
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
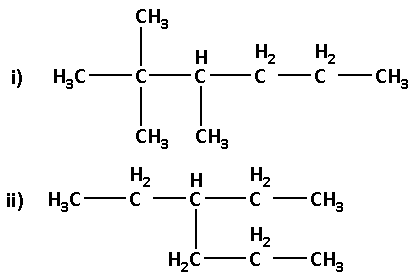

Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint:The method of naming organic compounds is known as the IUPAC nomenclature. In order to name organic compounds ,we must memorize a few basic names.We should remember the names of substituents attached.We need to remember the basic rules and follow them stepwise .In the given structure, methyl groups are attached as substituents.
Complete Answer :
(1) The given structure with all of its atoms is as follows:
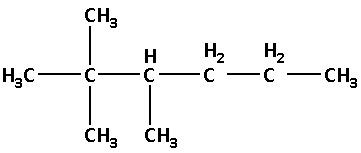
Select the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the structure of the molecule.
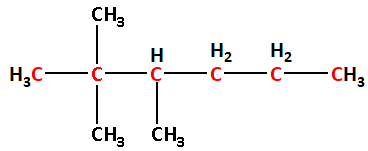
Number the carbon atoms in the selected carbon chain from the end which is nearest to the methyl substituents.
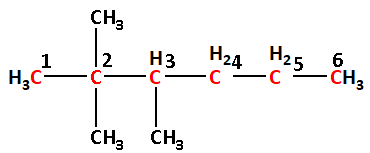
The longest chain contains six carbon atoms. Thus, the parent alkane is hexane.
The two methyl groups are attached to carbon number 2 and one methyl group is attached to carbon number 3. Thus, 2,2,3-trimethyl.
Thus, the IUPAC name is 2,2,3-trimethylhexane.
(2) The given structure with all of its atoms is as follows:
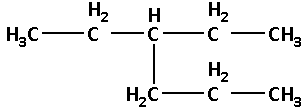
Select the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the structure of the molecule.
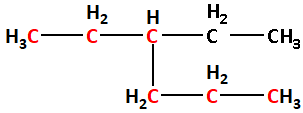
Number the carbon atoms in the selected carbon chain from the end which is nearest to the methyl substituents.
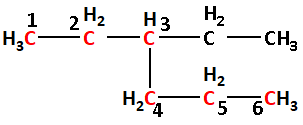
The longest chain contains six carbon atoms. Thus, the parent alkane is hexane.
The one ethyl group is attached to carbon number 3. Thus, 3-ethyl.
Thus, the IUPAC name is 3-ethylhexane.
Note:The rules for writing IUPAC name of alkanes are as follows:
(1) Select the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the structure of the molecule.
(2) Number the carbon atoms in the selected carbon chain from the end which is nearest to the substituents attached.
(3) Count the number of carbon atoms in the chain. This is the parent alkane.
(4) Write the number indicating the position of the substituents.
(5) Assign a number to each substituent according to the carbon atom it is attached to. If there are two substituents on the same carbon, assign the same number to them.
Complete Answer :
(1) The given structure with all of its atoms is as follows:

Select the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the structure of the molecule.

Number the carbon atoms in the selected carbon chain from the end which is nearest to the methyl substituents.

The longest chain contains six carbon atoms. Thus, the parent alkane is hexane.
The two methyl groups are attached to carbon number 2 and one methyl group is attached to carbon number 3. Thus, 2,2,3-trimethyl.
Thus, the IUPAC name is 2,2,3-trimethylhexane.
(2) The given structure with all of its atoms is as follows:

Select the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the structure of the molecule.

Number the carbon atoms in the selected carbon chain from the end which is nearest to the methyl substituents.

The longest chain contains six carbon atoms. Thus, the parent alkane is hexane.
The one ethyl group is attached to carbon number 3. Thus, 3-ethyl.
Thus, the IUPAC name is 3-ethylhexane.
Note:The rules for writing IUPAC name of alkanes are as follows:
(1) Select the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the structure of the molecule.
(2) Number the carbon atoms in the selected carbon chain from the end which is nearest to the substituents attached.
(3) Count the number of carbon atoms in the chain. This is the parent alkane.
(4) Write the number indicating the position of the substituents.
(5) Assign a number to each substituent according to the carbon atom it is attached to. If there are two substituents on the same carbon, assign the same number to them.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




