
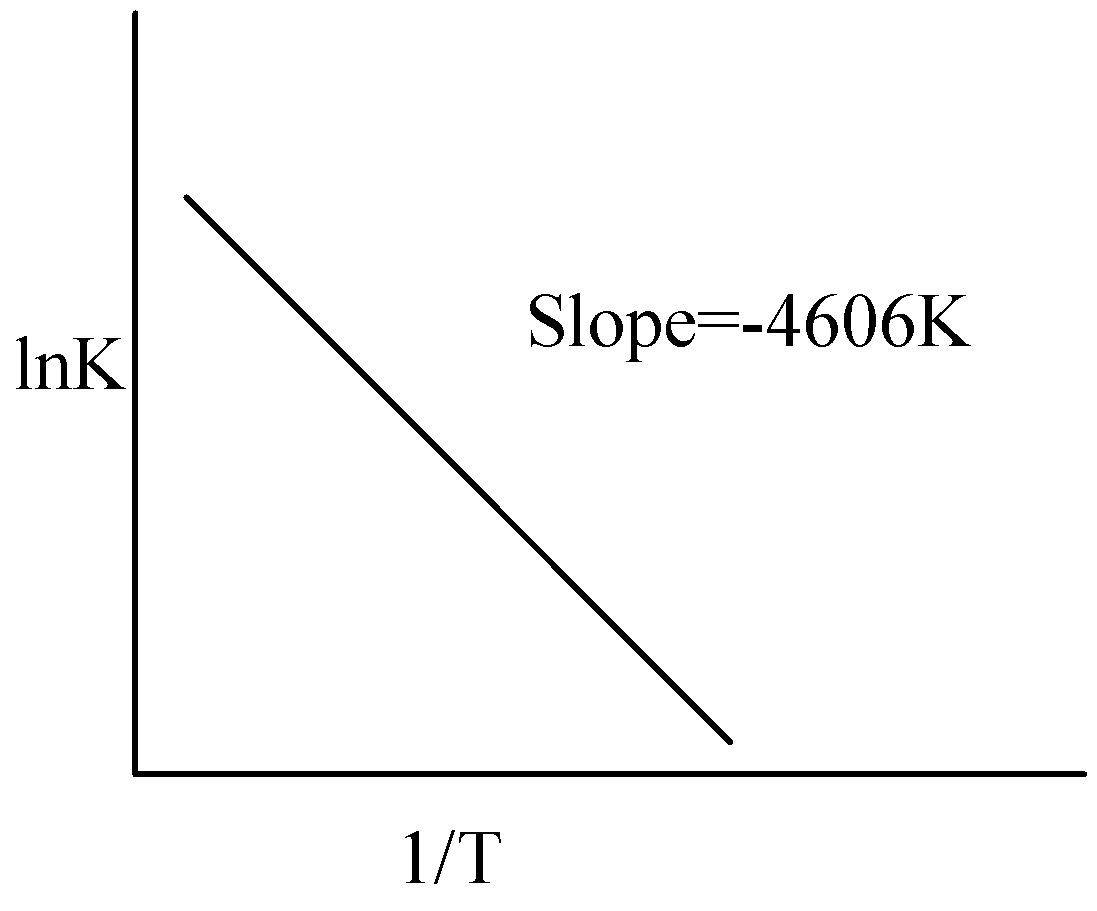
For a reaction consider the plot of $\ln K$ versus $1/T$ given in the figure. If the rate constant of this reaction at $400K$ is ${10^{ - 5}}{s^{ - 1}}$ , then the rate constant at $500K$ is:
A.$2 \times {10^{ - 4}}{s^{ - 1}}$
B.${10^{ - 4}}{s^{ - 1}}$
C.${10^{ - 6}}{s^{ - 1}}$
D.$4 \times {10^{ - 4}}{s^{ - 1}}$

Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint:We have to know that the rate constant could be calculated using the Arrhenius equation. We have to derive the rate constant using the rate constant at $400K$, both the temperatures and value of slope. The value of slope is $ - 4606K$.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to know that the Arrhenius equation is useful in determining the rate of reaction and plays a significant portion in chemical kinetics. We could give Arrhenius equation as,
$K = A{e^{ - {E_a}/RT}}$
Here, K is the rate constant
A is the pre-exponential factor
${E_a}$ is the activation energy
R is the gas constant
T is the temperature (in Kelvin)
The integrated form of Arrhenius equation is,
$\log \left( {\dfrac{{{K_2}}}{{{K_1}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{T_2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{T_1}}}} \right]$
The value of temperature ${T_1}$ is $400K$ .
The value of temperature ${T_2}$ is $500K$ .
The rate constant at $400K$ is ${10^{ - 5}}{s^{ - 1}}$ .
We can write integrated equation as,
$\log \left( {\dfrac{{{K_2}}}{{{K_1}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{T_2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{T_1}}}} \right]$
Let us substitute the known values in the above expression to calculate the rate constant.
We can calculate the rate constant as,
$\log \left( {\dfrac{{{K_2}}}{{{K_1}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{T_2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{T_1}}}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow 2.303\log \left( {\dfrac{{{K_2}}}{{{K_1}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{R}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{T_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{T_2}}}} \right]$
Now we can substitute the known values we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2.303\log \left( {\dfrac{{{K_2}}}{{{{10}^{ - 5}}}}} \right) = 4606\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{400}} - \dfrac{1}{{500}}} \right]$
On simplifying we get,
${K_2} = {10^{ - 4}}{s^{ - 1}}$
The value of rate constant at $500K$ is ${10^{ - 4}}{s^{ - 1}}$.
Therefore, the option (B) is correct.
Note:
We have to know that the fundamentals of the Arrhenius equation is collision theory. According to this theory, a reaction happens because of a collision between two molecules to form an intermediate. The formed intermediate is unstable and stays for a shorter period of time. The unstable intermediate gets broken into two product molecules and the energy used in formation of the intermediate is known as energy of activation. With the use of Arrhenius equation, we could determine the temperature, frequency, presence of catalyst, effect of energy wall and collision orientation.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to know that the Arrhenius equation is useful in determining the rate of reaction and plays a significant portion in chemical kinetics. We could give Arrhenius equation as,
$K = A{e^{ - {E_a}/RT}}$
Here, K is the rate constant
A is the pre-exponential factor
${E_a}$ is the activation energy
R is the gas constant
T is the temperature (in Kelvin)
The integrated form of Arrhenius equation is,
$\log \left( {\dfrac{{{K_2}}}{{{K_1}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{T_2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{T_1}}}} \right]$
The value of temperature ${T_1}$ is $400K$ .
The value of temperature ${T_2}$ is $500K$ .
The rate constant at $400K$ is ${10^{ - 5}}{s^{ - 1}}$ .
We can write integrated equation as,
$\log \left( {\dfrac{{{K_2}}}{{{K_1}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{T_2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{T_1}}}} \right]$
Let us substitute the known values in the above expression to calculate the rate constant.
We can calculate the rate constant as,
$\log \left( {\dfrac{{{K_2}}}{{{K_1}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{T_2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{T_1}}}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow 2.303\log \left( {\dfrac{{{K_2}}}{{{K_1}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{R}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{{T_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{T_2}}}} \right]$
Now we can substitute the known values we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2.303\log \left( {\dfrac{{{K_2}}}{{{{10}^{ - 5}}}}} \right) = 4606\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{400}} - \dfrac{1}{{500}}} \right]$
On simplifying we get,
${K_2} = {10^{ - 4}}{s^{ - 1}}$
The value of rate constant at $500K$ is ${10^{ - 4}}{s^{ - 1}}$.
Therefore, the option (B) is correct.
Note:
We have to know that the fundamentals of the Arrhenius equation is collision theory. According to this theory, a reaction happens because of a collision between two molecules to form an intermediate. The formed intermediate is unstable and stays for a shorter period of time. The unstable intermediate gets broken into two product molecules and the energy used in formation of the intermediate is known as energy of activation. With the use of Arrhenius equation, we could determine the temperature, frequency, presence of catalyst, effect of energy wall and collision orientation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




