
Find the locus of the third vertex of a right-angled triangle, the ends of whose hypotenuse are (4, 0), (0, 4).
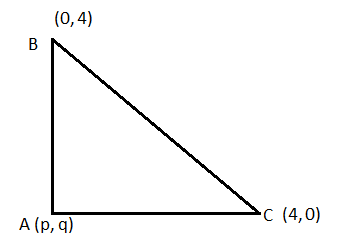
Answer
555k+ views
Hint: A locus is a set of all points whose location satisfies or is determined by one or more specified conditions. In other words, the set of points that satisfy some property is often called the locus of points satisfying this property.
The locus of a point P is such that it is equidistant from two given points. A and b that is, $PA = PB$. The locus of the point at fixed distance d, from point P, is a circle with given point P as its center and d as its radius. Here in this question, we can use the distance formula for two given points.
Distance formula $ = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} $.
Complete step by step solution:
Let the point be (p, q).
Then, $\vartriangle ABC$ is right-angled at point A.
$ \Rightarrow B{C^2} = A{B^2} + A{C^2}$ (By Pythagoras theorem)
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {\left( {4 - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {0 - 4} \right)^2} = {\left( {p - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {q - 4} \right)^2} + {\left( {p - 4} \right)^2} + {\left( {q - 0} \right)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow 16 + 16 = {p^2} + {q^2} + 16 - 8q + {p^2} + 16 - 8p + {q^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow 32 = 2\left( {{p^2} + {q^2} - 4p - 4q} \right) + 32 \cr} $
Or, ${p^2} + {q^2} - 4p - 4q = 0$.
Replacing $p \to x$ and $q \to y$.
$\therefore {x^2} + {y^2} - 4p - 4q = 0$ is the locus of the equation.
Note: We can also find this finding slope of two lines AB as ${m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$, and AC as ${m_2} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$.
And for perpendicular lines ${m_1}{m_2} = - 1$.
We get the required locus of the third vertex.
The locus of a point P is such that it is equidistant from two given points. A and b that is, $PA = PB$. The locus of the point at fixed distance d, from point P, is a circle with given point P as its center and d as its radius. Here in this question, we can use the distance formula for two given points.
Distance formula $ = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} $.
Complete step by step solution:
Let the point be (p, q).
Then, $\vartriangle ABC$ is right-angled at point A.
$ \Rightarrow B{C^2} = A{B^2} + A{C^2}$ (By Pythagoras theorem)
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {\left( {4 - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {0 - 4} \right)^2} = {\left( {p - 0} \right)^2} + {\left( {q - 4} \right)^2} + {\left( {p - 4} \right)^2} + {\left( {q - 0} \right)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow 16 + 16 = {p^2} + {q^2} + 16 - 8q + {p^2} + 16 - 8p + {q^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow 32 = 2\left( {{p^2} + {q^2} - 4p - 4q} \right) + 32 \cr} $
Or, ${p^2} + {q^2} - 4p - 4q = 0$.
Replacing $p \to x$ and $q \to y$.
$\therefore {x^2} + {y^2} - 4p - 4q = 0$ is the locus of the equation.
Note: We can also find this finding slope of two lines AB as ${m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$, and AC as ${m_2} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$.
And for perpendicular lines ${m_1}{m_2} = - 1$.
We get the required locus of the third vertex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

What is the color of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this color change after heating? Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this type of change.

A narrow strip of water body joining two large water class 9 social science CBSE

What is the Full Form of ICSE / ISC ?

A gulab jamun contains sugar syrup up to about 30 of class 9 maths CBSE




