
Find the area bounded by the ellipse \[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\] and the ordinates $x = 0$and $x = ae$, where ${b^2} = {a^2}\left( {1 - {e^2}} \right)$ and $e < 1$.
Answer
631.8k+ views
Hint: Simplify the given ellipse equation and integrate within the given ordinate limits to find the area.
An ellipse of the form \[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\] will meet the X-axis at (a, 0) and the Y-axis at (0, b). Let these points be P (a,0) and Q (0, b). It is symmetrical about the axes.
The ordinates given are $x = 0$and $x = ae$ which will be parallel to the Y-axis as shown in the figure.
The shaded area is the area bounded by the ellipse and the given ordinates.
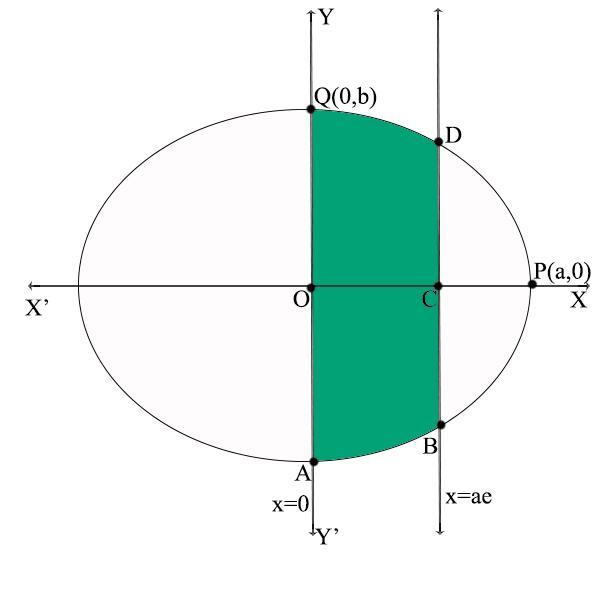
Required area = Area of the shaded region
= $2 \times $Area of QOCD
=$2 \times \int_0^{ae} y dx$ …(1)
The given equation is \[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\]. Let us find the value of y from this equation and substitute in equation (1).
$\begin{gathered}
\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1 \\
\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
\begin{gathered}
\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = \dfrac{{{a^2} - {x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
\end{gathered} \\
{{y^2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\left( {{a^2} - {x^2}} \right)} \\
{y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\left( {{a^2} - {x^2}} \right)} } \\
{y = \pm \dfrac{b}{a}\sqrt {\left( {{a^2} - {x^2}} \right)} }
\end{array} \\
\end{gathered} $
Since, the area in equation (1) which is the area of QOCD is in the 1st quadrant. Hence, the value of y will be positive.
Hence, $y = \dfrac{b}{a}\sqrt {\left( {{a^2} - {x^2}} \right)} $ …(2)
Substituting (2) in (1),
Required area =$2 \times \int_0^{ae} y dx$
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{ = 2\mathop \smallint \limits_0^{ae} \dfrac{b}{a}\sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} dx} \\
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}\mathop \smallint \limits_0^{ae} \sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} dx}
\end{array}\] (Since a and b are constants)
We know that, \[\mathop \smallint \nolimits^ \sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} dx = \dfrac{{x\sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} }}{2} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{\sin ^{ - 1}}(\dfrac{x}{a}) + c\]
Using this in the previous step, we get
Required area = \[\dfrac{{2b}}{a}[\dfrac{1}{2}x\sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{x}{a}]_0^{ae}\] \[\begin{gathered}
\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}[(\dfrac{{ae}}{2}\sqrt {{a^2} - {{(ae)}^2}} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{ae}}{a}) - (\dfrac{0}{2}\sqrt {{a^2} - 0} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}(\dfrac{0}{a}))]} \\
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}[\dfrac{{ae}}{2}\sqrt {{a^2} - {a^2}{e^2}} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}(e) - 0 - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}(0)]} \\
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}[\dfrac{{ae}}{2} \cdot a\sqrt {1 - {e^2}} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}e - 0]}
\end{array} \\
\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}[\dfrac{{{a^2}e}}{2}\sqrt {1 - {e^2}} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}e]} \\
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}(\dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2})[e\sqrt {1 - {e^2}} + {{\sin }^{ - 1}}e]} \\
{ = ab[e\sqrt {1 - {e^2}} + {{\sin }^{ - 1}}e]}
\end{array} \\
\end{gathered} \]
Required Area bounded by the ellipse \[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\] and the ordinates $x = 0$and $x = ae$
\[ = ab[e\sqrt {1 - {e^2}} + {\sin ^{ - 1}}e]\]
Note: The required area can also be found by integrating the entire shaded area QOABCD instead of finding $2 \times $Area of QOCD. It would be a little lengthier and more unnecessary because the given ellipse is symmetrical about the origin.
An ellipse of the form \[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\] will meet the X-axis at (a, 0) and the Y-axis at (0, b). Let these points be P (a,0) and Q (0, b). It is symmetrical about the axes.
The ordinates given are $x = 0$and $x = ae$ which will be parallel to the Y-axis as shown in the figure.
The shaded area is the area bounded by the ellipse and the given ordinates.

Required area = Area of the shaded region
= $2 \times $Area of QOCD
=$2 \times \int_0^{ae} y dx$ …(1)
The given equation is \[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\]. Let us find the value of y from this equation and substitute in equation (1).
$\begin{gathered}
\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1 \\
\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
\begin{gathered}
\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1 - \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = \dfrac{{{a^2} - {x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
\end{gathered} \\
{{y^2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\left( {{a^2} - {x^2}} \right)} \\
{y = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}\left( {{a^2} - {x^2}} \right)} } \\
{y = \pm \dfrac{b}{a}\sqrt {\left( {{a^2} - {x^2}} \right)} }
\end{array} \\
\end{gathered} $
Since, the area in equation (1) which is the area of QOCD is in the 1st quadrant. Hence, the value of y will be positive.
Hence, $y = \dfrac{b}{a}\sqrt {\left( {{a^2} - {x^2}} \right)} $ …(2)
Substituting (2) in (1),
Required area =$2 \times \int_0^{ae} y dx$
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{ = 2\mathop \smallint \limits_0^{ae} \dfrac{b}{a}\sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} dx} \\
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}\mathop \smallint \limits_0^{ae} \sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} dx}
\end{array}\] (Since a and b are constants)
We know that, \[\mathop \smallint \nolimits^ \sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} dx = \dfrac{{x\sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} }}{2} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{\sin ^{ - 1}}(\dfrac{x}{a}) + c\]
Using this in the previous step, we get
Required area = \[\dfrac{{2b}}{a}[\dfrac{1}{2}x\sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{x}{a}]_0^{ae}\] \[\begin{gathered}
\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}[(\dfrac{{ae}}{2}\sqrt {{a^2} - {{(ae)}^2}} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{ae}}{a}) - (\dfrac{0}{2}\sqrt {{a^2} - 0} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}(\dfrac{0}{a}))]} \\
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}[\dfrac{{ae}}{2}\sqrt {{a^2} - {a^2}{e^2}} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}(e) - 0 - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}(0)]} \\
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}[\dfrac{{ae}}{2} \cdot a\sqrt {1 - {e^2}} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}e - 0]}
\end{array} \\
\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}[\dfrac{{{a^2}e}}{2}\sqrt {1 - {e^2}} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{ - 1}}e]} \\
{ = \dfrac{{2b}}{a}(\dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2})[e\sqrt {1 - {e^2}} + {{\sin }^{ - 1}}e]} \\
{ = ab[e\sqrt {1 - {e^2}} + {{\sin }^{ - 1}}e]}
\end{array} \\
\end{gathered} \]
Required Area bounded by the ellipse \[\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\] and the ordinates $x = 0$and $x = ae$
\[ = ab[e\sqrt {1 - {e^2}} + {\sin ^{ - 1}}e]\]
Note: The required area can also be found by integrating the entire shaded area QOABCD instead of finding $2 \times $Area of QOCD. It would be a little lengthier and more unnecessary because the given ellipse is symmetrical about the origin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




