
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve $y={{x}^{2}}$, the x-axis and the ordinates x = 1 and x= 3.
Answer
606.9k+ views
Hint: Plot the graph on a graph. Identify the region whose area is to be found. Use the fact that the area of the region bounded by y=f(x), the x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x= b is given by
$y=\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$. Hence argue that the required area is given by $A=\int_{1}^{2}{{{x}^{2}}}dx$. Integrate and hence find the required area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
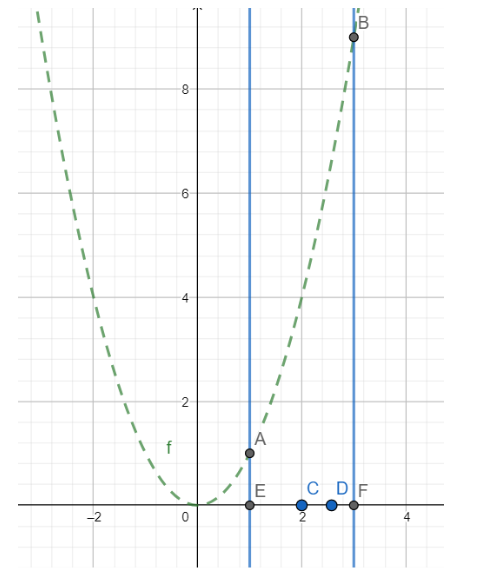
Hence the area bounded by the curve $y={{x}^{2}}$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= 1 and x= 2 is the area of the region AECDFBA.
We know that the area of the region bounded by y=f(x), the x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x= b is given by
$y=\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$.
Hence the required area $=\int_{1}^{3}{\left| {{x}^{2}} \right|dx}$
We know that $\forall x\in R,\left| {{x}^{2}} \right|={{x}^{2}}$
Hence, we have
Required area $=\int_{1}^{3}{{{x}^{2}}dx}$
We know that $\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}$ and according to the first fundamental theorem of calculus if F’(x) = f(x), then $\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}=F\left( b \right)-F\left( a \right)$
Hence, we have
Required area $=\left. \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3} \right|_{1}^{3}=\dfrac{27}{3}-\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{26}{3}$
Hence the required area is $\dfrac{26}{3}$ square units.
Note: Alternative Solution:
The area bounded by the curve $y={{x}^{n}}$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= a, and x= b, $a,b\ge 0$ is given by
$\dfrac{{{b}^{n+1}}-{{a}^{n+1}}}{n+1}$
Hence the required area $=\dfrac{{{3}^{3}}-{{1}^{3}}}{3}=\dfrac{26}{3}$ square units.
$y=\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$. Hence argue that the required area is given by $A=\int_{1}^{2}{{{x}^{2}}}dx$. Integrate and hence find the required area.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Hence the area bounded by the curve $y={{x}^{2}}$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= 1 and x= 2 is the area of the region AECDFBA.
We know that the area of the region bounded by y=f(x), the x-axis and the ordinates x = a and x= b is given by
$y=\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$.
Hence the required area $=\int_{1}^{3}{\left| {{x}^{2}} \right|dx}$
We know that $\forall x\in R,\left| {{x}^{2}} \right|={{x}^{2}}$
Hence, we have
Required area $=\int_{1}^{3}{{{x}^{2}}dx}$
We know that $\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}}$ and according to the first fundamental theorem of calculus if F’(x) = f(x), then $\int_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}=F\left( b \right)-F\left( a \right)$
Hence, we have
Required area $=\left. \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3} \right|_{1}^{3}=\dfrac{27}{3}-\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{26}{3}$
Hence the required area is $\dfrac{26}{3}$ square units.
Note: Alternative Solution:
The area bounded by the curve $y={{x}^{n}}$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= a, and x= b, $a,b\ge 0$ is given by
$\dfrac{{{b}^{n+1}}-{{a}^{n+1}}}{n+1}$
Hence the required area $=\dfrac{{{3}^{3}}-{{1}^{3}}}{3}=\dfrac{26}{3}$ square units.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




