
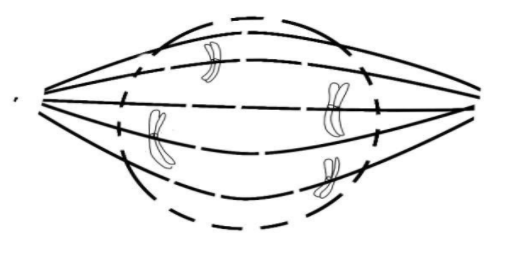
Given below is a diagram representing a stage during mitotic cell division. Study it carefully and answer the question that below:
How will you differentiate between mitosis and meiosis on the basis of chromosome number in the daughter cells?

Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: During this phase of mitotic cell division The nucleus becomes round and the cytoplasm becomes thicker. Chromatin slowly condenses into well-defined chromosomes. Each chromosome appears as two sister chromatids connected in a centromere. Mitosis is also known as equational division while meiosis is known as reductional division.
Complete answer:
During this phase of mitotic cell division The nucleus becomes round and the cytoplasm becomes thicker. Chromatin slowly condenses into well-defined chromosomes. Each chromosome appears as two sister chromatids connected in a centromere. Mitosis is also known as equational division while meiosis is known as reductional division.
In the final phase the chromosomes appear more visible, are shorter and thicker and are doubled in length. Two chromatids on each chromosome located at the centromere are visible under a light microscope.
Metaphase-This phase starts after prophase. The spindle tube forms and the chromosomes are aligned in the middle of the equatorial plate. The chromosomes are attached to the spindle tube at the centromere. Chromosomes are clearly visible in the metaphase.
Anaphase-This is the phase in which the chromatids in the centromere separate and move to opposite sides or poles. The chromatids on each chromosome become free at the centromere, but each chromatid is attached to the spindle tube.
Telophase-When the chromosomes reach the poles, the final stage begins with telophase. The spindle tube collapses and forms a new nuclear membrane at each pole, which covers the chromosomes. The nucleus also reappears at each pole.
By correlating above points with the diagrams it’s clear that given diagram is of mitotic prophase. And from the given table it’s clear that in mitosis the number of chromosomes remains the same in daughter cells and in meiosis the number of chromosomes reduced to half in daughter cells.
Note:
In mitosis, homologous (mother and father) chromosomes are replicated and duplicated in two chromatids. New chromosomes are formed by dividing the chromatids in half. From each of these mother and father chromosomes, the chromatids reach the daughter cells. Therefore, the type and number of chromosomes in the parent cell are maintained by the daughter cells. There are no synapses between homologous chromosomes.
In meiosis of two homologous chromosomes, only one type of chromosome (i.e. mother or father) moves into the daughter cell. Hence, daughter cells receive the mother or father chromosomes from the homologous pair. In this way, the number of chromosomes in the daughter cell remains half the number of the parent cell. In meiosis, pairs or synapses occur between homologous chromosomes.
Complete answer:
During this phase of mitotic cell division The nucleus becomes round and the cytoplasm becomes thicker. Chromatin slowly condenses into well-defined chromosomes. Each chromosome appears as two sister chromatids connected in a centromere. Mitosis is also known as equational division while meiosis is known as reductional division.
In the final phase the chromosomes appear more visible, are shorter and thicker and are doubled in length. Two chromatids on each chromosome located at the centromere are visible under a light microscope.
Metaphase-This phase starts after prophase. The spindle tube forms and the chromosomes are aligned in the middle of the equatorial plate. The chromosomes are attached to the spindle tube at the centromere. Chromosomes are clearly visible in the metaphase.
Anaphase-This is the phase in which the chromatids in the centromere separate and move to opposite sides or poles. The chromatids on each chromosome become free at the centromere, but each chromatid is attached to the spindle tube.
Telophase-When the chromosomes reach the poles, the final stage begins with telophase. The spindle tube collapses and forms a new nuclear membrane at each pole, which covers the chromosomes. The nucleus also reappears at each pole.
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| Mitosis always occurs in somatic and reproductive cells. When finished, one cell forms two daughter cells. | Meiosis occurs only in reproductive cells, that is. When meiosis is complete, one cell forms four daughter cells. |
| The number of chromosomes in each daughter cell equals the number of stem cells (usually 2n). All daughter cells are genetically homogeneous. | The number of chromosomes in each daughter cell is half (n) the number of stem cells (2n). All daughter cells are genetically distinct due to segregation and recombination. Meiosis occurs only in reproductive cells, that is. When meiosis is complete, one cell forms four daughter cells. The number of chromosomes in each daughter cell is half (n) the number of stem cells (2n). All daughter cells are genetically distinct due to segregation and recombination |
By correlating above points with the diagrams it’s clear that given diagram is of mitotic prophase. And from the given table it’s clear that in mitosis the number of chromosomes remains the same in daughter cells and in meiosis the number of chromosomes reduced to half in daughter cells.
Note:
In mitosis, homologous (mother and father) chromosomes are replicated and duplicated in two chromatids. New chromosomes are formed by dividing the chromatids in half. From each of these mother and father chromosomes, the chromatids reach the daughter cells. Therefore, the type and number of chromosomes in the parent cell are maintained by the daughter cells. There are no synapses between homologous chromosomes.
In meiosis of two homologous chromosomes, only one type of chromosome (i.e. mother or father) moves into the daughter cell. Hence, daughter cells receive the mother or father chromosomes from the homologous pair. In this way, the number of chromosomes in the daughter cell remains half the number of the parent cell. In meiosis, pairs or synapses occur between homologous chromosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




