
Find the velocity of image of given object:
(A) 4cm/sec
(B) 2.5cm/sec
(C) 6cm/sec
(D)None of the above

Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: In this question, we first calculate the image distance. Then we differentiate the lens formula given for object distance, image distance and focal length to convert it into a formula involving velocities to calculate the value of velocity of the image.
Formula used:
The lens formula is given by
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
Differentiating the lens formula, we have
$-\dfrac{V}{{{v}^{2}}}+\dfrac{U}{{{u}^{2}}}=0$
Complete answer:
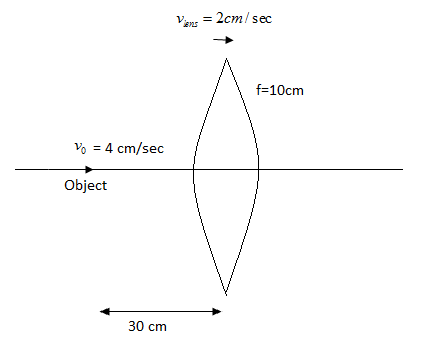
From the diagram given in the question, we have
Given,
u = -30 cm (Applying the New Sign convention)
f =10 cm ($\because $ The lens is convex)
Velocity of the object,${{v}_{0}}=$ 4cm/sec
Velocity of image, ${{v}_{lens}}$ = 2cm/sec
To find: The velocity of image
Using the lens formula, we first calculate the image distance by plugging the values for f and u,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{10}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{(-30)} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{30}=\dfrac{1}{v} \\
& \Rightarrow v=15cm \\
\end{align}\]
Here, f is the focal length
v is the image distance
u is the object distance
Therefore, the image distance here is calculated as 15 cm
Now, we differentiate the lens equation, to get
$\dfrac{-V}{{{v}^{2}}}+\dfrac{U}{{{u}^{2}}}=0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{V}{{{v}^{2}}}=\dfrac{U}{{{u}^{2}}}$
Where, V is the image distance.
U is the object distance.
v is the velocity of the image.
u is the velocity of the image.
Plugging the values of U,V and u from the given and calculated values, we have
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{15}{{{v}^{2}}}=\dfrac{30}{{{4}^{2}}}$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=16 \\
& \Rightarrow v=4cm/\sec \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
If there had been a mirror placed instead of a lens, the image velocity and object velocity can be calculated in a similar manner by just switching from the lens equation to the mirror equation. The mirror equation can be differentiated to obtain the equation for image and object velocity in a similar manner.
Note:
In every situation where the lens equation or the mirror equation is used, special care must be taken while writing the sign convention. A small mistake in the sign convention can result in an incorrect answer. It must always be remembered that for convex lenses the positive sign for focal length is used and for concave lenses, the negative sign is used for focal length.
Formula used:
The lens formula is given by
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
Differentiating the lens formula, we have
$-\dfrac{V}{{{v}^{2}}}+\dfrac{U}{{{u}^{2}}}=0$
Complete answer:
From the diagram given in the question, we have
Given,
u = -30 cm (Applying the New Sign convention)
f =10 cm ($\because $ The lens is convex)
Velocity of the object,${{v}_{0}}=$ 4cm/sec
Velocity of image, ${{v}_{lens}}$ = 2cm/sec
To find: The velocity of image
Using the lens formula, we first calculate the image distance by plugging the values for f and u,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{10}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{(-30)} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{30}=\dfrac{1}{v} \\
& \Rightarrow v=15cm \\
\end{align}\]
Here, f is the focal length
v is the image distance
u is the object distance
Therefore, the image distance here is calculated as 15 cm
Now, we differentiate the lens equation, to get
$\dfrac{-V}{{{v}^{2}}}+\dfrac{U}{{{u}^{2}}}=0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{V}{{{v}^{2}}}=\dfrac{U}{{{u}^{2}}}$
Where, V is the image distance.
U is the object distance.
v is the velocity of the image.
u is the velocity of the image.
Plugging the values of U,V and u from the given and calculated values, we have
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{15}{{{v}^{2}}}=\dfrac{30}{{{4}^{2}}}$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=16 \\
& \Rightarrow v=4cm/\sec \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
If there had been a mirror placed instead of a lens, the image velocity and object velocity can be calculated in a similar manner by just switching from the lens equation to the mirror equation. The mirror equation can be differentiated to obtain the equation for image and object velocity in a similar manner.
Note:
In every situation where the lens equation or the mirror equation is used, special care must be taken while writing the sign convention. A small mistake in the sign convention can result in an incorrect answer. It must always be remembered that for convex lenses the positive sign for focal length is used and for concave lenses, the negative sign is used for focal length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




