
Find the bond order of ${\text{N }} - {\text{ O}}$ bond in ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - $ .
A. $1$
B. $2$
C. $3$
D. $1.33$
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint:
We can find the bond order by drawing the lewis structure or lewis dot structure. This structure gives us the information of the bonds between the atoms and lone pairs of electrons present on the atoms. The bond order by lewis structure can be given by $\dfrac{{{\text{Total number of bonds}}}}{{{\text{Number of the bond groups}}}}$ . You can refer to the figure for the lewis structure of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - $ .
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first discuss bond order.
Bond order is basically the number of chemical bonds between two atoms of a compound or molecule. According to molecular orbital theory, bond order can also be defined as the difference between the bonds and the anti-bonds. Bonds are formed due to sharing of electrons in bonding orbitals and anti-bonds are formed due to sharing of electrons in antibonding orbitals.
We can find the bond order by drawing the lewis structure or lewis dot structure. This structure gives us the information of the bonds between the atoms and lone pairs of electrons present on the atoms.
Lewis structure of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - $ is given in the figure.
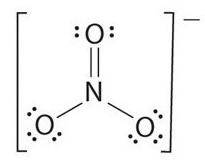
As clear from the figure that the total number of ${\text{N }} - {\text{ O}}$ bonds is $4$ and there are $3$ bond groups between the individual atoms.
We know that the bond order by lewis structure can be given by $\dfrac{{{\text{Total number of bonds}}}}{{{\text{Number of the bond groups}}}}$ .
Therefore, bond order of ${\text{N }} - {\text{ O}}$ bond in ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - $ is $\dfrac{4}{3} = 1.33$ .
Hence the correct option is D.
Note:
Although lewis dot structures can be used to identify the bond orders and bond lengths in a compound, it has certain limitations. It is not able to describe the actual shape of a compound such as for resonance structures. It is primarily based on the concept of octet rule which has further limitations as in electron deficient compounds and odd electrons species.
We can find the bond order by drawing the lewis structure or lewis dot structure. This structure gives us the information of the bonds between the atoms and lone pairs of electrons present on the atoms. The bond order by lewis structure can be given by $\dfrac{{{\text{Total number of bonds}}}}{{{\text{Number of the bond groups}}}}$ . You can refer to the figure for the lewis structure of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - $ .
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first discuss bond order.
Bond order is basically the number of chemical bonds between two atoms of a compound or molecule. According to molecular orbital theory, bond order can also be defined as the difference between the bonds and the anti-bonds. Bonds are formed due to sharing of electrons in bonding orbitals and anti-bonds are formed due to sharing of electrons in antibonding orbitals.
We can find the bond order by drawing the lewis structure or lewis dot structure. This structure gives us the information of the bonds between the atoms and lone pairs of electrons present on the atoms.
Lewis structure of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - $ is given in the figure.

As clear from the figure that the total number of ${\text{N }} - {\text{ O}}$ bonds is $4$ and there are $3$ bond groups between the individual atoms.
We know that the bond order by lewis structure can be given by $\dfrac{{{\text{Total number of bonds}}}}{{{\text{Number of the bond groups}}}}$ .
Therefore, bond order of ${\text{N }} - {\text{ O}}$ bond in ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - $ is $\dfrac{4}{3} = 1.33$ .
Hence the correct option is D.
Note:
Although lewis dot structures can be used to identify the bond orders and bond lengths in a compound, it has certain limitations. It is not able to describe the actual shape of a compound such as for resonance structures. It is primarily based on the concept of octet rule which has further limitations as in electron deficient compounds and odd electrons species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




