
If \[0 < x < 1\] ,then \[\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} = \]
A) \[\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\]
B) \[x\]
C) \[x\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \]
D) \[\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \]
Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint: In this question, we have to find the value given expression. We proceed by considering, the inverse term \[y = {\cot ^{ - 1}}x\] and solve it to find the value of \[y = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\] and \[y = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\]. Now we put this value in the expression and simplify to find the required answer. We will also use the fact that \[\cos \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}\theta } \right) = \theta \] and \[\sin \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\theta } \right) = \theta \] where \[\theta \] is the angle.
Complete step by step answer:
This question is based on the inverse trigonometric function.
Consider the given question,
We have to find the value of \[\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
Let us consider the inverse trigonometric ratio \[y = {\cot ^{ - 1}}x\],
now taking inverse , we have
This implies , \[x = \cot y\]
Now we find the value of \[\sin y\] and \[\cos y\]
i.e. \[\sin y = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\] and \[\cos y = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\].
Taking inverse in both the values we get
\[y = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\] and \[y = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\]
Thus, we have \[y = {\cot ^{ - 1}}x = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }} = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\]
Thus from the given question, we have,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
Putting the value from above, we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right)} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
We know that \[\cos \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}\theta } \right) = \theta \] and \[\sin \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\theta } \right) = \theta \],
Hence we have,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }} + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
Taking LCM inside the curly bracket, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {\dfrac{{{x^2} + 1}}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
By cancelling on dividing \[1 + {x^2}\] by \[\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} } \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
On squaring we have,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {1 + {x^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
On simplifying we have,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{x^2}} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
Hence on simplifying we have,
\[ \Rightarrow x\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \]
Hence, \[\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} = x\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \]. So, option \[C\] is correct.
Note:
To find the value of inverse trigonometric ratio when value of one of the trigonometric ratio is given , we proceed as follow:
For example , we find the value of inverse other inverse trigonometric ratio , when we are given \[\theta = {\cot ^{ - 1}}x\]
This imply \[x = \cot \theta \]
We know that \[\cot \theta = \dfrac{{base}}{{perpendicular}}\]
Now from the right angle triangle , we have
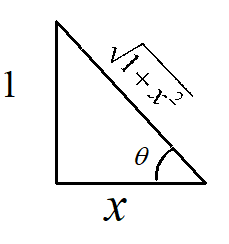
From Pythagoras theorem we have
\[\text{hypotenuse} = \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \]
Hence, \[\sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\]
Taking the inverse of the values we get .
Hence , \[\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\] .
Similarly we can find the value of other inverse trigonometric ratios.
Complete step by step answer:
This question is based on the inverse trigonometric function.
Consider the given question,
We have to find the value of \[\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
Let us consider the inverse trigonometric ratio \[y = {\cot ^{ - 1}}x\],
now taking inverse , we have
This implies , \[x = \cot y\]
Now we find the value of \[\sin y\] and \[\cos y\]
i.e. \[\sin y = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\] and \[\cos y = \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\].
Taking inverse in both the values we get
\[y = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\] and \[y = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\]
Thus, we have \[y = {\cot ^{ - 1}}x = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }} = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\]
Thus from the given question, we have,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
Putting the value from above, we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right)} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
We know that \[\cos \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}\theta } \right) = \theta \] and \[\sin \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\theta } \right) = \theta \],
Hence we have,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }} + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
Taking LCM inside the curly bracket, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {\dfrac{{{x^2} + 1}}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
By cancelling on dividing \[1 + {x^2}\] by \[\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} } \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
On squaring we have,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {1 + {x^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
On simplifying we have,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{x^2}} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
Hence on simplifying we have,
\[ \Rightarrow x\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \]
Hence, \[\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} {\left[ {{{\left\{ {x\cos \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right) + \sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right\}}^2} - 1} \right]^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} = x\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \]. So, option \[C\] is correct.
Note:
To find the value of inverse trigonometric ratio when value of one of the trigonometric ratio is given , we proceed as follow:
For example , we find the value of inverse other inverse trigonometric ratio , when we are given \[\theta = {\cot ^{ - 1}}x\]
This imply \[x = \cot \theta \]
We know that \[\cot \theta = \dfrac{{base}}{{perpendicular}}\]
Now from the right angle triangle , we have
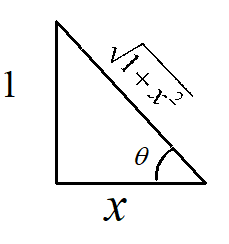
From Pythagoras theorem we have
\[\text{hypotenuse} = \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \]
Hence, \[\sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\]
Taking the inverse of the values we get .
Hence , \[\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}\] .
Similarly we can find the value of other inverse trigonometric ratios.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




