
Five charges ${q_{1,\,}}{q_{2,\,}}{q_{3,\,}}{q_4}$ and ${q_{5\,}}$ are fixed at their positions as shown in the figure. $S$ is a Gaussian surface. The Gauss’s law is given by $\oint_s {\vec E.d\vec s} = \dfrac{q}{{{ \in _0}}}$ . Which of the following statements is correct?
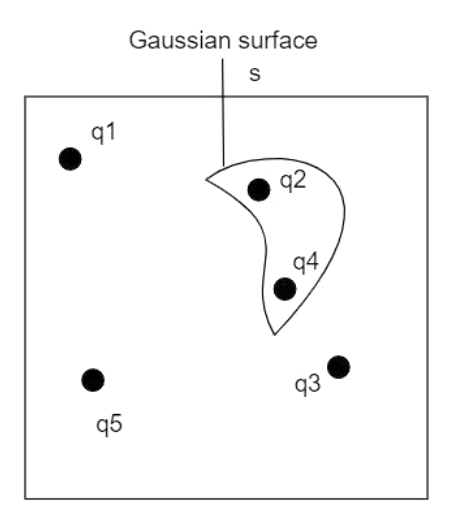
a. $\vec E$ on the LHS of the above equation will have contribution from ${q_1},{q_2}$ and ${q_3}$ while $q$ on the RHS will have contribution from ${q_2}\,and\,{q_1}$
b. $\vec E$ on the LHS of the above equation will have contribution from all the charges while $q$ on the RHS will have contribution from ${q_2}\,and\,{q_4}$ only.
c. $\vec E$ on the LHS of the above equation will have contribution from all the charges while $q$ on the RHS will have contribution from ${q_1},{q_3}\,and\,{q_5}$ only.
d. Both $\vec E$ on the LHS and $q$ on the RHS will have contributions from ${q_2}\,and\,{q_4}$ only.

Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: The Gauss law is applicable only for the charges that are included in the closed surface area, all the other charges that are outside the closed area are neglected or remain unconsidered for the electric flux calculation.
Formula used:
The Gauss’s law is given by
$\oint_s {\vec E.d\vec s} = \dfrac{q}{{{ \in _0}}}$
Where $\vec E$ is the electric field, $ds$ is the small area considered, $q$ is the charge in the closed area and ${ \in _0}$ is the permittivity due to free space.
Complete step by step answer:
The Gauss law states that the electric flux over a closed area is the charge enclosed in the particular closed area to that of the permittivity.
$\oint_s {\vec E.d\vec s} = \dfrac{q}{{{ \in _0}}}$
The right side of the equation is the sum of the charge enclosed in a closed area. In the above diagram, the charges ${q_2}$ and ${q_4}$ only in closed areas. Hence these two alone are responsible for the electric flux in that area. The other charges ${q_1}$ and ${q_3}$ are not enclosed inside the closed surfaces. Hence these charges do not contribute the electric flux over the area. $\vec E$ on the LHS of the above equation will have contributions from all the charges while $q$ on the RHS will have contributions from ${q_2}$ and ${q_4}$ only. Except the option (B), all the other options are incorrect.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The Gauss law is applicable to only closed surfaces, this is because only closed surfaces possess all the electric field lines pointing in the same direction and also these charges have the field lines that end up in zero. This is not possible if charges are present in an open area.
Formula used:
The Gauss’s law is given by
$\oint_s {\vec E.d\vec s} = \dfrac{q}{{{ \in _0}}}$
Where $\vec E$ is the electric field, $ds$ is the small area considered, $q$ is the charge in the closed area and ${ \in _0}$ is the permittivity due to free space.
Complete step by step answer:
The Gauss law states that the electric flux over a closed area is the charge enclosed in the particular closed area to that of the permittivity.
$\oint_s {\vec E.d\vec s} = \dfrac{q}{{{ \in _0}}}$
The right side of the equation is the sum of the charge enclosed in a closed area. In the above diagram, the charges ${q_2}$ and ${q_4}$ only in closed areas. Hence these two alone are responsible for the electric flux in that area. The other charges ${q_1}$ and ${q_3}$ are not enclosed inside the closed surfaces. Hence these charges do not contribute the electric flux over the area. $\vec E$ on the LHS of the above equation will have contributions from all the charges while $q$ on the RHS will have contributions from ${q_2}$ and ${q_4}$ only. Except the option (B), all the other options are incorrect.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The Gauss law is applicable to only closed surfaces, this is because only closed surfaces possess all the electric field lines pointing in the same direction and also these charges have the field lines that end up in zero. This is not possible if charges are present in an open area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




