
How do you find the centre, vertices and foci of an ellipse$\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y + 2} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$?
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint:
Here we need to compare the general equation of the ellipse which is $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - k} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$with the given ellipse $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y + 2} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$ to get the centre $\left( {h,k} \right)$, vertices on the major axis as $\left( {h - a,k} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h + a,k} \right)$ and the vertices on the minor axis as $\left( {h,k - b} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h,k + b} \right)$ and the foci $\left( {h - \sqrt {{a^2} - {b^2}} ,k} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h + \sqrt {{a^2} - {b^2}} ,k} \right)$
Complete step by step solution:
Here we are given the ellipse whose equation is $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y + 2} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$ and we need to find the vertices, centre and foci of this ellipse. So we must know that general equation of the ellipse is written in the form $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - k} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ but we are given $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y + 2} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$
If we compare both the equations we will get the values of $a,b,h,k$ as:
$
h = 3 \\
k = - 2 \\
{b^2} = 9,b = 3 \\
{a^2} = 16,a = 4 \\
$
We can draw the ellipse as:
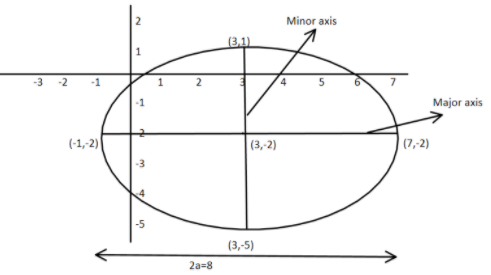
Now we can see that the centre of the ellipse is written as $\left( {h,k} \right)$ according to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - k} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ but we are given $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y + 2} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$
So on comparing we can write given ellipse as:
$\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - ( - 2)} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$
So we can say that the centre of the ellipse is $\left( {3, - 2} \right)$
Now we must know that it is the horizontal ellipse as its major axis is greater in length than the minor axis as $a > b$ and therefore we can say that its major axis will be parallel to $x - {\text{axis}}$ and the minor axis will be parallel to the $y - {\text{axis}}$
Now we can say that there will be $4$ vertices, two on the major axis and two on the minor axis.
On the major axis the vertices are written as $\left( {h - a,k} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h + a,k} \right)$ and the vertices on the minor axis as $\left( {h,k - b} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h,k + b} \right)$
So we can say:
Vertices on major axis
$\left( {h - a,k} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h + a,k} \right)$
$
= \left( {3 - 4, - 2} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3 + 4, - 2} \right) \\
= \left( { - 1, - 2} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {7,2} \right) \\
$
Vertices on minor axis:
$\left( {h,k - b} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h,k + b} \right)$
$
= \left( {3, - 2 - 3} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3, - 2 + 3} \right) \\
= \left( {3, - 5} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3,1} \right) \\
$
Now to calculate foci we must know that foci for the horizontal ellipse is given by:
Coordinate $\left( {h - \sqrt {{a^2} - {b^2}} ,k} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h + \sqrt {{a^2} - {b^2}} ,k} \right)$ for the general equation $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - k} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$
So we can substitute the values and get:
Foci
$
= \left( {\left( {3 - \sqrt {{4^2} - {3^2}} , - 2} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3 + \sqrt {{4^2} - {3^2}} , - 2} \right)} \right) \\
= \left( {\left( {3 - \sqrt 7 , - 2} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3 + \sqrt 7 , - 2} \right)} \right) \\
$
Note:
Here in these types of problems the student must try to draw the figure according to the type of ellipse that is given as this makes the understanding level of the question clearer. One must know all the general equations of the ellipse and also the way to calculate all the terms using the comparison method.
Here we need to compare the general equation of the ellipse which is $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - k} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$with the given ellipse $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y + 2} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$ to get the centre $\left( {h,k} \right)$, vertices on the major axis as $\left( {h - a,k} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h + a,k} \right)$ and the vertices on the minor axis as $\left( {h,k - b} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h,k + b} \right)$ and the foci $\left( {h - \sqrt {{a^2} - {b^2}} ,k} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h + \sqrt {{a^2} - {b^2}} ,k} \right)$
Complete step by step solution:
Here we are given the ellipse whose equation is $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y + 2} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$ and we need to find the vertices, centre and foci of this ellipse. So we must know that general equation of the ellipse is written in the form $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - k} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ but we are given $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y + 2} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$
If we compare both the equations we will get the values of $a,b,h,k$ as:
$
h = 3 \\
k = - 2 \\
{b^2} = 9,b = 3 \\
{a^2} = 16,a = 4 \\
$
We can draw the ellipse as:

Now we can see that the centre of the ellipse is written as $\left( {h,k} \right)$ according to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - k} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ but we are given $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y + 2} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$
So on comparing we can write given ellipse as:
$\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - ( - 2)} \right)}^2}}}{9} = 1$
So we can say that the centre of the ellipse is $\left( {3, - 2} \right)$
Now we must know that it is the horizontal ellipse as its major axis is greater in length than the minor axis as $a > b$ and therefore we can say that its major axis will be parallel to $x - {\text{axis}}$ and the minor axis will be parallel to the $y - {\text{axis}}$
Now we can say that there will be $4$ vertices, two on the major axis and two on the minor axis.
On the major axis the vertices are written as $\left( {h - a,k} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h + a,k} \right)$ and the vertices on the minor axis as $\left( {h,k - b} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h,k + b} \right)$
So we can say:
Vertices on major axis
$\left( {h - a,k} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h + a,k} \right)$
$
= \left( {3 - 4, - 2} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3 + 4, - 2} \right) \\
= \left( { - 1, - 2} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {7,2} \right) \\
$
Vertices on minor axis:
$\left( {h,k - b} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h,k + b} \right)$
$
= \left( {3, - 2 - 3} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3, - 2 + 3} \right) \\
= \left( {3, - 5} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3,1} \right) \\
$
Now to calculate foci we must know that foci for the horizontal ellipse is given by:
Coordinate $\left( {h - \sqrt {{a^2} - {b^2}} ,k} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {h + \sqrt {{a^2} - {b^2}} ,k} \right)$ for the general equation $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - k} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$
So we can substitute the values and get:
Foci
$
= \left( {\left( {3 - \sqrt {{4^2} - {3^2}} , - 2} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3 + \sqrt {{4^2} - {3^2}} , - 2} \right)} \right) \\
= \left( {\left( {3 - \sqrt 7 , - 2} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {3 + \sqrt 7 , - 2} \right)} \right) \\
$
Note:
Here in these types of problems the student must try to draw the figure according to the type of ellipse that is given as this makes the understanding level of the question clearer. One must know all the general equations of the ellipse and also the way to calculate all the terms using the comparison method.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




