
(i) Deficiency of which vitamin causes rickets?
(ii) Give an example for each fibrous protein and globular protein.
(iii) Write the product formed on reaction of D-glucose with $B{{r}_{2}}$ water.
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint (i) Vitamins are biomolecules that are required for normal growth and health of an organism. Sun is one of the important sources of this vitamin. Rickets is caused by the deficiency of a particular vitamin, and this vitamin is produced in our body.
(ii) Proteins are the fundamental basis of structure and functions of organisms. Based on their tertiary structure, proteins are classified into globular and fibrous proteins. Globular proteins are coiled to get a spherical shape whereas fibrous proteins are arranged one parallel to another in a fibre like structure.
(iii) D-Glucose undergoes oxidation with Bromine water. This reaction is an indication of the fact that the carbonyl group of glucose is aldehyde.
Complete step by step solution:
Biomolecules are some lifeless molecules but very essential for sustenance and maintenance of life. Carbohydrates, proteins, vitamines, enzymes, nucleic acids, hormones are some examples of biomolecules.
(i) Vitamins are biomolecules that are required in diet in small quantities for normal growth and health of an organism.They have specific biological functions. They are represented by alphabets .
Eg: A, B, C, D ,E, K.
Rickets is a disease caused by the deficiency of Vitamin D in our body. Rickets is the softening and weakening of bones in children, usually because of an extreme and prolonged vitamin D deficiency. Rare inherited problems also can cause rickets.
VItamin D is also known as Elgo calciferol. Deficiency of Vitamin D also causes Osteomalacia. Vitamin D helps your child's body absorb calcium and phosphorus from food.
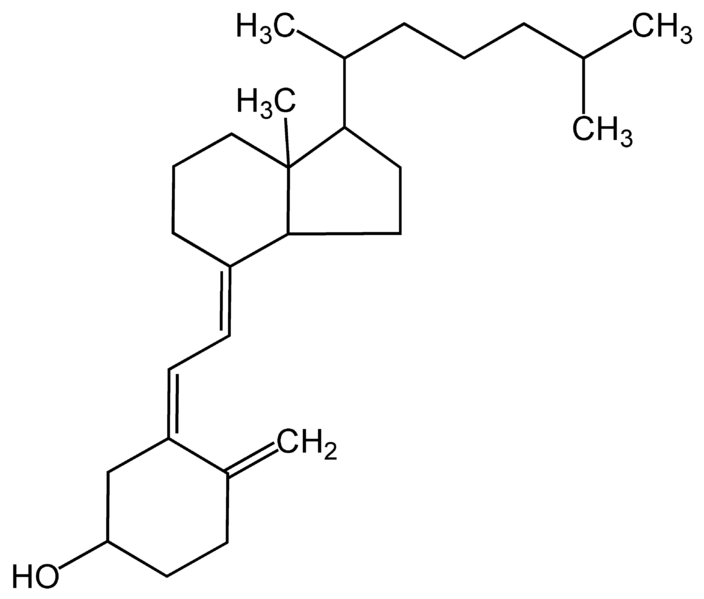
Structure of Vitamin D
(ii) Proteins form the fundamental basis of structure and functions of organisms. They are very essential for the growth and health of our body. Chemically they are - amino acids. Proteins are polypeptides having more than 100 amino acid units.[Except insulin, which is having only 51 amino acid units].
Proteins are classified as Globulin proteins and Fibrous Proteins based on their tertiary structure.
(iii) Glucose $\left( { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 } \right)$ is an aldohexose. It is dextrorotatory $(+{{52.5}^{0}})$ So it is also called Dextrose.
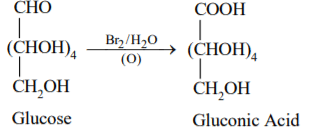
Glucose on oxidation using $B{{r}_{2}}$ water (Mild oxidising agent) gives gluconic acid. It indicates that the carbonyl group of glucose is aldehyde.
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}\,\,+\,\,B{{r}_{2}}\,\,\to \,\,{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{7}}$
Note: (i) Deficiency of each of the vitamins causes certain impacts on our body. So make sure that you study the deficiencies of each and every vitamin thoroughly. Also in order to avoid such mistakes, try to include the foods in your diet to be a healthy person.
(ii)Globular proteins and fibrous proteins are two different kinds of proteins. Before studying the example make sure that you have a picture in your mind about how the globular and fibrous protein look like.
(iii) Make sure that you know the structure of glucose and gluconic acid. Little changes in the structure may lead to a different compound.
(ii) Proteins are the fundamental basis of structure and functions of organisms. Based on their tertiary structure, proteins are classified into globular and fibrous proteins. Globular proteins are coiled to get a spherical shape whereas fibrous proteins are arranged one parallel to another in a fibre like structure.
(iii) D-Glucose undergoes oxidation with Bromine water. This reaction is an indication of the fact that the carbonyl group of glucose is aldehyde.
Complete step by step solution:
Biomolecules are some lifeless molecules but very essential for sustenance and maintenance of life. Carbohydrates, proteins, vitamines, enzymes, nucleic acids, hormones are some examples of biomolecules.
(i) Vitamins are biomolecules that are required in diet in small quantities for normal growth and health of an organism.They have specific biological functions. They are represented by alphabets .
Eg: A, B, C, D ,E, K.
Rickets is a disease caused by the deficiency of Vitamin D in our body. Rickets is the softening and weakening of bones in children, usually because of an extreme and prolonged vitamin D deficiency. Rare inherited problems also can cause rickets.
VItamin D is also known as Elgo calciferol. Deficiency of Vitamin D also causes Osteomalacia. Vitamin D helps your child's body absorb calcium and phosphorus from food.

Structure of Vitamin D
(ii) Proteins form the fundamental basis of structure and functions of organisms. They are very essential for the growth and health of our body. Chemically they are - amino acids. Proteins are polypeptides having more than 100 amino acid units.[Except insulin, which is having only 51 amino acid units].
Proteins are classified as Globulin proteins and Fibrous Proteins based on their tertiary structure.
- •
| GLOBULAR PROTEIN | FIBROUS PROTEIN |
| Here polypeptide chains get coiled to get a spherical shape. | Here polypeptide chains are arranged parallel to another to get a fibre like structure. |
| They are soluble in water. | Insoluble in water |
| Eg: Albumin, Insulin, Enzymes, Haemoglobin. | Eg: Keratin, Myosin |
(iii) Glucose $\left( { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 } \right)$ is an aldohexose. It is dextrorotatory $(+{{52.5}^{0}})$ So it is also called Dextrose.
Glucose on oxidation using $B{{r}_{2}}$ water (Mild oxidising agent) gives gluconic acid. It indicates that the carbonyl group of glucose is aldehyde.
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}\,\,+\,\,B{{r}_{2}}\,\,\to \,\,{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{7}}$

Note: (i) Deficiency of each of the vitamins causes certain impacts on our body. So make sure that you study the deficiencies of each and every vitamin thoroughly. Also in order to avoid such mistakes, try to include the foods in your diet to be a healthy person.
(ii)Globular proteins and fibrous proteins are two different kinds of proteins. Before studying the example make sure that you have a picture in your mind about how the globular and fibrous protein look like.
(iii) Make sure that you know the structure of glucose and gluconic acid. Little changes in the structure may lead to a different compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




