
Explain cyclic structure of glucose.
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: The answer here is based on the basic concept of forms of glucose molecules that exists in the cyclic structure which is called the Haworth structure or the pyranose structure. This fact can lead you to the required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
We have come across the facts about the glucose and its derivatives that come under the class of carbohydrates.
Let us now see in which other forms this molecule can exist and how the structure looks like.
- To start with, let us see what a glucose molecule is. Glucose is the class of compound that comes under the sub category of carbohydrates and its molecular formula is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$ .
- It is a monosaccharide and is the most abundant molecule that occurs naturally in many plants, algae during the process of photosynthesis. During this process, plants and algae make use of water and carbon dioxide along with energy from sunlight here it is used to make cell walls.
- Glucose has two types of projection that is open chain structure called Fischer projection and the ring structure called Haworth projection.
- Glucose has six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group and hence is an aldohexose. The two structures are as shown below,
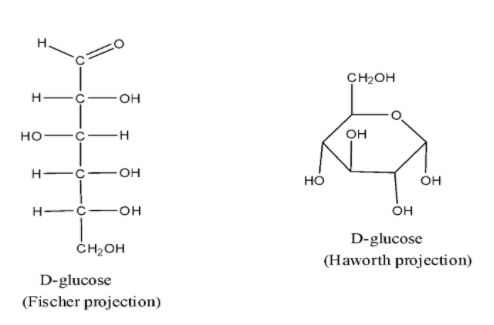
Here, the $-OH$ group of fifth carbon of glucose added to the aldehyde group results in the formation of cyclic hemiacetal that is pyranose structure. This projection is called Haworth projection for glucose.
Note: Glucose is the naturally occurring monosaccharide and is found in the fruits and also other parts of the plants in the free state and in the case of animals, the glucose is released because of the breakdown of the glycogen in the process which is called as glycogenolysis. This fact can help you define the process when the questions are asked on this basis.
Complete step by step answer:
We have come across the facts about the glucose and its derivatives that come under the class of carbohydrates.
Let us now see in which other forms this molecule can exist and how the structure looks like.
- To start with, let us see what a glucose molecule is. Glucose is the class of compound that comes under the sub category of carbohydrates and its molecular formula is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$ .
- It is a monosaccharide and is the most abundant molecule that occurs naturally in many plants, algae during the process of photosynthesis. During this process, plants and algae make use of water and carbon dioxide along with energy from sunlight here it is used to make cell walls.
- Glucose has two types of projection that is open chain structure called Fischer projection and the ring structure called Haworth projection.
- Glucose has six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group and hence is an aldohexose. The two structures are as shown below,

Here, the $-OH$ group of fifth carbon of glucose added to the aldehyde group results in the formation of cyclic hemiacetal that is pyranose structure. This projection is called Haworth projection for glucose.
Note: Glucose is the naturally occurring monosaccharide and is found in the fruits and also other parts of the plants in the free state and in the case of animals, the glucose is released because of the breakdown of the glycogen in the process which is called as glycogenolysis. This fact can help you define the process when the questions are asked on this basis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Prove that a parallelogram circumscribing a circle-class-12-maths-CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

The probability that a leap year will have only 52 class 12 maths CBSE




