
How do you find the value of $\cos (\operatorname{arc} (tanx))$?
Answer
559.8k+ views
Hint: Here basically we need to know that inverse of the trigonometric function can also be represented in the form by using the prefix $arc$ .Here we need to proceed by letting the value inside the bracket which is ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x$ to be any variable say $a$ and then we will get $\tan a = x$ and now we can easily find the value of $\cos a$ which is required by using Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here we are given to simplify the term which is given as $\cos (\operatorname{arc} (tanx)) = \cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$
So let us consider the term inside the bracket which is ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x$ to be any variable say $a$
So we get ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = a$
So we will get $\tan a = x$
We can also write it as $\tan a = \dfrac{x}{1}$
Now we need to find the value of $\cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$ which can be written as $\cos a$according to the variable which we have let ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = a$
So let us consider the triangle $ABC$in which we can let the angle $a$ as $\angle A$ and it is right angles at\[B\]
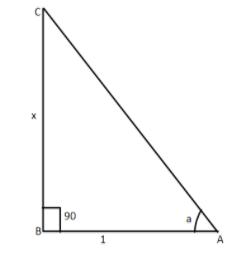
Now we are given:
$\tan a = \dfrac{x}{1}$$ - - - - (1)$
So we know that $\tan a = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}}$$ - - - - - (2)$
So by comparing the equation (1) and (2) we will get:
$
BC = x \\
AB = 1 \\
$
Now we know that by Pythagoras theorem we can say that in the right angles triangle:
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Now we can put in it:
$
BC = x \\
AB = 1 \\
$
We will get:
$
A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} \\
A{C^2} = {1^2} + {x^2} \\
AC = \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \\
$
Now we know that in the right angles triangle:
$\cos a = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
Now we can substitute the values of $AB,AC$ in the above equation of $\cos a$
$\cos a = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
$\cos a = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
Now we can substitute the value of $a$ and get:
$\cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$$ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
So we can write $\cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \cos (\operatorname{arc} (tanx))$$ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
Hence in this way by the use of Pythagoras theorem we can easily solve such types of problems where we need to find the trigonometric function of the inverse function.
Note: In such types of problems the student must keep in mind the basic trigonometric formula and the properties and also the use of Pythagoras theorem. We must know that $\cos \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \sin \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$ because:
$\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - {{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \sin \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here we are given to simplify the term which is given as $\cos (\operatorname{arc} (tanx)) = \cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$
So let us consider the term inside the bracket which is ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x$ to be any variable say $a$
So we get ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = a$
So we will get $\tan a = x$
We can also write it as $\tan a = \dfrac{x}{1}$
Now we need to find the value of $\cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$ which can be written as $\cos a$according to the variable which we have let ${\tan ^{ - 1}}x = a$
So let us consider the triangle $ABC$in which we can let the angle $a$ as $\angle A$ and it is right angles at\[B\]

Now we are given:
$\tan a = \dfrac{x}{1}$$ - - - - (1)$
So we know that $\tan a = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{base}}}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}}$$ - - - - - (2)$
So by comparing the equation (1) and (2) we will get:
$
BC = x \\
AB = 1 \\
$
Now we know that by Pythagoras theorem we can say that in the right angles triangle:
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Now we can put in it:
$
BC = x \\
AB = 1 \\
$
We will get:
$
A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} \\
A{C^2} = {1^2} + {x^2} \\
AC = \sqrt {1 + {x^2}} \\
$
Now we know that in the right angles triangle:
$\cos a = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
Now we can substitute the values of $AB,AC$ in the above equation of $\cos a$
$\cos a = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
$\cos a = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
Now we can substitute the value of $a$ and get:
$\cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$$ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
So we can write $\cos \left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \cos (\operatorname{arc} (tanx))$$ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}$
Hence in this way by the use of Pythagoras theorem we can easily solve such types of problems where we need to find the trigonometric function of the inverse function.
Note: In such types of problems the student must keep in mind the basic trigonometric formula and the properties and also the use of Pythagoras theorem. We must know that $\cos \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \sin \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$ because:
$\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - {{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right) = \sin \left( {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}x} \right)$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

What is the difference between biodegradable and nonbiodegradable class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE

Bond order ofO2 O2+ O2 and O22 is in order A O2 langle class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




