
Explain the structure of microsporangium and write the functions of its different layers.
Answer
525.5k+ views
Hint: It is found in plants. It is a part of the male reproductive organ in the plants. It is the primary part and is responsible for the development of pollen grains. It is a sporangial structure that contains microspores.
Complete answer:
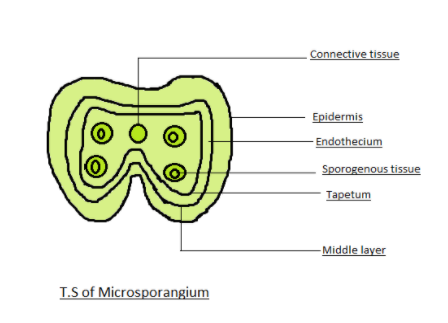
Structure and functions of layers- Microsporangium(singular) or microsporangia(plural) is a part of the male reproductive organs in plants which are the pollen sacs giving rise to male gametes in an angiosperm.
When viewed transversely, a microsporangium appears to have a circular outline. It is embarked further by four layers:
* Epidermis- It is a single layer and outermost layer. The main function lies in the protection of pollen.
* Endothecium- It is the layer that is present beneath the epidermis and it helps in thickening or provides thickening.
* Middle layers- It is made of further 2-3 layers.
* Tapetum- It is the innermost multinucleated layer with dense cytoplasm. The main function lies in nourishment.
* Sporogenous Tissue - These are situated at the focal point of every microsporangium in a youthful anther. With the advancement of the anther, the sporogenous cells go through meiotic division to frame microspore quadruplicates. Each sporogenous cell is known as a microspore mother cell. This cycle by which a microspore is shaped from the dust mother cell is known as microsporogenesis. The microspores are orchestrated as a quadruplicate. As the anther develops it dries out and the microspores separate from one another and form into a dust grain.
* Pollen Grain - The developed pollen contains two cells: a generative cell and a pollen tube cell.
Additional information: The anther finally matures and releases the pollen grain through a pollen tube which undergoes fertilization with the female gamete to form a zygote.
Note:
The outer layer will always perform the function of protection and the innermost layer is responsible for nourishment. Also, the corresponding term of microsporangia is megasporangia which is used for males and females respectively.
Complete answer:

Structure and functions of layers- Microsporangium(singular) or microsporangia(plural) is a part of the male reproductive organs in plants which are the pollen sacs giving rise to male gametes in an angiosperm.
When viewed transversely, a microsporangium appears to have a circular outline. It is embarked further by four layers:
* Epidermis- It is a single layer and outermost layer. The main function lies in the protection of pollen.
* Endothecium- It is the layer that is present beneath the epidermis and it helps in thickening or provides thickening.
* Middle layers- It is made of further 2-3 layers.
* Tapetum- It is the innermost multinucleated layer with dense cytoplasm. The main function lies in nourishment.
* Sporogenous Tissue - These are situated at the focal point of every microsporangium in a youthful anther. With the advancement of the anther, the sporogenous cells go through meiotic division to frame microspore quadruplicates. Each sporogenous cell is known as a microspore mother cell. This cycle by which a microspore is shaped from the dust mother cell is known as microsporogenesis. The microspores are orchestrated as a quadruplicate. As the anther develops it dries out and the microspores separate from one another and form into a dust grain.
* Pollen Grain - The developed pollen contains two cells: a generative cell and a pollen tube cell.
Additional information: The anther finally matures and releases the pollen grain through a pollen tube which undergoes fertilization with the female gamete to form a zygote.
Note:
The outer layer will always perform the function of protection and the innermost layer is responsible for nourishment. Also, the corresponding term of microsporangia is megasporangia which is used for males and females respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




