
How do you find the exact value of $\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}2 \right)$?
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: We explain the function $\arctan \left( x \right)$. We express the inverse function of tan in the form of $\arctan \left( x \right)={{\tan }^{-1}}x$. We draw the graph of $\arctan \left( x \right)$ and the line $x=2$ to find the intersection point. Thereafter we take the cos ratio of that angle to find the solution. We also use the representation of a right-angle triangle with height and base ratio being 2 and the angle being $\theta $.
Complete step by step solution:
The internal part \[{{\tan }^{-1}}2\] of $\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}2 \right)$ is an angle. We assume \[{{\tan }^{-1}}2=\theta \].
This gives in ratio \[\tan \theta =2\]. We know \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{height}}{\text{base}}\].
We can take the representation of a right-angle triangle with height and base ratio being 2 and the angle being $\theta $. The height and base were considered with respect to that particular angle $\theta $.
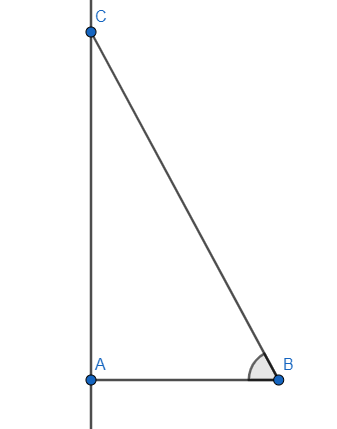
In this case we take $AB=x$ and keeping the ratio in mind we have $AC=2x$ as the ratio has to be 8.
Now we apply the Pythagoras’ theorem to find the length of BC. $B{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}$.
So, $B{{C}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{\left( 2x \right)}^{2}}=5{{x}^{2}}$ which gives $BC=\sqrt{5}x$.
We need to find $\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}2 \right)$ which is equal to \[\cos \theta \].
This ratio gives \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{base}}{\text{hypotenuse}}\]. So, \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{5}x}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\].
Therefore, $\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}2 \right)$ is equal to \[\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\].
Note: We can also apply the trigonometric image form to get the value of $\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}2 \right)$.
It’s given that \[\tan \theta =2\] and we need to find \[\cos \theta \]. We know $\cos \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }}$.
Putting the values, we get $\cos \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+4}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}$.
Complete step by step solution:
The internal part \[{{\tan }^{-1}}2\] of $\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}2 \right)$ is an angle. We assume \[{{\tan }^{-1}}2=\theta \].
This gives in ratio \[\tan \theta =2\]. We know \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{height}}{\text{base}}\].
We can take the representation of a right-angle triangle with height and base ratio being 2 and the angle being $\theta $. The height and base were considered with respect to that particular angle $\theta $.

In this case we take $AB=x$ and keeping the ratio in mind we have $AC=2x$ as the ratio has to be 8.
Now we apply the Pythagoras’ theorem to find the length of BC. $B{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}$.
So, $B{{C}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{\left( 2x \right)}^{2}}=5{{x}^{2}}$ which gives $BC=\sqrt{5}x$.
We need to find $\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}2 \right)$ which is equal to \[\cos \theta \].
This ratio gives \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{base}}{\text{hypotenuse}}\]. So, \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{5}x}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\].
Therefore, $\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}2 \right)$ is equal to \[\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\].
Note: We can also apply the trigonometric image form to get the value of $\cos \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}2 \right)$.
It’s given that \[\tan \theta =2\] and we need to find \[\cos \theta \]. We know $\cos \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }}$.
Putting the values, we get $\cos \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+4}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




