
Draw a well-labeled diagram of an antibody molecule.
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: An antibody (Ab), otherwise called immunoglobulin (Ig),[1] is a huge, Y-formed protein delivered mostly by plasma cells that are utilized by the safe framework to kill microorganisms, for example, pathogenic microbes and infections. The antibody perceives a novel particle of the microorganism, called an antigen, by means of the piece antigen-official (Fab) variable region.
Complete answer:
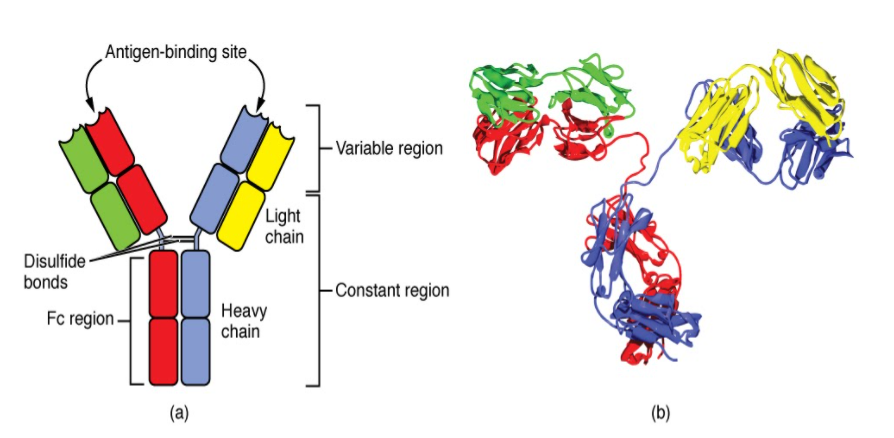
Antibodies are resistant framework related proteins called immunoglobulins. Every counteracting agent comprises four polypeptides–two substantial chains and two light ties joined to frame a "Y" molded atom.
The amino corrosive grouping in the tips of the "Y" changes extraordinarily among various antibodies. This variable area, made out of 110-130 amino acids, gives the immune response its particularity for restricting antigen. The variable area incorporates the finishes of the light and hefty chains. Treating the immune response with a protease can divide this area, delivering Fab or section antigen restricting that incorporates the variable finishes of a counteracting agent. The material utilized for the investigations that appeared underneath started from Fab.
The steady area decides the system used to decimate the antigen. Antibodies are separated into five significant classes, IgM, IgG, Iga, IgD, and IgE, in view of their consistent locale structure and resistant capacity.
The variable area is additionally partitioned into hypervariable (HV) and structure (FR) locales. Hypervariable districts have a high proportion of various amino acids in a given position, comparative with the most widely recognized amino corrosive in that position. Inside light and weighty chains, three hypervariable areas exist – HV 1, 2, and 3. Four FR areas that have more steady amino acids arrangements separate the HV locales.
Note:
The HV districts straightforwardly contact a part of the antigen's surface. Hence, HV districts are additionally at times alluded to as complementarity deciding areas or CDRs. The FR districts structure a beta-sheet structure which fills in as a framework to hold the HV locales in position to contact antigen.
Complete answer:

Antibodies are resistant framework related proteins called immunoglobulins. Every counteracting agent comprises four polypeptides–two substantial chains and two light ties joined to frame a "Y" molded atom.
The amino corrosive grouping in the tips of the "Y" changes extraordinarily among various antibodies. This variable area, made out of 110-130 amino acids, gives the immune response its particularity for restricting antigen. The variable area incorporates the finishes of the light and hefty chains. Treating the immune response with a protease can divide this area, delivering Fab or section antigen restricting that incorporates the variable finishes of a counteracting agent. The material utilized for the investigations that appeared underneath started from Fab.
The steady area decides the system used to decimate the antigen. Antibodies are separated into five significant classes, IgM, IgG, Iga, IgD, and IgE, in view of their consistent locale structure and resistant capacity.
The variable area is additionally partitioned into hypervariable (HV) and structure (FR) locales. Hypervariable districts have a high proportion of various amino acids in a given position, comparative with the most widely recognized amino corrosive in that position. Inside light and weighty chains, three hypervariable areas exist – HV 1, 2, and 3. Four FR areas that have more steady amino acids arrangements separate the HV locales.
Note:
The HV districts straightforwardly contact a part of the antigen's surface. Hence, HV districts are additionally at times alluded to as complementarity deciding areas or CDRs. The FR districts structure a beta-sheet structure which fills in as a framework to hold the HV locales in position to contact antigen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




