
Explain the mechanism of DNA replication and highlight the role of enzymes in the process.
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: DNA replication is a complex process that takes place during cell division, (S phase, interphase). In this process DNA makes duplicates before the cell divides through meiosis and mitosis.
Complete answer:
• The process of DNA replication begins in definite regions or at a point called the origin of replication (origin), to form a replication fork. Replication occurs within a small opening of the DNA otherwise referred to as Y shaped replication fork (uncoiling of DNA is done by some enzymes eg: Topoisomerase and Helicase),
• The separated strands act as the templates for the synthesis of new strands.
• DNA then replicates in the $5' \to 3'$ direction.
• Deoxyribonucleoside-triose phosphates or the DNTPs act as substrates and it also provides energy for polymerization of nucleotides.
• DNA polymerase is an enzyme that assembles a new DNA strand that is complementary to the template strand.
• Until the entire genome is replicated, along the template strand, DNA polymerase continues to move and add new nucleotides to the growing or complement any strand.
• The DNA polymerase forms one new strand or the leading strand in a continuous stretch in $5' \to 3'$ direction (Continuous synthesis).
• In the $5' \to 3'$ direction, another new strand is formed in small stretches (Okazaki fragments) known as discontinuous synthesis.
• The Okazaki fragments are then joined together by an enzyme called DNA ligase, to form a new strand. This new strand is called a lagging strand.
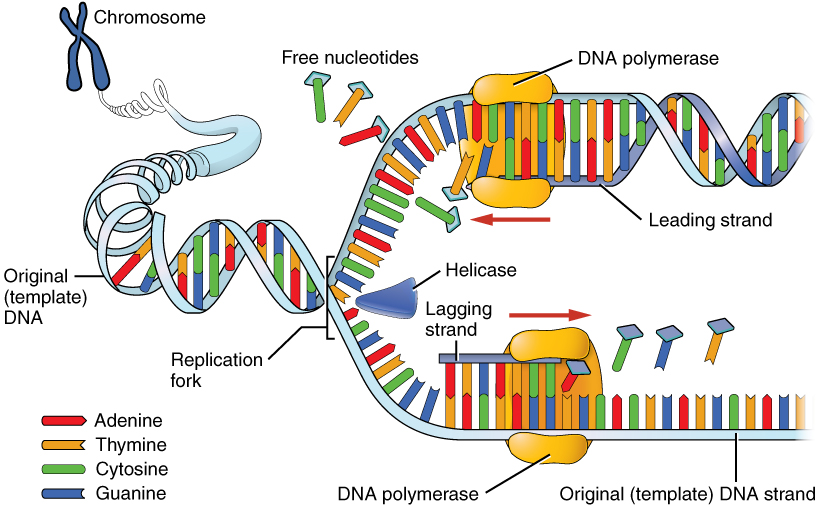
> DNA replication proteins and enzymes.:
DNA polymerase:
These are enzymes that help in the synthesis of DNA by adding nucleotides one by one to the DNA chain that is growing. The enzyme also incorporates complementary amino acids to the template or parent strand.
DNA polymerase is found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. They both contain several various DNA polymerases responsible for different functions in DNA repair mechanisms and DNA replication.
DNA Helicase enzyme:
The enzyme that is involved in unwinding the double-helical structure of DNA is the DNA helicase enzyme and thereby allowing DNA replication to commence.
The energy released during ATP hydrolysis is used to break the hydrogen bond between the DNA bases and then separate the strands.
This forms two replication forks on each separated strand which opens up in the opposite directions.
The parental DNA strand must unwind at each replication fork, exposing new sections of single-stranded templates.
The helicase enzyme accurately unwinds the strands and also maintains the topography on the DNA molecule.
DNA primase enzyme:
This is a type of RNA polymerase enzyme that is used to generate or synthesize RNA primers, which are short RNA molecules that act as the templates for the initiation of DNA replication.
DNA ligase enzyme:
DNA fragments are joined together by forming phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides. This is the enzyme involved in this joining.
Exonuclease:
From the end of a DNA chain nucleotide bases are removed using this group of enzymes.
Topoisomerase:
During unwinding, these enzyme solves the problem of the topological stress
One or both strands of the DNA are cut by these enzymes, and before it rejoins the ends, allowing the strand to move around each other to release tension.
By joining the broken strands, the enzyme catalysts the reversible breakage.
In E. coli, this enzyme is also known as DNA gyrase.
Telomerase:
This is an enzyme found in eukaryotic cells. These enzymes add a specific sequence of DNA to the telomeres of chromosomes after they divide, by stabilizing the chromosomes over time.
Note: DNA replication is a semi conservative process. Here, a parental strand also referred to as a template is used to synthesize a new complementary daughter strand using several protein elements that include RNA molecules and enzymes.
Complete answer:
• The process of DNA replication begins in definite regions or at a point called the origin of replication (origin), to form a replication fork. Replication occurs within a small opening of the DNA otherwise referred to as Y shaped replication fork (uncoiling of DNA is done by some enzymes eg: Topoisomerase and Helicase),
• The separated strands act as the templates for the synthesis of new strands.
• DNA then replicates in the $5' \to 3'$ direction.
• Deoxyribonucleoside-triose phosphates or the DNTPs act as substrates and it also provides energy for polymerization of nucleotides.
• DNA polymerase is an enzyme that assembles a new DNA strand that is complementary to the template strand.
• Until the entire genome is replicated, along the template strand, DNA polymerase continues to move and add new nucleotides to the growing or complement any strand.
• The DNA polymerase forms one new strand or the leading strand in a continuous stretch in $5' \to 3'$ direction (Continuous synthesis).
• In the $5' \to 3'$ direction, another new strand is formed in small stretches (Okazaki fragments) known as discontinuous synthesis.
• The Okazaki fragments are then joined together by an enzyme called DNA ligase, to form a new strand. This new strand is called a lagging strand.

> DNA replication proteins and enzymes.:
DNA polymerase:
These are enzymes that help in the synthesis of DNA by adding nucleotides one by one to the DNA chain that is growing. The enzyme also incorporates complementary amino acids to the template or parent strand.
DNA polymerase is found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. They both contain several various DNA polymerases responsible for different functions in DNA repair mechanisms and DNA replication.
DNA Helicase enzyme:
The enzyme that is involved in unwinding the double-helical structure of DNA is the DNA helicase enzyme and thereby allowing DNA replication to commence.
The energy released during ATP hydrolysis is used to break the hydrogen bond between the DNA bases and then separate the strands.
This forms two replication forks on each separated strand which opens up in the opposite directions.
The parental DNA strand must unwind at each replication fork, exposing new sections of single-stranded templates.
The helicase enzyme accurately unwinds the strands and also maintains the topography on the DNA molecule.
DNA primase enzyme:
This is a type of RNA polymerase enzyme that is used to generate or synthesize RNA primers, which are short RNA molecules that act as the templates for the initiation of DNA replication.
DNA ligase enzyme:
DNA fragments are joined together by forming phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides. This is the enzyme involved in this joining.
Exonuclease:
From the end of a DNA chain nucleotide bases are removed using this group of enzymes.
Topoisomerase:
During unwinding, these enzyme solves the problem of the topological stress
One or both strands of the DNA are cut by these enzymes, and before it rejoins the ends, allowing the strand to move around each other to release tension.
By joining the broken strands, the enzyme catalysts the reversible breakage.
In E. coli, this enzyme is also known as DNA gyrase.
Telomerase:
This is an enzyme found in eukaryotic cells. These enzymes add a specific sequence of DNA to the telomeres of chromosomes after they divide, by stabilizing the chromosomes over time.
Note: DNA replication is a semi conservative process. Here, a parental strand also referred to as a template is used to synthesize a new complementary daughter strand using several protein elements that include RNA molecules and enzymes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




