
Find the domain and the range of the cube root function, \[f:\mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}:f(x) = {x^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\] for all \[x \in \mathbb{R}\]. Also draw its graph.
Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, we have to find out the domain and the range of the cube root function.
To find the domain we need to consider the denominator equals zero and find out the restrictions. Then we can write the domain in interval form excluding the restriction values from the domain.
To find the range first we need to take \[f(x) = y\] and find out x in terms of y. After that finding the domain of x we will get the range of the function.
Complete step-by-step solution:
It is given that, \[f:\mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}:f(x) = {x^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\] for all \[x \in \mathbb{R}\].
We need to find the domain and the range of the cube root function.
For finding the domain we need to find the restrictions of the function f.
Since there is no denominator in the function f, there is no restriction on the function where the function is undefined.
We know that the real number set varies from \[ - \infty \]to\[\infty \].
Thus, we get the domain of the required function f is\[\left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)\]\[\left\{ {x|x \in \mathbb{R}} \right\}\].
Now for finding the range first we need to take \[f(x) = y\] and evaluating the domain for \[x = g(y)\]
is the range of f.
Now, considering \[f(x) = y\] we get, \[y = {x^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\]
Taking cube both sides we get,
\[x = {y^3}\]
The domain of the function g is \[\left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)\]\[\left\{ {x|x \in \mathbb{R}} \right\}\].
Hence the range of f is also \[\left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)\]\[\left\{ {x|x \in \mathbb{R}} \right\}\].
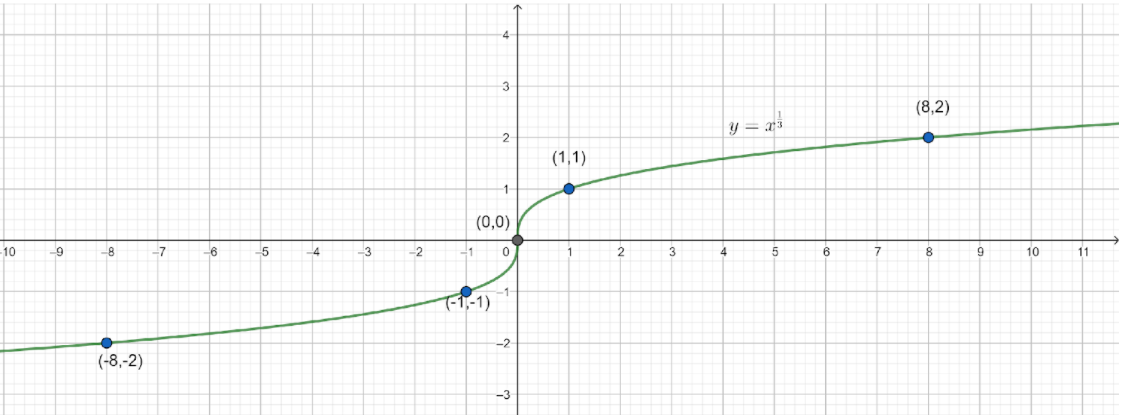
Now we need to draw the graph of \[f:\mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}:f(x) = {x^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\], for all \[x \in \mathbb{R}\].
Again, \[y = {x^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\] can be written as \[x = {y^3}\].
To do that we need to put \[y = 0, - 1,1, - 2,2,...\] in the function and get the value of x. Putting\[y = 0, - 1,1, - 2,2\] we get, \[x = 0, - 1,1, - 8,8\]
We get the points \[(0,0),( - 1, - 1),(1,1),(8, - 2),(8,2)\]. Joining these points we will get the graph.
Note: Range of a function:
The complete set of possible values of the dependent variable is known as the range of a function
The domain of a function:
The complete set of possible values of the independent variable is known as the domain of a function
For example,
If \[y = f(x)\] is a function then the complete set of possible values of x is known as Domain and y is known as the Range of the function f.
To find the domain we need to consider the denominator equals zero and find out the restrictions. Then we can write the domain in interval form excluding the restriction values from the domain.
To find the range first we need to take \[f(x) = y\] and find out x in terms of y. After that finding the domain of x we will get the range of the function.
Complete step-by-step solution:
It is given that, \[f:\mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}:f(x) = {x^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\] for all \[x \in \mathbb{R}\].
We need to find the domain and the range of the cube root function.
For finding the domain we need to find the restrictions of the function f.
Since there is no denominator in the function f, there is no restriction on the function where the function is undefined.
We know that the real number set varies from \[ - \infty \]to\[\infty \].
Thus, we get the domain of the required function f is\[\left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)\]\[\left\{ {x|x \in \mathbb{R}} \right\}\].
Now for finding the range first we need to take \[f(x) = y\] and evaluating the domain for \[x = g(y)\]
is the range of f.
Now, considering \[f(x) = y\] we get, \[y = {x^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\]
Taking cube both sides we get,
\[x = {y^3}\]
The domain of the function g is \[\left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)\]\[\left\{ {x|x \in \mathbb{R}} \right\}\].
Hence the range of f is also \[\left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)\]\[\left\{ {x|x \in \mathbb{R}} \right\}\].
Now we need to draw the graph of \[f:\mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}:f(x) = {x^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\], for all \[x \in \mathbb{R}\].
Again, \[y = {x^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\] can be written as \[x = {y^3}\].
To do that we need to put \[y = 0, - 1,1, - 2,2,...\] in the function and get the value of x. Putting\[y = 0, - 1,1, - 2,2\] we get, \[x = 0, - 1,1, - 8,8\]
We get the points \[(0,0),( - 1, - 1),(1,1),(8, - 2),(8,2)\]. Joining these points we will get the graph.

Note: Range of a function:
The complete set of possible values of the dependent variable is known as the range of a function
The domain of a function:
The complete set of possible values of the independent variable is known as the domain of a function
For example,
If \[y = f(x)\] is a function then the complete set of possible values of x is known as Domain and y is known as the Range of the function f.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




