
Find out the product of reaction.
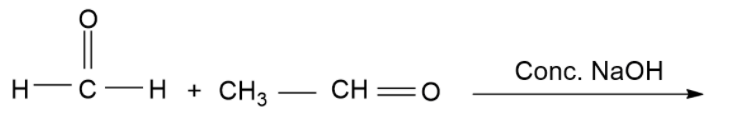
(A)- $C{H_3}C{O_2}Na\& C{H_3}OH$
(B)- $C{H_3}C{H_2}OH\& C{H_3}OH$
(C)- $C{H_3}C{H_2}OH\& HC{O_2}Na$
(D)- $C{H_3}C{H_2}ONa\& HC{O_2}Na$
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: The above question is based on Cannizzaro reaction. It is a chemical reaction named after Stanislao Cannizzaro that involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules of a non-enolizable aldehyde to yield a carboxylic acid and a primary alcohol as a product.
Complete answer:
This reaction is based on the crossed Cannizzaro reaction. Let's try to understand what the Cannizzaro reaction is.
Aldehydes with alpha hydrogen atoms undergo deprotonation due to the strongly alkaline conditions of the reaction, leading to enolates or aldol reactions of these enolates where beta-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones are obtained. Therefore, it is not surprising that the reaction produces only 50% of the required alcohol and carboxylic acid. That's why the crossed Cannizzaro reaction is more commonly used. A sacrificial aldehyde is combined with a more valuable chemical. The required alcohol is obtained from the reduction of the aldehyde chemical. Since 2 different aldehydes can be completely converted into the required product, the valuable chemical is increased.
Let's try to understand how the Cannizzaro reaction proceeds.
The Cannizzaro Reaction Mechanism method is used to get one molecule of alcohol and one molecule of carboxylic acid from two molecules of a given aldehyde. The reaction is executed by a nucleophilic acyl substitution on an aldehyde where the leaving group (which is a negatively charged hydrogen) attacks another aldehyde. A tetrahedral intermediate is formed from the attack of hydroxide on a carbonyl. This tetrahedral intermediate collapse, reforming the carbonyl and transferring a hydride which attacks another aldehyde.
A proton is then exchanged by an acid and alkoxide ions. When a base of high concentration is introduced, the aldehyde forms an anion. From this, a hydride ion is transferred to another aldehyde, forming carboxylate and alkoxide ions. The alkoxide ion also obtains a proton from the solvent.
Now, let's see the mechanism of the above reaction.
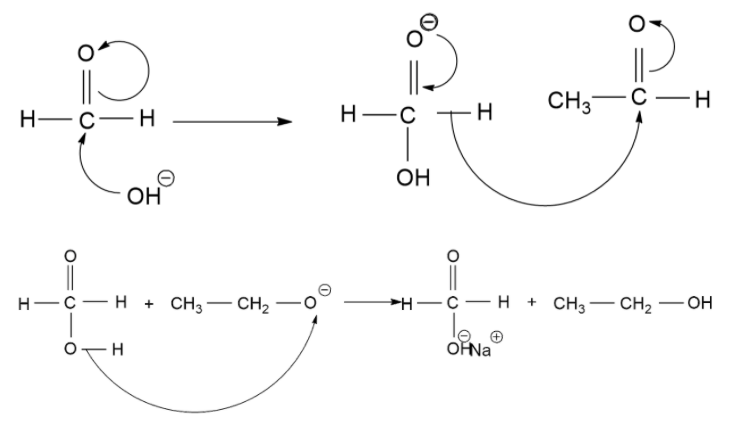
Therefore, the correct answer to the above question is (A)- $C{H_3}C{O_2}Na\& C{H_3}OH$.
Note:
Remember that in this reaction, one aldehyde is oxidized to give a carboxylic acid whereas the other aldehyde undergoes reduction to yield the alcohol. Since both oxidation and reduction occurs in the hydride transfer in the reaction, the reaction is said to be a redox process.
Complete answer:
This reaction is based on the crossed Cannizzaro reaction. Let's try to understand what the Cannizzaro reaction is.
Aldehydes with alpha hydrogen atoms undergo deprotonation due to the strongly alkaline conditions of the reaction, leading to enolates or aldol reactions of these enolates where beta-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones are obtained. Therefore, it is not surprising that the reaction produces only 50% of the required alcohol and carboxylic acid. That's why the crossed Cannizzaro reaction is more commonly used. A sacrificial aldehyde is combined with a more valuable chemical. The required alcohol is obtained from the reduction of the aldehyde chemical. Since 2 different aldehydes can be completely converted into the required product, the valuable chemical is increased.
Let's try to understand how the Cannizzaro reaction proceeds.
The Cannizzaro Reaction Mechanism method is used to get one molecule of alcohol and one molecule of carboxylic acid from two molecules of a given aldehyde. The reaction is executed by a nucleophilic acyl substitution on an aldehyde where the leaving group (which is a negatively charged hydrogen) attacks another aldehyde. A tetrahedral intermediate is formed from the attack of hydroxide on a carbonyl. This tetrahedral intermediate collapse, reforming the carbonyl and transferring a hydride which attacks another aldehyde.
A proton is then exchanged by an acid and alkoxide ions. When a base of high concentration is introduced, the aldehyde forms an anion. From this, a hydride ion is transferred to another aldehyde, forming carboxylate and alkoxide ions. The alkoxide ion also obtains a proton from the solvent.
Now, let's see the mechanism of the above reaction.

Therefore, the correct answer to the above question is (A)- $C{H_3}C{O_2}Na\& C{H_3}OH$.
Note:
Remember that in this reaction, one aldehyde is oxidized to give a carboxylic acid whereas the other aldehyde undergoes reduction to yield the alcohol. Since both oxidation and reduction occurs in the hydride transfer in the reaction, the reaction is said to be a redox process.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




