
Following figures show the arrangement of bar magnets in different configurations. Each magnet has a magnetic dipole moment \[\vec{m}\]. Which configuration has the highest net magnetic dipole moment?
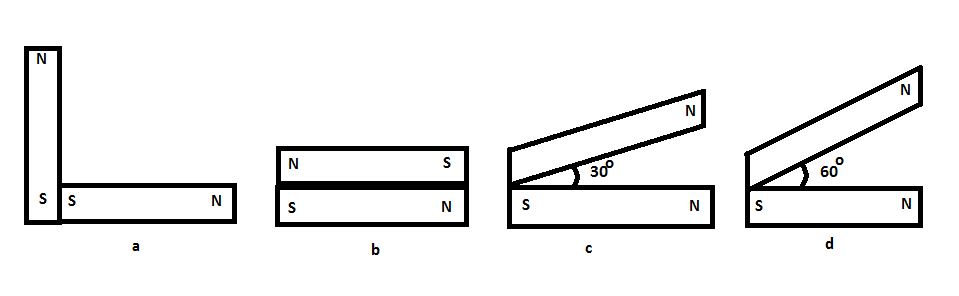
A \[a\]
B \[b\]
C \[c\]
D \[d\]

Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Here, each bar magnet has a magnetic dipole moment as \[\vec{m}\]. Since magnetic dipole moment is a vector quantity, we can find the resultant magnetic dipole moment using the formula for finding magnitude of a vector quantity. Thus
we can determine which configuration has the highest net magnetic moment.
Formula used:
\[{{m}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{m}_{1}}^{2}+{{m}_{2}}^{2}+2{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}cos\theta }\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that, each bar magnet has a magnetic dipole moment \[\vec{m}\]. Magnetic dipole moment has its direction from north to south. Now let’s find out the net magnetic dipole moment of each configuration using a vector diagram.
In the first configuration, bar magnets have an angle \[{{90}^{0}}\] between them. The resultant vector will be in a \[{{45}^{0}}\] angle with both the magnets.
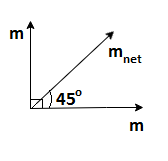
Magnitude of a vector m can be found using the formula,
\[{{m}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{m}_{1}}^{2}+{{m}_{2}}^{2}+2{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}cos\theta }\]
Then,
\[{{m}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}+2{{m}^{2}}\cos 90}=\sqrt{2}m\]
In the second configuration, the bar magnets are parallel to each other.

Hence,
\[{{m}_{net}}=m-m=0\]
In the third configuration, magnets have a \[30{}^\circ \] angle between them.
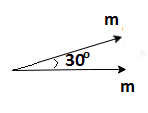
\[{{m}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}+2{{m}^{2}}\cos
30}=m\sqrt{3.732}=1.93m\]
In the fourth configuration, magnets have \[60{}^\circ \] angle between them.
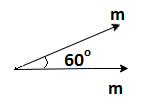
\[{{m}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}+2{{m}^{2}}\cos
60}=m\sqrt{3}=1.732m\]
Hence, configuration \[c\] has the highest net magnetic dipole moment. Answer is option C
Additional information:
Consider a magnetic dipole with two equal and opposite magnetic charges of strengths \[+m\] and \[-m\] and separated by a distance \[2l\]. Then, its magnetic dipole moment can be given by, \[M=m\times 2l\]
Note: A bar magnet is usually considered as a dipole with dipole moment\[\vec{m}\]. Magnetic dipole moment is a vector quantity and has direction from \[-m\] to \[+m\]. Its S.I unit is \[\text{Ampere }{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\].
we can determine which configuration has the highest net magnetic moment.
Formula used:
\[{{m}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{m}_{1}}^{2}+{{m}_{2}}^{2}+2{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}cos\theta }\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that, each bar magnet has a magnetic dipole moment \[\vec{m}\]. Magnetic dipole moment has its direction from north to south. Now let’s find out the net magnetic dipole moment of each configuration using a vector diagram.
In the first configuration, bar magnets have an angle \[{{90}^{0}}\] between them. The resultant vector will be in a \[{{45}^{0}}\] angle with both the magnets.

Magnitude of a vector m can be found using the formula,
\[{{m}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{m}_{1}}^{2}+{{m}_{2}}^{2}+2{{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}cos\theta }\]
Then,
\[{{m}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}+2{{m}^{2}}\cos 90}=\sqrt{2}m\]
In the second configuration, the bar magnets are parallel to each other.

Hence,
\[{{m}_{net}}=m-m=0\]
In the third configuration, magnets have a \[30{}^\circ \] angle between them.

\[{{m}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}+2{{m}^{2}}\cos
30}=m\sqrt{3.732}=1.93m\]
In the fourth configuration, magnets have \[60{}^\circ \] angle between them.

\[{{m}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{m}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}+2{{m}^{2}}\cos
60}=m\sqrt{3}=1.732m\]
Hence, configuration \[c\] has the highest net magnetic dipole moment. Answer is option C
Additional information:
Consider a magnetic dipole with two equal and opposite magnetic charges of strengths \[+m\] and \[-m\] and separated by a distance \[2l\]. Then, its magnetic dipole moment can be given by, \[M=m\times 2l\]
Note: A bar magnet is usually considered as a dipole with dipole moment\[\vec{m}\]. Magnetic dipole moment is a vector quantity and has direction from \[-m\] to \[+m\]. Its S.I unit is \[\text{Ampere }{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




