
Guanine is an example of:
A.a nitrogenous base
B.a nucleoside
C.a nucleotide
D.phosphate
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: We must know that the nitrogen bases are basic components of nucleic acid. Guanine is one of the five important nitrogen bases of nucleic acids – DNA and RNA. The nitrogenous bases, with the sugars and phosphate group form the backbone of the DNA molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
Purines and pyrimidine are the two groups of nitrogenous bases that build up nucleic acids DNA and RNA.
There are two main types of purine compounds present, namely, Adenine and Guanine.
Following is a structure of guanine.
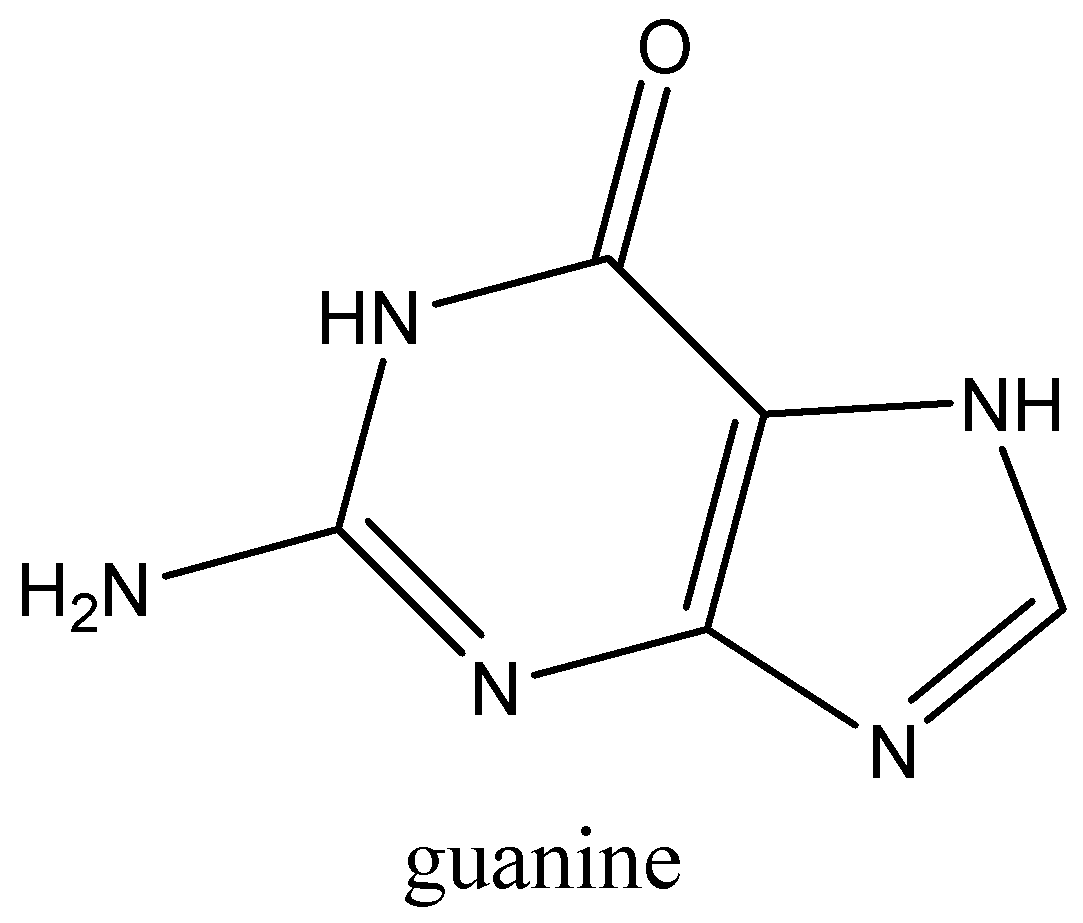
Type of purine paired with the type of pyrimidine is always constant, based upon the number of hydrogen bonds between them. So, adenine always pairs with thymine with two hydrogen bonds and guanine always pairs with cytosine with three hydrogen bonds.
Hence, Guanine is an example of a nitrogenous base.
Hence, the correct option is option A.
Additional information:
Following are some applications of Guanine:
We can use it in the cosmetics Industry as an additive to various products like shampoos. It provides shimmering luster to eye shadow and nail polish products.
Guanine is also used in metallic paints and simulated pearls and plastics.
Guano deposits, droppings of birds rich in guanine, are used for Facial treatments in Japan.
Guanine produces a pearly luster hence it is used in spray, painting, or dipping.
Note:
There are four nitrogenous bases present in DNA and are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). Both purines occur in both DNA and RNA. But in case of pyrimidine, Cytosine occurs in both DNA and RNA, whereas Uracil only in RNA and Thymine is found only in DNA.
Complete step by step answer:
Purines and pyrimidine are the two groups of nitrogenous bases that build up nucleic acids DNA and RNA.
There are two main types of purine compounds present, namely, Adenine and Guanine.
Following is a structure of guanine.

Type of purine paired with the type of pyrimidine is always constant, based upon the number of hydrogen bonds between them. So, adenine always pairs with thymine with two hydrogen bonds and guanine always pairs with cytosine with three hydrogen bonds.
Hence, Guanine is an example of a nitrogenous base.
Hence, the correct option is option A.
Additional information:
Following are some applications of Guanine:
We can use it in the cosmetics Industry as an additive to various products like shampoos. It provides shimmering luster to eye shadow and nail polish products.
Guanine is also used in metallic paints and simulated pearls and plastics.
Guano deposits, droppings of birds rich in guanine, are used for Facial treatments in Japan.
Guanine produces a pearly luster hence it is used in spray, painting, or dipping.
Note:
There are four nitrogenous bases present in DNA and are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). Both purines occur in both DNA and RNA. But in case of pyrimidine, Cytosine occurs in both DNA and RNA, whereas Uracil only in RNA and Thymine is found only in DNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




