
What is the electron dot diagram of magnesium oxide?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: Electron dot diagrams represent the total valence electrons of any atoms drawn around the symbol of that atom. For it, the total valence electrons have to be calculated. Magnesium oxide consists of magnesium and oxygen and has the formula MgO, which consist of ionic bonds.
Complete answer:
Electron dot diagram or structure is the diagram that represents the electrons of an atom, that are present in the valence shell in the form of dots. These dots are made around the symbol of the atom. For compounds, the total valence electrons are calculated and then distributed as bond pairs and lone pairs. But for ionic compounds the cations that lose electrons having a positive charge and the anions that gain electrons having a negative charge are written with their respective charges.
The magnesium oxide molecule consists of magnesium and oxygen in the formula MgO. They form an ionic bond as, magnesium being a metal has 2 electrons in its valence shells, so it gives these 2 electrons to oxygen that has 6 electrons in its valence shell to complete its octet.
So, magnesium contains 2 electrons and oxygen consist 6 valence electrons as,
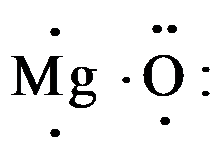
When magnesium donates 2 valence electrons it acquires a charge of 2+ and becomes, $M{{g}^{2+}}$ , and oxygen which gains 2 electrons acquire all the 8 valence electrons and have charge of 2-; so the electron dot structure of magnesium oxide is drawn as,
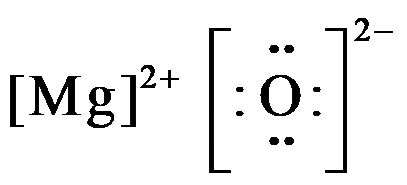
Hence, the electron dot diagram for magnesium oxide consists of magnesium in $M{{g}^{2+}}$form, and oxygen shown with 8 valence electrons (dots) with a negative charge of 2.
Note:
The electron dot diagram of any atom or molecule is also called the Lewis dot structure of atoms. This representation consists of rules like, total valence electrons are added for combining atoms, the more electronegative atom acquires the central position in polyatomic molecules, and the electrons are distributed as lone and bond pairs.
Complete answer:
Electron dot diagram or structure is the diagram that represents the electrons of an atom, that are present in the valence shell in the form of dots. These dots are made around the symbol of the atom. For compounds, the total valence electrons are calculated and then distributed as bond pairs and lone pairs. But for ionic compounds the cations that lose electrons having a positive charge and the anions that gain electrons having a negative charge are written with their respective charges.
The magnesium oxide molecule consists of magnesium and oxygen in the formula MgO. They form an ionic bond as, magnesium being a metal has 2 electrons in its valence shells, so it gives these 2 electrons to oxygen that has 6 electrons in its valence shell to complete its octet.
So, magnesium contains 2 electrons and oxygen consist 6 valence electrons as,
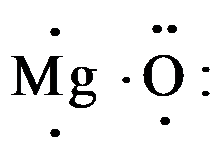
When magnesium donates 2 valence electrons it acquires a charge of 2+ and becomes, $M{{g}^{2+}}$ , and oxygen which gains 2 electrons acquire all the 8 valence electrons and have charge of 2-; so the electron dot structure of magnesium oxide is drawn as,
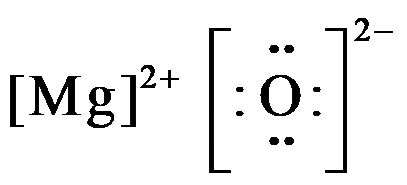
Hence, the electron dot diagram for magnesium oxide consists of magnesium in $M{{g}^{2+}}$form, and oxygen shown with 8 valence electrons (dots) with a negative charge of 2.
Note:
The electron dot diagram of any atom or molecule is also called the Lewis dot structure of atoms. This representation consists of rules like, total valence electrons are added for combining atoms, the more electronegative atom acquires the central position in polyatomic molecules, and the electrons are distributed as lone and bond pairs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




