - 2} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
On expanding the bracket and simplifying the terms
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[{r^2} - 2r + 1 + 4 = {r^2}\]
Hence, the value of r can be given as
\[
\Rightarrow 2r = 5 \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{5}{2} \\
\]
So, the centre of circle is given as \[C\left( { - \dfrac{5}{2},2} \right)\]
The general coordinate of the point M on the x axis can be given as \[M\left( { - \dfrac{5}{2},0} \right)\] and it is quite clear through the diagram.
As the length of chord is \[AB\]
It can be given as \[AB = AM + BM\]
And \[AM\] can be calculated using the distance formula \[d = \sqrt {{{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2}} \] as both points coordinates are known,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[AM = \sqrt {{{\left( {0 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 1 - \left( { - \dfrac{5}{2}} \right)} \right)}^2}} \]
On simplifying further we cans see that,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[AM = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^2}} \]
Hence, on squaring and taking square root we can say that,
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[AM = \dfrac{3}{2}\]
As \[AM = BM\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[AB = 2AM\]
Hence, \[AB = 2 \times \dfrac{3}{2} = 3\]
Therefore, the length of chord is \[3\].
Hence, option (D) is our correct answer.
Note: The chord is a line segment that joins 2 points on the circumference of the circle. A chord only covers the part inside the circle. A chord of a circle is a straight line segment whose endpoints both lie on the circle. The infinite line extension of a chord is a secant line or just secant. More generally, a chord is a line segment joining two points on any curve, for instance, an ellipse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




