
During acetylation of amines, what is replaced by acetyl group?
A. Hydrogen atom attached to a nitrogen atom.
B. One or more hydrogen atoms attached to a carbon atom.
C. One or more hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen atoms.
D. Hydrogen atoms attached to either carbon atom or nitrogen atom.
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: Amines are the organic compounds formed by the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia molecules by the alkyl or aryl group. Depending upon the basis of the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by the alkyl or aryl groups, the amines are classified into three categories namely; primary, secondary and tertiary.
Complete Step by step answer: Amines are the organic compounds formed by the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia molecules by the alkyl or aryl group. Depending upon the basis of the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by the alkyl or aryl groups, the amines are classified into three categories namely; primary, secondary and tertiary.
We know that acetylation is the chemical reaction in which acetyl functional groups are introduced to the organic compounds. It is also referred to as acylation. During the process of acetylation, the acetyl group replaces one or more active hydrogen atom(s) of the respective compounds. The acetyl group is represented by $C{H_3}CO - $.
The acetylation / acylation of amines takes place when the acetyl group substitutes the active hydrogen atom(s) attached to the nitrogen atom of the amine. This can take place by the attack of acetyl chloride on ammines.
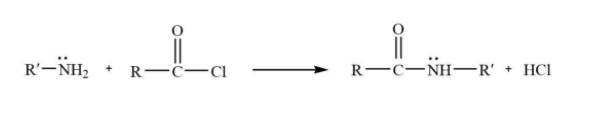
Now, we can see in the other example that acetyl group is replaced-
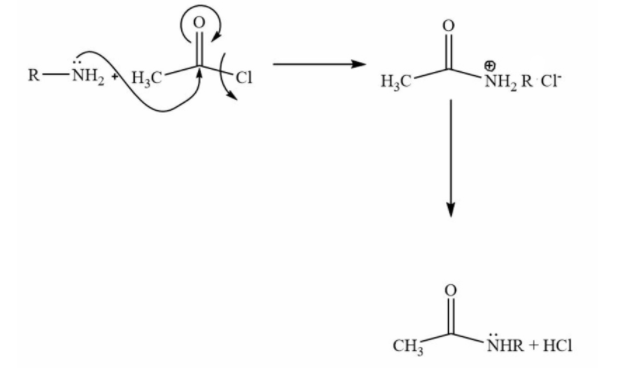
This is an excellent example of nucleophilic acyl substitution. In this reaction nitrogen’s lone pair will attack at the electrophilic site at the carbonyl carbon. Then there will be the removal of the leaving group. In this case chlorine is the leaving group.
Hence, option (C) One or more hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen atoms, is the correct option.
Note: Thus, the condition for this reaction there must be a presence of hydrogen atom on nitrogen atom. So primary and secondary amines only will react with acid halides to form corresponding amides.
Complete Step by step answer: Amines are the organic compounds formed by the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia molecules by the alkyl or aryl group. Depending upon the basis of the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by the alkyl or aryl groups, the amines are classified into three categories namely; primary, secondary and tertiary.
We know that acetylation is the chemical reaction in which acetyl functional groups are introduced to the organic compounds. It is also referred to as acylation. During the process of acetylation, the acetyl group replaces one or more active hydrogen atom(s) of the respective compounds. The acetyl group is represented by $C{H_3}CO - $.
The acetylation / acylation of amines takes place when the acetyl group substitutes the active hydrogen atom(s) attached to the nitrogen atom of the amine. This can take place by the attack of acetyl chloride on ammines.

Now, we can see in the other example that acetyl group is replaced-

This is an excellent example of nucleophilic acyl substitution. In this reaction nitrogen’s lone pair will attack at the electrophilic site at the carbonyl carbon. Then there will be the removal of the leaving group. In this case chlorine is the leaving group.
Hence, option (C) One or more hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen atoms, is the correct option.
Note: Thus, the condition for this reaction there must be a presence of hydrogen atom on nitrogen atom. So primary and secondary amines only will react with acid halides to form corresponding amides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




