
Identify A and B in the following reaction ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}\xrightarrow{{\text{A}}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}\xleftarrow{{\text{B}}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}{\text{.}}$
A.${\text{A = aq}}{\text{.KOH,B = AgOH}}$
B.${\text{A = alc}}{\text{.KOH,B = aq}}{\text{.NaOH}}$
C.${\text{A = aq}}{\text{.NaOH,B = AgN}}{{\text{O}}_2}$
D.${\text{A = AgN}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{,B = KN}}{{\text{O}}_2}$
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint:
(1) For monohydric alcohols, i.e., alcohols containing only one hydroxyl group, there are many preparation methods. One of the most generally used methods is by heating haloalkanes or alkyl halides with aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. The alkyl halides then undergo hydrolysis to produce alcohols. Another way is to heat the alkyl halides with moist silver oxide.
(2) Dehydration of alkyl halides by alcoholic alkalies give alkenes.
Complete step by step answer:
The given reaction is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}\xrightarrow{{\text{A}}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}\xleftarrow{{\text{B}}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}{\text{.}}$
We need to identify A and B, i.e., the reagents used for converting ethyl chloride to ethyl alcohol.
Ethyl chloride is an alkyl halide and ethyl alcohol is a monohydric alcohol.
So, when ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous potassium hydroxide, we will get ethyl alcohol.
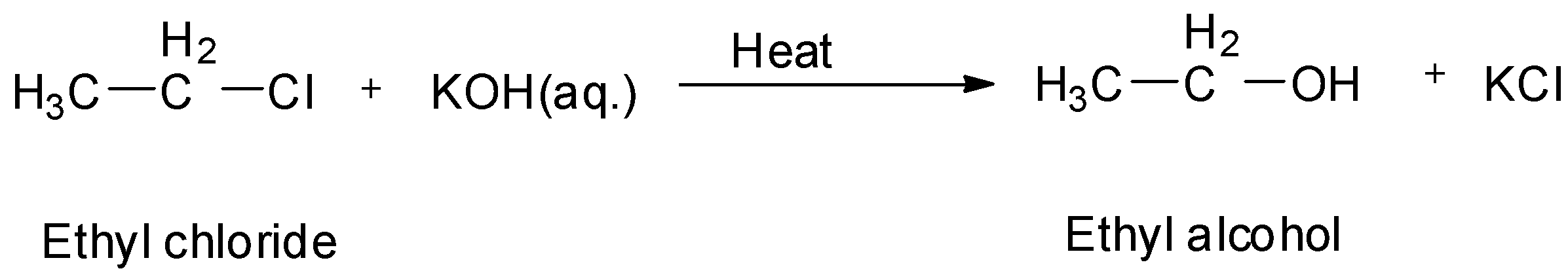
Also, if ethyl chloride is treated with moist silver oxide which is ${\text{AgOH}}$ , we will again get ethyl alcohol.
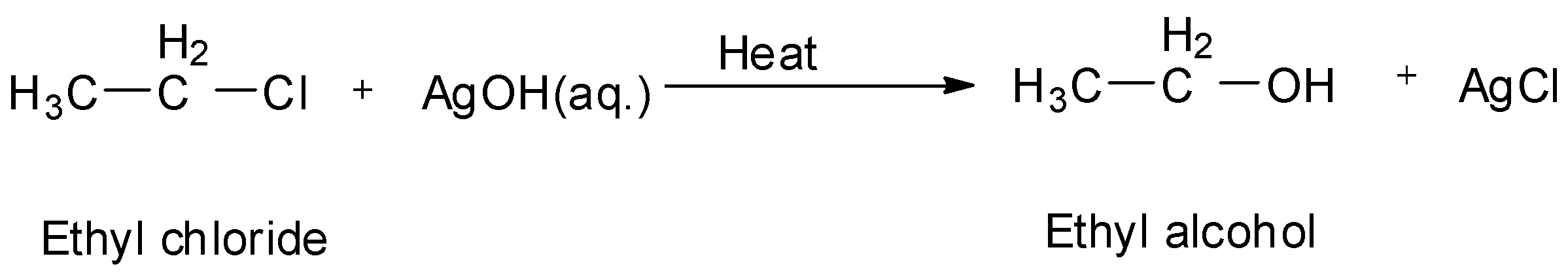
So, A is aq. ${\text{KOH}}$ and B is ${\text{AgOH}}$ .
So, option A is correct.
-When alkyl halide is heated with a concentrated alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide, a molecule of hydrogen halide will be eliminated and an alkene is produced. The hydrogen of the alkyl halide that gets eliminated comes from the carbon atom next to that which carries the halogen, i.e., the ${\text{beta }}$ -carbon and the halogen is eliminated from the carbon atom carrying the halogen, i.e., the ${\text{alpha }}$ -carbon. Therefore, from ethyl chloride, ethene will be formed.
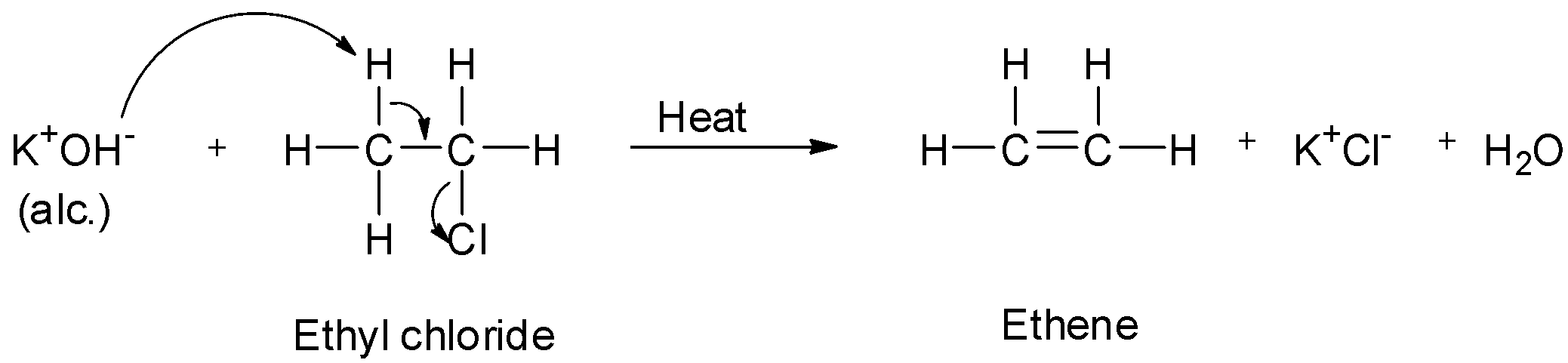
-On treating aqueous sodium hydroxide, it will give ethyl alcohol just like aqueous potassium hydroxide. But, since one of the reagents which is alcoholic potassium hydroxide does not give alcohol, so option B is wrong.
-One of the reagents in the third option is ${\text{AgN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ , i.e., silver nitrite. When aqueous ethanolic solution of haloalkanes are treated with ${\text{AgN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ , nitroalkanes are formed. So, treatment of ethyl chloride with silver nitrite will give nitroethane. So, option C is also not correct.
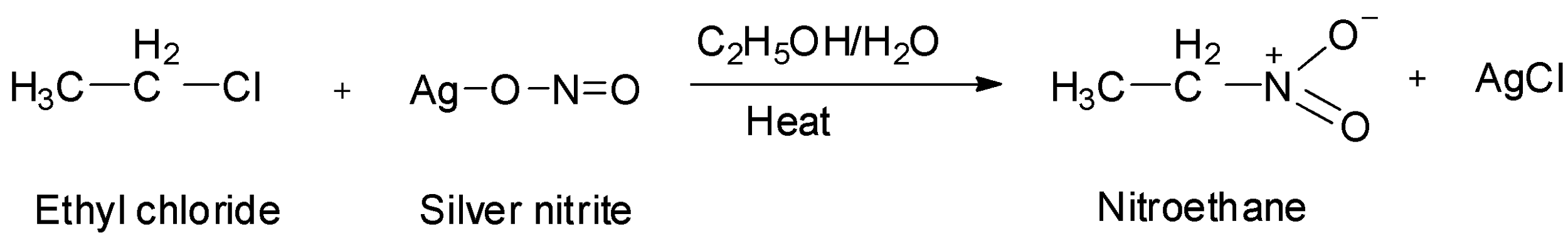
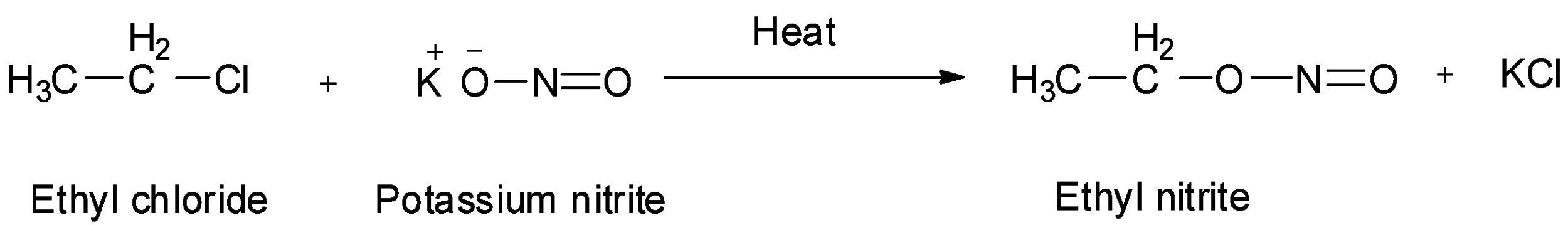
-One of the reagents in the fourth option is ${\text{KN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ , i.e., potassium nitrite. Haloalkanes when treated with potassium nitrite, alkyl nitrites are formed. So, treatment of ethyl chloride with potassium nitrite will give ethyl nitrite. So, option D is wrong.
Note:
There are several other methods for preparation of alcohol. Few of them are by reduction of carboxylic acids and esters, from Grignard reagents, by reduction of aldehydes and ketones and by hydroboration-oxidation of alkenes.
(1) For monohydric alcohols, i.e., alcohols containing only one hydroxyl group, there are many preparation methods. One of the most generally used methods is by heating haloalkanes or alkyl halides with aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. The alkyl halides then undergo hydrolysis to produce alcohols. Another way is to heat the alkyl halides with moist silver oxide.
(2) Dehydration of alkyl halides by alcoholic alkalies give alkenes.
Complete step by step answer:
The given reaction is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}\xrightarrow{{\text{A}}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}\xleftarrow{{\text{B}}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}{\text{.}}$
We need to identify A and B, i.e., the reagents used for converting ethyl chloride to ethyl alcohol.
Ethyl chloride is an alkyl halide and ethyl alcohol is a monohydric alcohol.
So, when ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous potassium hydroxide, we will get ethyl alcohol.

Also, if ethyl chloride is treated with moist silver oxide which is ${\text{AgOH}}$ , we will again get ethyl alcohol.

So, A is aq. ${\text{KOH}}$ and B is ${\text{AgOH}}$ .
So, option A is correct.
-When alkyl halide is heated with a concentrated alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide, a molecule of hydrogen halide will be eliminated and an alkene is produced. The hydrogen of the alkyl halide that gets eliminated comes from the carbon atom next to that which carries the halogen, i.e., the ${\text{beta }}$ -carbon and the halogen is eliminated from the carbon atom carrying the halogen, i.e., the ${\text{alpha }}$ -carbon. Therefore, from ethyl chloride, ethene will be formed.

-On treating aqueous sodium hydroxide, it will give ethyl alcohol just like aqueous potassium hydroxide. But, since one of the reagents which is alcoholic potassium hydroxide does not give alcohol, so option B is wrong.
-One of the reagents in the third option is ${\text{AgN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ , i.e., silver nitrite. When aqueous ethanolic solution of haloalkanes are treated with ${\text{AgN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ , nitroalkanes are formed. So, treatment of ethyl chloride with silver nitrite will give nitroethane. So, option C is also not correct.
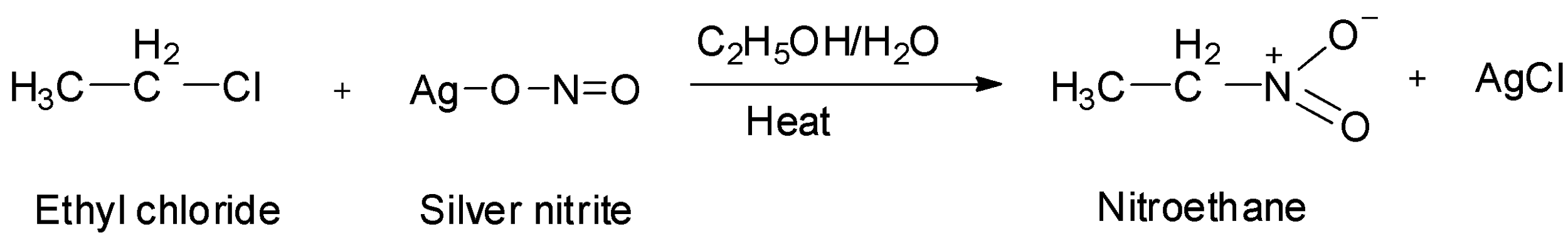
-One of the reagents in the fourth option is ${\text{KN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ , i.e., potassium nitrite. Haloalkanes when treated with potassium nitrite, alkyl nitrites are formed. So, treatment of ethyl chloride with potassium nitrite will give ethyl nitrite. So, option D is wrong.

Note:
There are several other methods for preparation of alcohol. Few of them are by reduction of carboxylic acids and esters, from Grignard reagents, by reduction of aldehydes and ketones and by hydroboration-oxidation of alkenes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




