
Explain the process of sex determination in honey bees.
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: The male and female bees develop by different processes. The sex determination process seen in honey bees is Haplodiploidy type.
Complete answer:
The most important step in the process of fertilisation is syngamy. This is a fusion of male and female gametes. In some organisms, the fusion does not take place and the male or female gametes directly form new individuals. This is known as parthenogenesis. These individuals will be naturally haploid.
Parthenogenesis is of the following types.
>Thelytoky : In this type, only females are formed by parthenogenesis. Example : Rotifers
>Arrhenotoky : In this type, males are formed by parthenogenesis. Example : honey bees.
>Amphitoky : In this type, the parthenogenetic egg can form any sex. Example : Aphis
Thus honey bees show Arrhenotoky.
The sex determination in honey bees is as follows
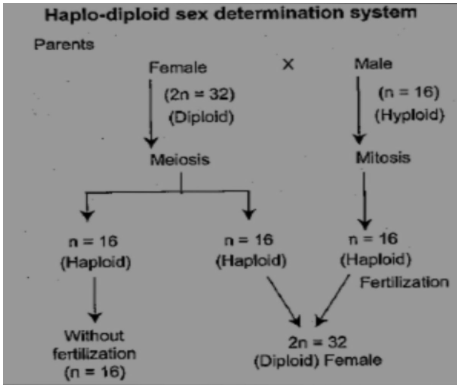
In Arrhenotoky, the males are haploid (as they are formed from parthenogenesis). The females are diploid. The male gametes (haploid) will undergo Mitosis and form male sex cells (sperms are also haploid). The diploid eggs will undergo Meiosis and form daughter cells or eggs that are haploid.
If the haploid egg combines with haploid sperm, the result will be diploid female. If the haploid eggs do not combine with the sperms, they will form haploid males again.
Note: The beehive shows three different types of bees. Queen bee, Worker bees and male or drone bees. Queen bees and worker bees are females and hence diploid and drones are males hence haploid.
Complete answer:
The most important step in the process of fertilisation is syngamy. This is a fusion of male and female gametes. In some organisms, the fusion does not take place and the male or female gametes directly form new individuals. This is known as parthenogenesis. These individuals will be naturally haploid.
Parthenogenesis is of the following types.
>Thelytoky : In this type, only females are formed by parthenogenesis. Example : Rotifers
>Arrhenotoky : In this type, males are formed by parthenogenesis. Example : honey bees.
>Amphitoky : In this type, the parthenogenetic egg can form any sex. Example : Aphis
Thus honey bees show Arrhenotoky.
The sex determination in honey bees is as follows

In Arrhenotoky, the males are haploid (as they are formed from parthenogenesis). The females are diploid. The male gametes (haploid) will undergo Mitosis and form male sex cells (sperms are also haploid). The diploid eggs will undergo Meiosis and form daughter cells or eggs that are haploid.
If the haploid egg combines with haploid sperm, the result will be diploid female. If the haploid eggs do not combine with the sperms, they will form haploid males again.
Note: The beehive shows three different types of bees. Queen bee, Worker bees and male or drone bees. Queen bees and worker bees are females and hence diploid and drones are males hence haploid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




