
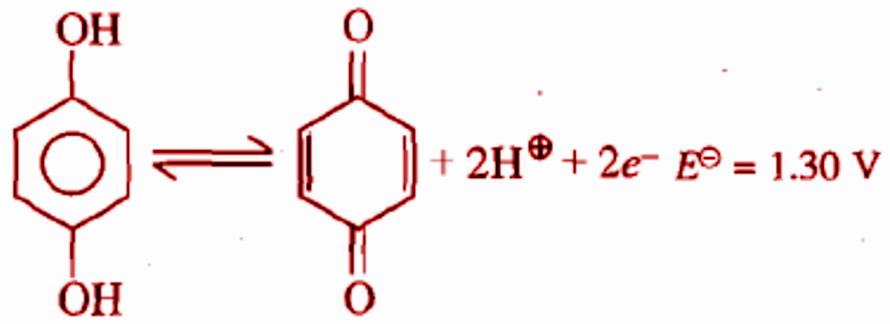
For the half cell, at ${{pH}} = 2$, the electrode potential is:
A. ${{1}}{{.36V}}$
B. ${{1}}{{.30V}}$
C. $1.42{{V}}$
D. $1.20{{V}}$

Answer
567k+ views
Hint:As we know, potential means ability. Electrode potential is the tendency of an electrode to get oxidized or reduced in its aqueous solution. It can be oxidation potential or reduction potential.
Also we know that ${{pH}}$ is the negative logarithm of concentration of hydrogen ion. From the ${{pH}}$ value, we can determine the hydrogen ion concentration.
Complete step by step answer:
In the half-cell reaction, hydroquinone is converted to quinone which is represented in the question.
It is given that the ${{pH}} = 2$ and the cell potential, ${{{E}}^ \circ }{{ = 1}}{{.30V}}$
We have to find the electrode potential.
${{pH}} = - \log \left[ {{{{H}}^ + }} \right] = 2$
From the ${{pH}}$ value, it is clear that the concentration of hydrogen ion, \[\left[ {{{{H}}^ + }} \right] = {10^{ - 2}}\].
The reaction gives two moles of hydrogen ions. Let A be the reactant and B be the product formed. One mole of A reacts to form one mole of B and two moles of hydrogen ions.
So we can say that the concentration of A and B are equal.
i.e. $\left[ {{A}} \right] = \left[ {{B}} \right]$
Electrode potential can be calculated using Nernst equation. It is expressed as given below:
${{E}} = {{{E}}^ \circ } - \dfrac{{0.0591}}{{{F}}}\log {\left[ {{{{H}}^ + }} \right]^2}$, ${{E}}$ is the electrode potential, ${{{E}}^ \circ }$ is the cell potential at standard conditions, ${{F}}$ is faraday which is the number of electrons transferred, \[\left[ {{{{H}}^ + }} \right]\] is the hydrogen ion concentration.
Substituting the values of cell potential and hydrogen ion concentration, we get
${{E}} = 1.30 - \dfrac{{0.0591}}{2}\log {\left( {{{10}^{ - 2}}} \right)^2}$
Now on simplification, we get
${{E}} = 1.30 - \dfrac{{0.0591}}{2}\log \left( {{{10}^{ - 4}}} \right)$
i.e. ${{E}} = 1.30 - \dfrac{{0.0591}}{2} \times - 4 = 1.30 + \left( {0.0591 \times 2} \right) = 1.30 + 0.1182 = 1.42{{V}}$
Thus the electrode potential is $1.42{{V}}$.
Hence the correct option is C.
Note:
The product formed is called quinhydrone. Thus this electrode is called a quinhydrone electrode. It contains a solution of quinones and hydroquinones which is prepared from quinhydrone. The given reaction is a half-reaction taking place in a quinhydrone electrode.
Also we know that ${{pH}}$ is the negative logarithm of concentration of hydrogen ion. From the ${{pH}}$ value, we can determine the hydrogen ion concentration.
Complete step by step answer:
In the half-cell reaction, hydroquinone is converted to quinone which is represented in the question.
It is given that the ${{pH}} = 2$ and the cell potential, ${{{E}}^ \circ }{{ = 1}}{{.30V}}$
We have to find the electrode potential.
${{pH}} = - \log \left[ {{{{H}}^ + }} \right] = 2$
From the ${{pH}}$ value, it is clear that the concentration of hydrogen ion, \[\left[ {{{{H}}^ + }} \right] = {10^{ - 2}}\].
The reaction gives two moles of hydrogen ions. Let A be the reactant and B be the product formed. One mole of A reacts to form one mole of B and two moles of hydrogen ions.
So we can say that the concentration of A and B are equal.
i.e. $\left[ {{A}} \right] = \left[ {{B}} \right]$
Electrode potential can be calculated using Nernst equation. It is expressed as given below:
${{E}} = {{{E}}^ \circ } - \dfrac{{0.0591}}{{{F}}}\log {\left[ {{{{H}}^ + }} \right]^2}$, ${{E}}$ is the electrode potential, ${{{E}}^ \circ }$ is the cell potential at standard conditions, ${{F}}$ is faraday which is the number of electrons transferred, \[\left[ {{{{H}}^ + }} \right]\] is the hydrogen ion concentration.
Substituting the values of cell potential and hydrogen ion concentration, we get
${{E}} = 1.30 - \dfrac{{0.0591}}{2}\log {\left( {{{10}^{ - 2}}} \right)^2}$
Now on simplification, we get
${{E}} = 1.30 - \dfrac{{0.0591}}{2}\log \left( {{{10}^{ - 4}}} \right)$
i.e. ${{E}} = 1.30 - \dfrac{{0.0591}}{2} \times - 4 = 1.30 + \left( {0.0591 \times 2} \right) = 1.30 + 0.1182 = 1.42{{V}}$
Thus the electrode potential is $1.42{{V}}$.
Hence the correct option is C.
Note:
The product formed is called quinhydrone. Thus this electrode is called a quinhydrone electrode. It contains a solution of quinones and hydroquinones which is prepared from quinhydrone. The given reaction is a half-reaction taking place in a quinhydrone electrode.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




