
Explain different types of placentation in detail.
Answer
348.3k+ views
Hint: Placentation refers to how the ovules and developing seeds are fixed to the plant's ovary. Every single developing seed will fix with the ovary wall or a central structure in the ovary. A filament of plant tissue is defined as the funiculus that attaches the seed to the ovary wall.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Placentation indicates the structure, kind, formation and or arrangement of placentas. The area of the ovary wall in which the ovules are connected in a flower is known as the placenta. Several kinds of placentations found in flowering plants are
Marginal placentation: The placenta creates a ridge along through the ventral suture of the ovary, ovules are borne on the ridge to form two rows. Example: Pea
Axile placentation: The placenta is axial, and ovules are connected to it in a multilocular ovary. Example: Lemon
Parietal placentation: Ovules evolve on the peripheral or on the inner wall of the ovary. It is single-chambered, but because of the development of a false septum, it turns into two-chambered. Example: Mustard
Basal placentation: The placenta evolves at the base of the ovary in which a single ovule is connected to it. Example: Marigold
Free central placentation:On the middle axis ovules are borne and septa are not present. Example: Primrose
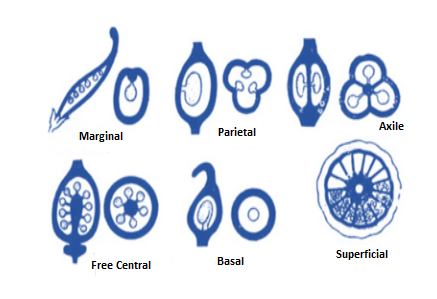
Image: Types of placentation
Note: Placentation is the layout of ovules in the ovary of a plant. The function of placentation is to transmit respiratory gases, nutrients, and water from maternal tissue to a growing embryo, and in certain cases to eliminate waste from the embryo.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Placentation indicates the structure, kind, formation and or arrangement of placentas. The area of the ovary wall in which the ovules are connected in a flower is known as the placenta. Several kinds of placentations found in flowering plants are
Marginal placentation: The placenta creates a ridge along through the ventral suture of the ovary, ovules are borne on the ridge to form two rows. Example: Pea
Axile placentation: The placenta is axial, and ovules are connected to it in a multilocular ovary. Example: Lemon
Parietal placentation: Ovules evolve on the peripheral or on the inner wall of the ovary. It is single-chambered, but because of the development of a false septum, it turns into two-chambered. Example: Mustard
Basal placentation: The placenta evolves at the base of the ovary in which a single ovule is connected to it. Example: Marigold
Free central placentation:On the middle axis ovules are borne and septa are not present. Example: Primrose

Image: Types of placentation
Note: Placentation is the layout of ovules in the ovary of a plant. The function of placentation is to transmit respiratory gases, nutrients, and water from maternal tissue to a growing embryo, and in certain cases to eliminate waste from the embryo.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




