
Find the power of each bulb and which bulb will glow brighter in the circuit shown below. If the power source is replaced by a 440V supply which bulb will fuse first.
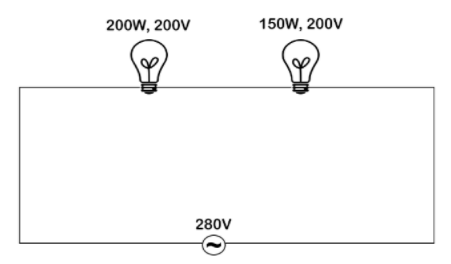

Answer
558k+ views
Hint: When two bulbs are connected in series, the voltage drop across them is different for each but the current through each bulb is the same. The bulb whose power rating is less will fuse before the bulb whose power rating is higher in comparison.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider the circuit below, the voltage drop across bulb ${{B}_{1}}$ is ${{V}_{1}}$ and the voltage drop across bulb ${{B}_{2}}$ is ${{V}_{2}}$. The current through the circuit is I and the voltage source is 280V.
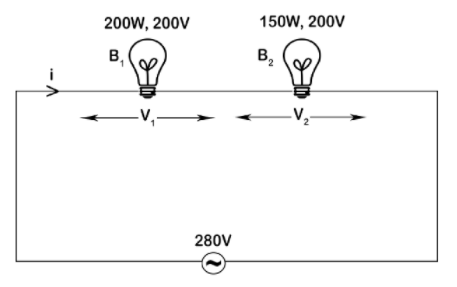
Let us calculate the resistances due to the bulbs in the circuit,
For bulb ${{B}_{1}}$,
${{R}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{1}}^{2}}{{{P}_{1}}}$ ….(i)
Putting the values in above equation we get,
${{R}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{200}^{2}}}{200}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {{R}_{1}}=200\Omega $
For bulb ${{B}_{2}}$,
${{R}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{2}}^{2}}{{{P}_{2}}}$ ….(ii)
Putting the values in above equation we get,
${{R}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{200}^{2}}}{150}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {{R}_{2}}=266.67\Omega $
(I) Now, calculating the voltages across each bulb:
For bulb ${{B}_{1}}$,
${{V}_{1}}={{V}_{s}}\times \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}=280\times \dfrac{200}{200+266.67}=119.99V$
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{1}}=120V$ on rounding it.
Where, ${{V}_{s}}$ is the source voltage.
For bulb ${{B}_{2}}$,
${{V}_{2}}={{V}_{s}}\times \dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}=280\times \dfrac{266.76}{200+266.67}=160V$
Therefore, the bulb ${{B}_{2}}$with greater voltage drop in the circuit will grow brighter than bulb ${{B}_{1}}$.
(II) Now, calculating the power consumed by both bulbs,
For bulb ${{B}_{1}}$,
${{P}_{1}}=\dfrac{V_{1}^{2}}{{{R}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{199.99}^{2}}}{200}W=199.98W=200W$
For bulb ${{B}_{2}}$,
${{P}_{2}}=\dfrac{V_{2}^{2}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{160}^{2}}}{266.67}W=95.99W=100W$
(III) If the source is replaced by 440V then,
For bulb ${{B}_{1}}$,
${{V}_{1}}={{V}_{s}}\times \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}=440\times \dfrac{200}{200+266.67}=188.57V=189V$
For bulb ${{B}_{2}}$,
${{V}_{2}}={{V}_{s}}\times \dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}=440\times \dfrac{266.76}{200+266.67}=251.43V=251V$
Therefore, bulb ${{B}_{2}}$ will fuse first as the voltage across ${{B}_{2}}$ is more than the allowed i.e. its rating voltage 200V.
Additional Information:
When two bulbs are connected in series, the voltage drop across them is different for each but the current through each bulb is the same and when two bulbs are connected in parallel, the voltage drop across them is same for each but the current through each bulb is different.
Note:
Bulbs when connected in series do not glow to their maximum brightness and if one of the bulbs in series if fused then the circuit becomes an open circuit and none of the bulbs glow. Thus, in everyday use the bulbs are connected in parallel connection to avoid such problems.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider the circuit below, the voltage drop across bulb ${{B}_{1}}$ is ${{V}_{1}}$ and the voltage drop across bulb ${{B}_{2}}$ is ${{V}_{2}}$. The current through the circuit is I and the voltage source is 280V.

Let us calculate the resistances due to the bulbs in the circuit,
For bulb ${{B}_{1}}$,
${{R}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{1}}^{2}}{{{P}_{1}}}$ ….(i)
Putting the values in above equation we get,
${{R}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{200}^{2}}}{200}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {{R}_{1}}=200\Omega $
For bulb ${{B}_{2}}$,
${{R}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{V}_{2}}^{2}}{{{P}_{2}}}$ ….(ii)
Putting the values in above equation we get,
${{R}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{200}^{2}}}{150}\Omega $
$\Rightarrow {{R}_{2}}=266.67\Omega $
(I) Now, calculating the voltages across each bulb:
For bulb ${{B}_{1}}$,
${{V}_{1}}={{V}_{s}}\times \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}=280\times \dfrac{200}{200+266.67}=119.99V$
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{1}}=120V$ on rounding it.
Where, ${{V}_{s}}$ is the source voltage.
For bulb ${{B}_{2}}$,
${{V}_{2}}={{V}_{s}}\times \dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}=280\times \dfrac{266.76}{200+266.67}=160V$
Therefore, the bulb ${{B}_{2}}$with greater voltage drop in the circuit will grow brighter than bulb ${{B}_{1}}$.
(II) Now, calculating the power consumed by both bulbs,
For bulb ${{B}_{1}}$,
${{P}_{1}}=\dfrac{V_{1}^{2}}{{{R}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{199.99}^{2}}}{200}W=199.98W=200W$
For bulb ${{B}_{2}}$,
${{P}_{2}}=\dfrac{V_{2}^{2}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{160}^{2}}}{266.67}W=95.99W=100W$
(III) If the source is replaced by 440V then,
For bulb ${{B}_{1}}$,
${{V}_{1}}={{V}_{s}}\times \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}=440\times \dfrac{200}{200+266.67}=188.57V=189V$
For bulb ${{B}_{2}}$,
${{V}_{2}}={{V}_{s}}\times \dfrac{{{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}=440\times \dfrac{266.76}{200+266.67}=251.43V=251V$
Therefore, bulb ${{B}_{2}}$ will fuse first as the voltage across ${{B}_{2}}$ is more than the allowed i.e. its rating voltage 200V.
Additional Information:
When two bulbs are connected in series, the voltage drop across them is different for each but the current through each bulb is the same and when two bulbs are connected in parallel, the voltage drop across them is same for each but the current through each bulb is different.
Note:
Bulbs when connected in series do not glow to their maximum brightness and if one of the bulbs in series if fused then the circuit becomes an open circuit and none of the bulbs glow. Thus, in everyday use the bulbs are connected in parallel connection to avoid such problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




