
Given a ray diagram shows the recombination of the spectrum of white light by using glass prisms. White light if $ n $ and $ n $ , are their respective indices while $ A $ and $ A' $ are respective angles of prism, then which of the following conditions is correct for the occurrence of recombination of white light?
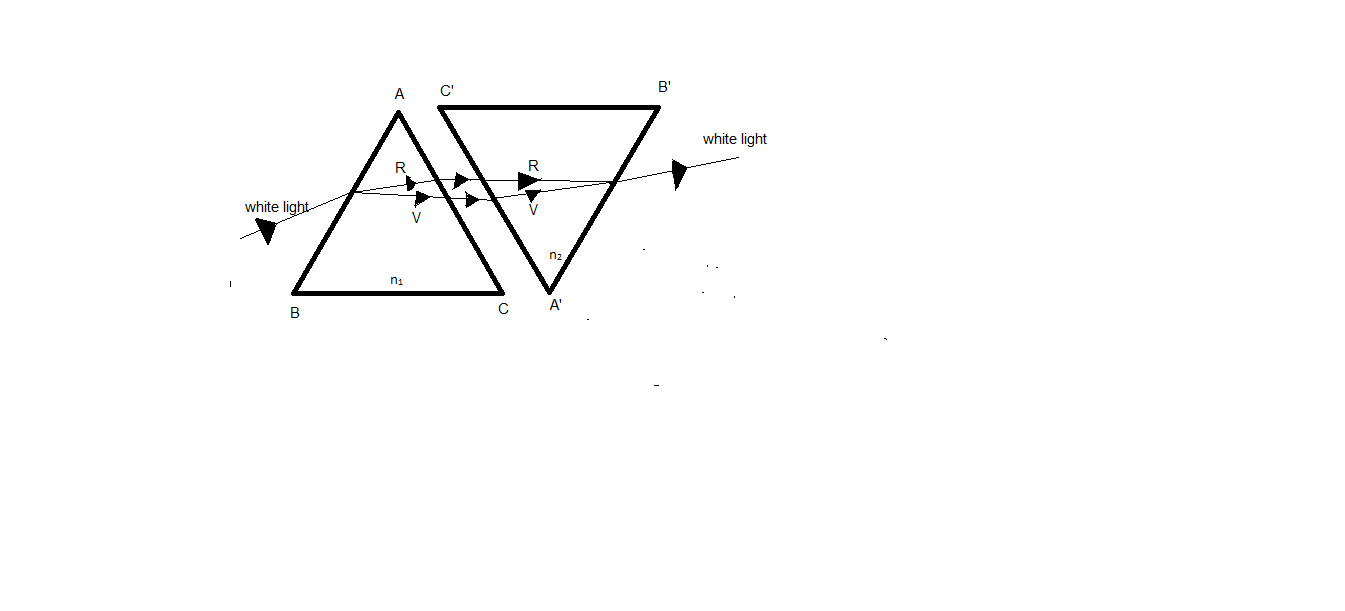
$ \left( A \right){n_1} = {n_2};\angle A < \angle A' \\
\left( B \right){n_1} = {n_2};\angle A = \angle A' \\
\left( C \right){n_1} > {n_2};\angle A = \angle A' \\
\left( D \right){n_1} = {n_2};\angle A > \angle A' \\ $

Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to first find the condition for the recombination of the two refracted rays, by taking the angle of deviation for the two prisms and also the angles of emergence conditions for the case of recombination of the rays. Then by putting the values for both the prisms, the relation between $ {n_1} $ , $ {n_2} $ , $ \angle A $ and $ \angle A' $ .
The angle of deviation is given by the formula
$ \delta = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)A $
Where $ A $ the angle of prism is, $ \mu $ is the refractive index.
If $ \theta $ is the angle of emergence, then we know that
$ \theta = \left( {{\mu _V} - {\mu _R}} \right)A $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know that the angle of deviation is given by the formula
$ \delta = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)A $
Where $ A $ is the angle of the prism
Now, for the recombination of the lights, the sum of the two angle of deviations must not be equal to zero, i.e.
$ {\delta _1} + {\delta _2} \ne 0 $
If $ \theta $ is the angle of emergence, then we know that
$ \theta = ({\mu_{V}}-{\mu_{R}})A $
Where $ {\mu _V} $ and $ {\mu _R} $ are the refractive indices for the violet and red colours
For there is no dispersion, $ {\theta _1} + {\theta _2} = 0 $
Putting the values for $ {\theta _1} $ and $ {\theta _2} $
$ \left( {{\mu _V} - {\mu _R}} \right)A + \left( {{\mu _V}' - {\mu _R}'} \right)A' = 0 $
Thus, the ratio of the angles of the prism
$ \dfrac{{A'}}{A} = \dfrac{{\left( {{\mu _V} - {\mu _R}} \right)}}{{\left( {{\mu _V}' - {\mu _R}'} \right)}} $
The difference of the refractive indices of colours violet and red is equal to the value $ n $ i.e. refractive index of the prism.
$ \dfrac{{A'}}{A} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{{{n_2}}} $
Thus, option $ \left( B \right){n_1} = {n_2};\angle A = \angle A' $ is the correct answer.
Note :
These are two identical prisms in which one is kept upside down, the reverse refraction of the rays from the second prism causes the rays that are refracted to recombine and produce the white light.
The refracting sides of the second prism are parallel to that of the refracting sides of the first prism.
The angle of deviation is given by the formula
$ \delta = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)A $
Where $ A $ the angle of prism is, $ \mu $ is the refractive index.
If $ \theta $ is the angle of emergence, then we know that
$ \theta = \left( {{\mu _V} - {\mu _R}} \right)A $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know that the angle of deviation is given by the formula
$ \delta = \left( {\mu - 1} \right)A $
Where $ A $ is the angle of the prism
Now, for the recombination of the lights, the sum of the two angle of deviations must not be equal to zero, i.e.
$ {\delta _1} + {\delta _2} \ne 0 $
If $ \theta $ is the angle of emergence, then we know that
$ \theta = ({\mu_{V}}-{\mu_{R}})A $
Where $ {\mu _V} $ and $ {\mu _R} $ are the refractive indices for the violet and red colours
For there is no dispersion, $ {\theta _1} + {\theta _2} = 0 $
Putting the values for $ {\theta _1} $ and $ {\theta _2} $
$ \left( {{\mu _V} - {\mu _R}} \right)A + \left( {{\mu _V}' - {\mu _R}'} \right)A' = 0 $
Thus, the ratio of the angles of the prism
$ \dfrac{{A'}}{A} = \dfrac{{\left( {{\mu _V} - {\mu _R}} \right)}}{{\left( {{\mu _V}' - {\mu _R}'} \right)}} $
The difference of the refractive indices of colours violet and red is equal to the value $ n $ i.e. refractive index of the prism.
$ \dfrac{{A'}}{A} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{{{n_2}}} $
Thus, option $ \left( B \right){n_1} = {n_2};\angle A = \angle A' $ is the correct answer.
Note :
These are two identical prisms in which one is kept upside down, the reverse refraction of the rays from the second prism causes the rays that are refracted to recombine and produce the white light.
The refracting sides of the second prism are parallel to that of the refracting sides of the first prism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




