
How do you solve $2{\cos ^2}x + \cos x = 0?$
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint: For solving the given expression take $\cos x$as common from the expression given in the
question, after taking common equalise and compare the equations to determine the general
solution of $\cos x$.
As, general solution for $\cos x = 0$ is $x = \dfrac{{\left( {2n + 1} \right)\pi }}{2},$ apply this to solve the expression given in the question.
Complete step by step solution: As per data given in the question,
We have,
$2{\cos ^2}x + \cos x = 0...(i)$
Here from equation $(i)$
Taking $\cos x$ as common.
We will get,
$\therefore \cos x\left( {2\cos x + 1} \right) = 0$
Hence, from above expression we can conclude that,
Either first part will be equal to zero or second part will be equal to zero.
So,
Either $\cos x = 0$ or $2\cos x + 1 = 0$
If, $\cos x = 0$
If, $2\cos x + 1 = 0$
Then,$\cos x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}$
Hence, general solution for $\cos x = 0$ will be,
$x = \dfrac{{\left( {2n + 1} \right)\pi }}{2},$ where $n$ is integer and general solution for \[\cos x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2} = \cos \left( { \pm \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right)\] is $x = n\pi \pm \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$, where $n$ is an integer.
Hence General solution for $2{\cos ^2}x + \cos x = 0$ will be,
$n = \dfrac{{\left( {2n + 1} \right)\pi }}{2}$ or \[x = 2\pi \pm \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}\]
Where $n$ is an integer.
Additional Information:
From the trigonometric triangle,
We have,
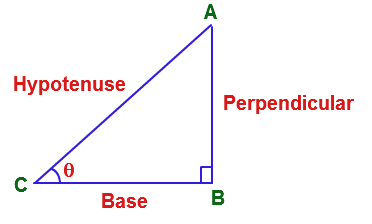
Here, AC is adjacent or base of triangle and BC is altitude or Opposite of triangle and AC is hypotenuse of triangle.
So, from here,
We have,
Angle of sine will be \[ = \operatorname{Sin} \theta = \dfrac{{Base}}{{Hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{b}{c}\]
Angle of Cosine will be \[ = \operatorname{Cos} \theta = \dfrac{{Opposite}}{{Hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{a}{c}\]
Angle of tangent will be \[ = \operatorname{Tan} \theta = \dfrac{{Base}}{{Opposite}} = \dfrac{b}{a}\]
Hence, from the above trigonometric triangle we can determine the relationship between all trigonometric variables.
Value of the angle of cosine decreases from 0 to 90, and after 90 it becomes negative.
Value of the angle of secant is inverse of the value of cosine.
Value of the angle of cosecant is the inverse of the value of the angle of Sine.
Value of the angle of Cot is the inverse of the value of angle of tangent.
Note:
As here,
From question,
As, $\cos x\left( {2\cos x + 1} \right) = 0$
Hence, from above expression we can conclude that,
Either the first part will be equal to zero or the second part will be equal to zero.
So,
The general equation of the expression given in the question will be an addition of the general equation of both the values.
question, after taking common equalise and compare the equations to determine the general
solution of $\cos x$.
As, general solution for $\cos x = 0$ is $x = \dfrac{{\left( {2n + 1} \right)\pi }}{2},$ apply this to solve the expression given in the question.
Complete step by step solution: As per data given in the question,
We have,
$2{\cos ^2}x + \cos x = 0...(i)$
Here from equation $(i)$
Taking $\cos x$ as common.
We will get,
$\therefore \cos x\left( {2\cos x + 1} \right) = 0$
Hence, from above expression we can conclude that,
Either first part will be equal to zero or second part will be equal to zero.
So,
Either $\cos x = 0$ or $2\cos x + 1 = 0$
If, $\cos x = 0$
If, $2\cos x + 1 = 0$
Then,$\cos x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}$
Hence, general solution for $\cos x = 0$ will be,
$x = \dfrac{{\left( {2n + 1} \right)\pi }}{2},$ where $n$ is integer and general solution for \[\cos x = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2} = \cos \left( { \pm \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right)\] is $x = n\pi \pm \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$, where $n$ is an integer.
Hence General solution for $2{\cos ^2}x + \cos x = 0$ will be,
$n = \dfrac{{\left( {2n + 1} \right)\pi }}{2}$ or \[x = 2\pi \pm \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}\]
Where $n$ is an integer.
Additional Information:
From the trigonometric triangle,
We have,

Here, AC is adjacent or base of triangle and BC is altitude or Opposite of triangle and AC is hypotenuse of triangle.
So, from here,
We have,
Angle of sine will be \[ = \operatorname{Sin} \theta = \dfrac{{Base}}{{Hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{b}{c}\]
Angle of Cosine will be \[ = \operatorname{Cos} \theta = \dfrac{{Opposite}}{{Hypotenuse}} = \dfrac{a}{c}\]
Angle of tangent will be \[ = \operatorname{Tan} \theta = \dfrac{{Base}}{{Opposite}} = \dfrac{b}{a}\]
Hence, from the above trigonometric triangle we can determine the relationship between all trigonometric variables.
Value of the angle of cosine decreases from 0 to 90, and after 90 it becomes negative.
Value of the angle of secant is inverse of the value of cosine.
Value of the angle of cosecant is the inverse of the value of the angle of Sine.
Value of the angle of Cot is the inverse of the value of angle of tangent.
Note:
As here,
From question,
As, $\cos x\left( {2\cos x + 1} \right) = 0$
Hence, from above expression we can conclude that,
Either the first part will be equal to zero or the second part will be equal to zero.
So,
The general equation of the expression given in the question will be an addition of the general equation of both the values.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




