
During a coordinate bond formation:
a.) One electron from an atom is transferred to other
b.) One electron is lost from both the atoms
c.) A pair of electrons are contributed by one atom and shared by both the atoms
d.) A pair of electrons are transferred to the other atom
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: A coordinate bond is a covalent bond formed between two atoms in which the shared pair of electrons is contributed by only one of the atoms.
Complete answer:
A coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond formed between two species in which a shared pair of electrons is denoted by one species only but shared by both species. It is also known as a dative bond.
For example:
${ NH }_{ 3 }$ shares the pair of electrons present on Nitrogen with ${ BF }_{ 3 }$, which is electron deficient.
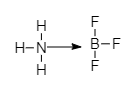
Hence when in a bond between two species both the electrons are donated by one atom (unlike a covalent bond in which both the atoms donate one electron each), the bond will be a coordinate bond. The coordinate bond is denoted by an arrow from the donor atom of the electron-donating species to the acceptor atom of the electron-deficient species.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Additional Information: Characteristics of Co-ordinate bond:
In this kind of bonding, the molecule that shares an electron pair from itself is named as the donor.
The other ion which acknowledges these common pairs of electrons is known as a receptor or acceptor.
The bond is shown with an arrow → pointing towards the acceptor from the donator.
Subsequent to the sharing of the electron pair every ion gets stability.
This sort of bonding is integral to the Lewis Theory.
Getting a decent comprehension of the coordination bonds can help inappropriately structuring complex organic particles.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option A. But one electron from an atom is transferred to another is known as an ionic bond, not a coordinate bond.
Complete answer:
A coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond formed between two species in which a shared pair of electrons is denoted by one species only but shared by both species. It is also known as a dative bond.
For example:
${ NH }_{ 3 }$ shares the pair of electrons present on Nitrogen with ${ BF }_{ 3 }$, which is electron deficient.

Hence when in a bond between two species both the electrons are donated by one atom (unlike a covalent bond in which both the atoms donate one electron each), the bond will be a coordinate bond. The coordinate bond is denoted by an arrow from the donor atom of the electron-donating species to the acceptor atom of the electron-deficient species.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Additional Information: Characteristics of Co-ordinate bond:
In this kind of bonding, the molecule that shares an electron pair from itself is named as the donor.
The other ion which acknowledges these common pairs of electrons is known as a receptor or acceptor.
The bond is shown with an arrow → pointing towards the acceptor from the donator.
Subsequent to the sharing of the electron pair every ion gets stability.
This sort of bonding is integral to the Lewis Theory.
Getting a decent comprehension of the coordination bonds can help inappropriately structuring complex organic particles.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option A. But one electron from an atom is transferred to another is known as an ionic bond, not a coordinate bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




