
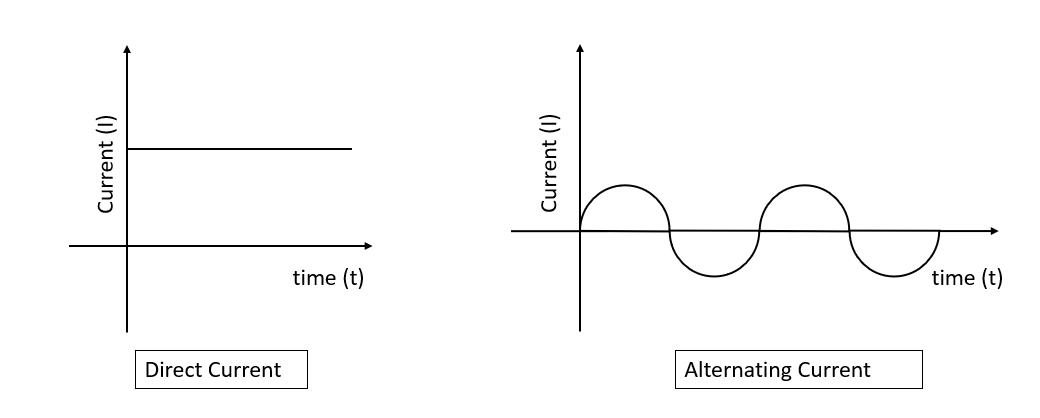
Graph of direct current and alternating current are-
Answer
522.3k+ views
Hint: Direct current (DC) is the transfer of electric charge in just one direction. It is the steady state of a fixed-voltage circuit. Most well-known uses, however, use a time-changing voltage source. An alternating current (AC) is the movement of an electric charge that is regularly in the opposite direction. If the source changes periodically, especially sinusoidally, the circuit is identified as an alternating current circuit.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Electric current moves in two ways: alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). In alternating current, current keeps changing directions periodically – forth and backward. While in the DC, it runs in a single direction regularly. The main variation between AC and DC occupies the direction in which the electrons move. In DC, the electrons run steadily in one direction while electrons persist, switching directions, going forth, and then backward in AC.
The primary use of DC is to provide power for electrical appliances and also to charge batteries. Example: flashlights, mobile phone batteries, flat-screen television, and electronic vehicles.
Everything that operates on a battery and utilizes an AC adapter while using a USB wire for energy relies on DC.
Note: Most high-power distribution arrangements are AC. Moreover, the power is transferred at much greater voltages than the $120-V\ AC$. Economies of range make it affordable to make a few concrete electric power-generation plants than to create many small ones. This requires sending large power distances, and energy wastes in the path must be decreased. High voltages can be transferred with much fewer power losses than moderate voltages.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Electric current moves in two ways: alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). In alternating current, current keeps changing directions periodically – forth and backward. While in the DC, it runs in a single direction regularly. The main variation between AC and DC occupies the direction in which the electrons move. In DC, the electrons run steadily in one direction while electrons persist, switching directions, going forth, and then backward in AC.

The primary use of DC is to provide power for electrical appliances and also to charge batteries. Example: flashlights, mobile phone batteries, flat-screen television, and electronic vehicles.
Everything that operates on a battery and utilizes an AC adapter while using a USB wire for energy relies on DC.
Note: Most high-power distribution arrangements are AC. Moreover, the power is transferred at much greater voltages than the $120-V\ AC$. Economies of range make it affordable to make a few concrete electric power-generation plants than to create many small ones. This requires sending large power distances, and energy wastes in the path must be decreased. High voltages can be transferred with much fewer power losses than moderate voltages.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




