
Find the equation to the tangent and normal at the ends of the latus rectum of the ellipse $9{x^2} + 16{y^2} = 144$.
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: First, write the coordinates of the latus rectum for the ellipse for all quadrants. To evaluate the equation of tangent and normal at the ends of the latus rectum, use the formula for the equation of tangent and normal at the given point.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Draw the figure of the ellipse and tangent at the end of the latus rectum in the first quadrant.
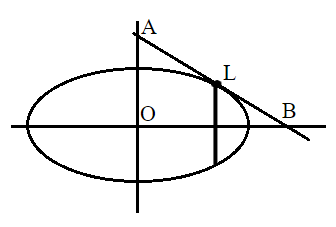
AB is the tangent and L is the point of the of latus rectum in first quadrant.
We are given an equation of ellipse $9{x^2} + 16{y^2} = 144$.
First, we write it in the standard form which is $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$
Divide both the sides by $144$.
\[
\dfrac{{9{x^2}}}{{144}} + \dfrac{{16{y^2}}}{{144}} = \dfrac{{144}}{{144}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} = 1 \\
\]
Therefore, ${a^2} = 16$ and ${b^2} = 9$
We have to find the equation of tangent and normal at the ends of the latus rectum.
We know that the coordinates of the latus rectum for the ellipse is \[\left( { \pm ae, \pm \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{a}} \right)\]
It means we have to evaluate the value of $e$.
$e$is the eccentricity of the ellipse which can be obtained by using the formula $e = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{a^2} - {b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $
Substitute the value ${a^2} = 16$ and ${b^2} = 9$.
$
e = \sqrt {\dfrac{{16 - 9}}{{16}}} \\
\Rightarrow e = \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{4} \\
$
Therefore, the coordinates of the latus rectum will be:
\[\left( { \pm \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{4}4, \pm \dfrac{9}{4}} \right) = \left( { \pm \sqrt 7 , \pm \dfrac{9}{4}} \right)\]
Let the end of the latus rectum lie in the first quadrant.
Therefore, coordinates of the latus rectum will be \[\left( {\sqrt 7 ,\dfrac{9}{4}} \right)\] because in the first quadrant the value of x and y are positive.
We know that the equation of the tangent at the end of the latus rectum is:
\[\dfrac{{x{x_1}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{y{y_1}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\], here $({x_1},{y_1})$is the coordinate of the latus rectum, $a$ and $b$ represents the distance of centre of the ellipse from major and minor axis.
Therefore, equation of the tangent at \[\left( {\sqrt 7 ,\dfrac{9}{4}} \right)\] will be:
\[\dfrac{{x\sqrt 7 }}{{16}} + \dfrac{{y\left( {\dfrac{9}{4}} \right)}}{9} = 1\]
Solve the equation by taking LCM and cross multiplying and evaluate the equation of the tangent.
$
\dfrac{{\sqrt 7 x}}{{16}} + \dfrac{y}{4} = 1 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 x + 4y}}{{16}} = 1 \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 7 x + 4y = 16 \\
$
Therefore, the equation of the tangent at the end of the latus rectum is $\sqrt 7 x + 4y = 16$.
We know that the equation of the normal at the end of the latus rectum is:
\[\dfrac{{{a^2}x}}{{{x_1}}} - \dfrac{{{b^2}y}}{{{y_1}}} = {a^2} - {b^2}\], here $({x_1},{y_1})$is the coordinate of the latus rectum, , $a$ and $b$ represents the distance of centre of the ellipse from major and minor axis.
Therefore, equation of the normal at \[\left( {\sqrt 7 ,\dfrac{9}{4}} \right)\] will be:
\[\dfrac{{16x}}{{\sqrt 7 }} - \dfrac{{9y}}{{\dfrac{9}{4}}} = 16 - 9\]
Solve the equation by taking LCM and cross multiplying and evaluate the equation of the normal.
\[
\dfrac{{16x}}{{\sqrt 7 }} - 4y = 7 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{16x - 4\sqrt 7 y}}{{\sqrt 7 }} = 7 \\
\Rightarrow 16x - 4\sqrt 7 y = 7\sqrt 7 \\
\]
$\therefore$ The equation of the normal at the end of the latus rectum is \[16x - 4\sqrt 7 y = 7\sqrt 7 \].
Similarly, we can also find the equation of tangents and the normal for the other quadrants.
Note:
The eccentricity of an ellipse is always less than $1$. Since the normal and tangent are perpendicular to each other, therefore, the product of their slope is $ - 1$. The Latus rectum of an ellipse is the chord of an ellipse though its one focus and perpendicular to the major axis.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Draw the figure of the ellipse and tangent at the end of the latus rectum in the first quadrant.

AB is the tangent and L is the point of the of latus rectum in first quadrant.
We are given an equation of ellipse $9{x^2} + 16{y^2} = 144$.
First, we write it in the standard form which is $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$
Divide both the sides by $144$.
\[
\dfrac{{9{x^2}}}{{144}} + \dfrac{{16{y^2}}}{{144}} = \dfrac{{144}}{{144}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} = 1 \\
\]
Therefore, ${a^2} = 16$ and ${b^2} = 9$
We have to find the equation of tangent and normal at the ends of the latus rectum.
We know that the coordinates of the latus rectum for the ellipse is \[\left( { \pm ae, \pm \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{a}} \right)\]
It means we have to evaluate the value of $e$.
$e$is the eccentricity of the ellipse which can be obtained by using the formula $e = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{a^2} - {b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $
Substitute the value ${a^2} = 16$ and ${b^2} = 9$.
$
e = \sqrt {\dfrac{{16 - 9}}{{16}}} \\
\Rightarrow e = \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{4} \\
$
Therefore, the coordinates of the latus rectum will be:
\[\left( { \pm \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{4}4, \pm \dfrac{9}{4}} \right) = \left( { \pm \sqrt 7 , \pm \dfrac{9}{4}} \right)\]
Let the end of the latus rectum lie in the first quadrant.
Therefore, coordinates of the latus rectum will be \[\left( {\sqrt 7 ,\dfrac{9}{4}} \right)\] because in the first quadrant the value of x and y are positive.
We know that the equation of the tangent at the end of the latus rectum is:
\[\dfrac{{x{x_1}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{y{y_1}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\], here $({x_1},{y_1})$is the coordinate of the latus rectum, $a$ and $b$ represents the distance of centre of the ellipse from major and minor axis.
Therefore, equation of the tangent at \[\left( {\sqrt 7 ,\dfrac{9}{4}} \right)\] will be:
\[\dfrac{{x\sqrt 7 }}{{16}} + \dfrac{{y\left( {\dfrac{9}{4}} \right)}}{9} = 1\]
Solve the equation by taking LCM and cross multiplying and evaluate the equation of the tangent.
$
\dfrac{{\sqrt 7 x}}{{16}} + \dfrac{y}{4} = 1 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 x + 4y}}{{16}} = 1 \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 7 x + 4y = 16 \\
$
Therefore, the equation of the tangent at the end of the latus rectum is $\sqrt 7 x + 4y = 16$.
We know that the equation of the normal at the end of the latus rectum is:
\[\dfrac{{{a^2}x}}{{{x_1}}} - \dfrac{{{b^2}y}}{{{y_1}}} = {a^2} - {b^2}\], here $({x_1},{y_1})$is the coordinate of the latus rectum, , $a$ and $b$ represents the distance of centre of the ellipse from major and minor axis.
Therefore, equation of the normal at \[\left( {\sqrt 7 ,\dfrac{9}{4}} \right)\] will be:
\[\dfrac{{16x}}{{\sqrt 7 }} - \dfrac{{9y}}{{\dfrac{9}{4}}} = 16 - 9\]
Solve the equation by taking LCM and cross multiplying and evaluate the equation of the normal.
\[
\dfrac{{16x}}{{\sqrt 7 }} - 4y = 7 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{16x - 4\sqrt 7 y}}{{\sqrt 7 }} = 7 \\
\Rightarrow 16x - 4\sqrt 7 y = 7\sqrt 7 \\
\]
$\therefore$ The equation of the normal at the end of the latus rectum is \[16x - 4\sqrt 7 y = 7\sqrt 7 \].
Similarly, we can also find the equation of tangents and the normal for the other quadrants.
Note:
The eccentricity of an ellipse is always less than $1$. Since the normal and tangent are perpendicular to each other, therefore, the product of their slope is $ - 1$. The Latus rectum of an ellipse is the chord of an ellipse though its one focus and perpendicular to the major axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




