
Explain the effect of the inductive effect on the reactivity of alkyl halides.
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: Halogen group is an electron-withdrawing group because it requires only one electron to become stable. So it acquires a negative charge and the alkyl group will acquire a positive charge.
Complete step by step solution:
The displacement of $\sigma -electrons$ along the saturated carbon chain whenever an electron-withdrawing or electron-donating group is present at the end of the carbon chain is called inductive effect or I-effect.
–I-Effect is when the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron-withdrawing.
+I-Effect is when the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron-donating.
So, when the atom or group like halogen which is an electron-withdrawing group attached to the alkyl carbon chain, the $\sigma -electrons$ of $C-X$ are attracted by or displaced to the more electronegative atom i.e., halogen atom. Due to which the halogen atom will acquire a small negative charge and the carbon atom of the alkyl group will acquire a small positive charge.
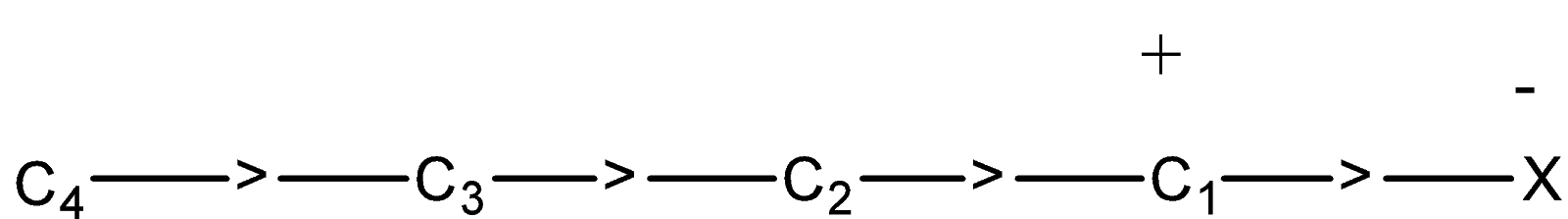
Now in this chain, there is a positive charge on ${{C}_{1}}$ atom, this, in turn, attracts the $\sigma -electrons$ of ${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{2}}$ bond towards it. Due to this ${{C}_{2}}$ will also have some positive charge and this, in turn, will attract the electrons of ${{C}_{2}}-{{C}_{3}}$ bond towards it. Due to this ${{C}_{3}}$ will also acquire a very small positive charge.
So, the reactivity of alkyl halide due to the inductive effect is that the alkyl part acts as an electron-donating group and the halide acts as an electron-withdrawing group.
Note: The same process occurs when an electron-donating group is attached to the alkyl group, but the difference is that the alkyl group will acquire the negative charge and the electron-donating group will acquire the positive charge.
Complete step by step solution:
The displacement of $\sigma -electrons$ along the saturated carbon chain whenever an electron-withdrawing or electron-donating group is present at the end of the carbon chain is called inductive effect or I-effect.
–I-Effect is when the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron-withdrawing.
+I-Effect is when the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron-donating.
So, when the atom or group like halogen which is an electron-withdrawing group attached to the alkyl carbon chain, the $\sigma -electrons$ of $C-X$ are attracted by or displaced to the more electronegative atom i.e., halogen atom. Due to which the halogen atom will acquire a small negative charge and the carbon atom of the alkyl group will acquire a small positive charge.

Now in this chain, there is a positive charge on ${{C}_{1}}$ atom, this, in turn, attracts the $\sigma -electrons$ of ${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{2}}$ bond towards it. Due to this ${{C}_{2}}$ will also have some positive charge and this, in turn, will attract the electrons of ${{C}_{2}}-{{C}_{3}}$ bond towards it. Due to this ${{C}_{3}}$ will also acquire a very small positive charge.
So, the reactivity of alkyl halide due to the inductive effect is that the alkyl part acts as an electron-donating group and the halide acts as an electron-withdrawing group.
Note: The same process occurs when an electron-donating group is attached to the alkyl group, but the difference is that the alkyl group will acquire the negative charge and the electron-donating group will acquire the positive charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




