
When glucose is treated with dilute NaOH, it gives a mixture of D-glucose and:
A. L-glucose and D-fructose
B. D-fructose and L-mannose
C. D-fructose and D-mannose
D. L-fructose and L-mannose
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: When glucose is treated with dilute NaOH, it converts the aldehyde group of glucose into the ketone group, so a ketose sugar forms. When the ketose sugar is treated with NaOH an epimer of glucose forms or again glucose can also form. All the reactions are reversible.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction of D-glucose with sodium hydroxide is shown as follows:
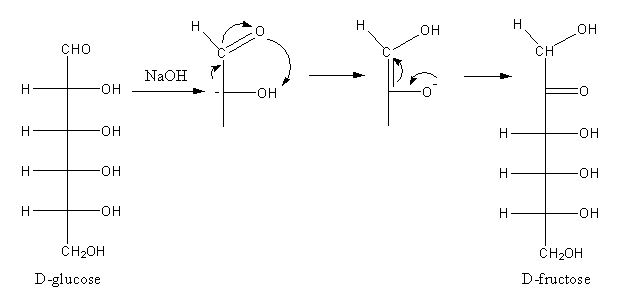
By the reaction of D-glucose with sodium hydroxide, D-glucose converts into D-fructose. Similarly, D-fructose reacts with sodium hydroxide to give D-mannose. D-mannose is an epimer of D-glucose.
D-fructose can form glucose or mannose because the ketose group in fructose has two faces. The protonation can form any face so there is an equal possibility of the formation of glucose or mannose so the reactions are reversible.
Base abstract protons form carbon of ${\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$ of fructose. The delocalization of charge generates negative charge on oxygen atoms. This oxygen gets proton to form a hydroxyl group at second carbon so, $1,2 - $ diol forms. This on rearrangement gives glucose and mannose.
The reaction of glucose with dilute sodium hydroxide is known as Lobry de Bruyn-van Ekentein rearrangement.
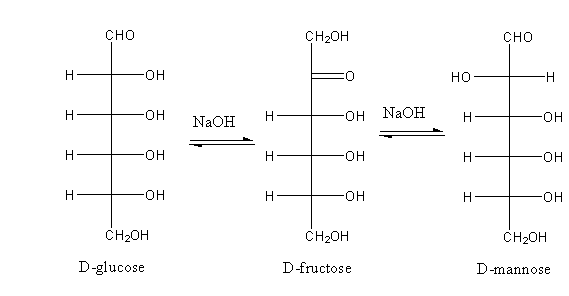
So, when glucose is treated with dilute NaOH, it gives a mixture of D-glucose, L-glucose and D-fructose.
Therefore, option (A) L-glucose and D-fructose, is correct.
Note:Epimers are the diastereomers. The epimers only differ in the position of the group at one chiral centre. D-glucose and D-mannose both have different configurations at carbon,so D-mannose is a carbon- epimer of D-glucose. The conversion of glucose into mannose is known as epimerization. Glucose is an aldose sugar as it has an aldehyde functional group. Fructose is a ketose sugar as it has a ketone functional group. The conversion of glucose, fructose, and mannose into each other is also known as tautomerism.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction of D-glucose with sodium hydroxide is shown as follows:

By the reaction of D-glucose with sodium hydroxide, D-glucose converts into D-fructose. Similarly, D-fructose reacts with sodium hydroxide to give D-mannose. D-mannose is an epimer of D-glucose.
D-fructose can form glucose or mannose because the ketose group in fructose has two faces. The protonation can form any face so there is an equal possibility of the formation of glucose or mannose so the reactions are reversible.
Base abstract protons form carbon of ${\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$ of fructose. The delocalization of charge generates negative charge on oxygen atoms. This oxygen gets proton to form a hydroxyl group at second carbon so, $1,2 - $ diol forms. This on rearrangement gives glucose and mannose.
The reaction of glucose with dilute sodium hydroxide is known as Lobry de Bruyn-van Ekentein rearrangement.

So, when glucose is treated with dilute NaOH, it gives a mixture of D-glucose, L-glucose and D-fructose.
Therefore, option (A) L-glucose and D-fructose, is correct.
Note:Epimers are the diastereomers. The epimers only differ in the position of the group at one chiral centre. D-glucose and D-mannose both have different configurations at carbon,so D-mannose is a carbon- epimer of D-glucose. The conversion of glucose into mannose is known as epimerization. Glucose is an aldose sugar as it has an aldehyde functional group. Fructose is a ketose sugar as it has a ketone functional group. The conversion of glucose, fructose, and mannose into each other is also known as tautomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




