
Form the differential equation of the family of ellipse having foci on the y-axis and centre at origin.
Answer
610.5k+ views
Hint: For solving this problem, we first try to form the general equation of ellipse passing through the origin having major axis at y and minor axis at x so that the foci lies on y-axis. After writing the general equation, we have to remove the variables a and b. To do so, we differentiate the whole equation until we obtain a variable free derivative form. This gives us the family of ellipses.
Complete step-by-step answer:
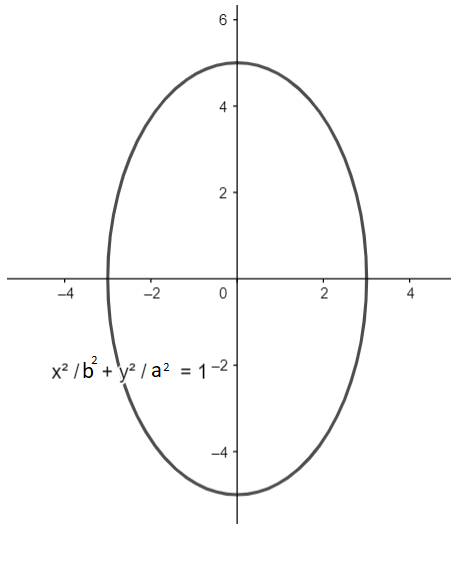
The general equation of ellipse passing through the origin having major axis at y and minor axis at x so that the foci lies on y axis can be given as: $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=1$, where a and b are major and minor axes respectively.
Some of the important differential rules which are useful can be stated as:
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n{{x}^{n-1}} \\
& \dfrac{dy}{dx}={y}' \\
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( mn \right)={m}'n+{n}'m \\
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \text{constant} \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
Now, the above equation cannot represent the family of ellipses as it contains two variables. So, to eliminate these variables we use differentiation. Since there are two variables, we can easily differentiate the equation twice.
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)}^{\prime }}={{\left( 1 \right)}^{\prime }} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2x}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{2y{y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}=0 ………….(1)\\
\end{align}$
Again, differentiating with respect to x, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{x}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{y}'}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)}^{\prime }}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{x}{{{b}^{2}}} \right)}^{\prime }}+{{\left( \dfrac{y{y}'}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)}^{\prime }}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y\cdot {y}''+{y}'\cdot {y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{b}^{2}}}=-\dfrac{y\cdot {y}''+{y}'\cdot {y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}\ldots \left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of equation (2) in the equation (1), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x\left[ -\dfrac{y\cdot {y}''+{y}'\cdot {y}'}{{{a}^{2}}} \right]+\dfrac{y\cdot {y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-x\cdot y\cdot {y}''-x\cdot {{\left( {{y}'} \right)}^{2}}+y\cdot {y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -x\cdot y\cdot {y}''-x\cdot {{\left( {{y}'} \right)}^{2}}+y\cdot {y}'=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x\cdot y\cdot {y}''+x\cdot {{\left( {{y}'} \right)}^{2}}-y\cdot {y}'=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the family of ellipse is \[x\cdot y\cdot {y}''+x\cdot {{\left( {{y}'} \right)}^{2}}-y\cdot {y}'=0\].
Note: Knowledge of the family of equations is required for solving this problem. The family of equations should be free of arbitrary variables. Students must remember the key step of differentiation and the number of times they are allowed to do the differentiation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The general equation of ellipse passing through the origin having major axis at y and minor axis at x so that the foci lies on y axis can be given as: $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=1$, where a and b are major and minor axes respectively.

Some of the important differential rules which are useful can be stated as:
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n{{x}^{n-1}} \\
& \dfrac{dy}{dx}={y}' \\
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( mn \right)={m}'n+{n}'m \\
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \text{constant} \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
Now, the above equation cannot represent the family of ellipses as it contains two variables. So, to eliminate these variables we use differentiation. Since there are two variables, we can easily differentiate the equation twice.
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)}^{\prime }}={{\left( 1 \right)}^{\prime }} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2x}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{2y{y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}=0 ………….(1)\\
\end{align}$
Again, differentiating with respect to x, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{x}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{y}'}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)}^{\prime }}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{x}{{{b}^{2}}} \right)}^{\prime }}+{{\left( \dfrac{y{y}'}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)}^{\prime }}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y\cdot {y}''+{y}'\cdot {y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{b}^{2}}}=-\dfrac{y\cdot {y}''+{y}'\cdot {y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}\ldots \left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of equation (2) in the equation (1), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x\left[ -\dfrac{y\cdot {y}''+{y}'\cdot {y}'}{{{a}^{2}}} \right]+\dfrac{y\cdot {y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-x\cdot y\cdot {y}''-x\cdot {{\left( {{y}'} \right)}^{2}}+y\cdot {y}'}{{{a}^{2}}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -x\cdot y\cdot {y}''-x\cdot {{\left( {{y}'} \right)}^{2}}+y\cdot {y}'=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x\cdot y\cdot {y}''+x\cdot {{\left( {{y}'} \right)}^{2}}-y\cdot {y}'=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the family of ellipse is \[x\cdot y\cdot {y}''+x\cdot {{\left( {{y}'} \right)}^{2}}-y\cdot {y}'=0\].
Note: Knowledge of the family of equations is required for solving this problem. The family of equations should be free of arbitrary variables. Students must remember the key step of differentiation and the number of times they are allowed to do the differentiation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




