
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing steps of PCR?
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: Polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, is a technique for generating several copies of a particular region of DNA. The double stranded DNA should be transformed into single strands to make copies, and each strand can be further amplified.
Complete answer:
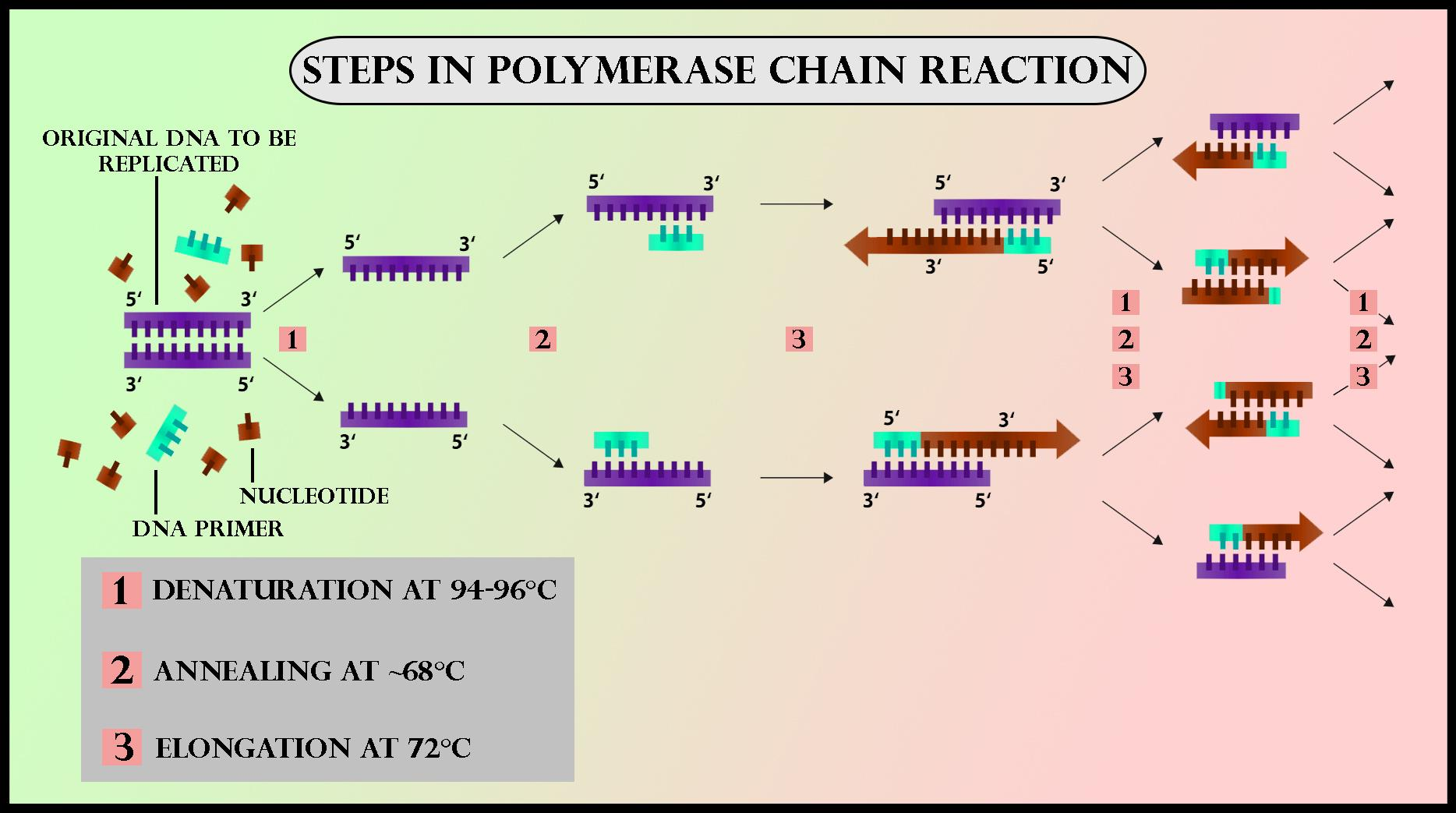
The PCR process includes the following steps.
Step 1: Denaturation
As with DNA replication it is important to separate the two strands in the double helix of DNA.
The separation happens by increasing the mixture temperature, allowing the hydrogen bonds to break down between the complementary DNA strands. That process is known as denaturation.
Step 2: Annealing
The primers bind to the sequences of target DNA and start polymerisation. This can only happen after the solution temperature has decreased. To each strand one primer gets bonded.
Step 3: Extension
New DNA strands are built using the initial strands as templates. An enzyme with DNA polymerase binds together free nucleotides of DNA. This enzyme is also Taq polymerase, an enzyme that was originally isolated from Thermus aquaticus, a thermophilic bacterium. The order in which the free nucleotides are inserted is determined by the nucleotide sequence at the original DNA strand (template).
The outcome of one PCR loop is two double-stranded target DNA sequences, each of which comprises one newly formed strand and one initial strand.
The cycle is repeated several times (usually 20–30), because the majority of processes using PCR involve large amounts of DNA. Having one billion or so copies takes only 2-3 hours.
Additional Information:
The US biochemist Kary Mullis initially invented the polymerase chain reaction ( PCR) in 1983. In 1993 he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his pioneering work. We need 5 key ingredients to perform a PCR. They are the copyable DNA template, primers, DNA nucleotide bases, Taq polymerase enzyme, and buffer.
Note: PCR's purpose is usually to make enough of the target DNA region that it can be analysed or otherwise used. For example, for further studies, DNA amplified by PCR may be sent for sequencing, visualised by gel electrophoresis or cloned into a plasmid. PCR has many practical applications and a lot of testing. It is used regularly in DNA cloning, medical diagnosis and DNA forensic analysis.
Complete answer:
The PCR process includes the following steps.
Step 1: Denaturation
As with DNA replication it is important to separate the two strands in the double helix of DNA.
The separation happens by increasing the mixture temperature, allowing the hydrogen bonds to break down between the complementary DNA strands. That process is known as denaturation.
Step 2: Annealing
The primers bind to the sequences of target DNA and start polymerisation. This can only happen after the solution temperature has decreased. To each strand one primer gets bonded.
Step 3: Extension
New DNA strands are built using the initial strands as templates. An enzyme with DNA polymerase binds together free nucleotides of DNA. This enzyme is also Taq polymerase, an enzyme that was originally isolated from Thermus aquaticus, a thermophilic bacterium. The order in which the free nucleotides are inserted is determined by the nucleotide sequence at the original DNA strand (template).
The outcome of one PCR loop is two double-stranded target DNA sequences, each of which comprises one newly formed strand and one initial strand.
The cycle is repeated several times (usually 20–30), because the majority of processes using PCR involve large amounts of DNA. Having one billion or so copies takes only 2-3 hours.

Additional Information:
The US biochemist Kary Mullis initially invented the polymerase chain reaction ( PCR) in 1983. In 1993 he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his pioneering work. We need 5 key ingredients to perform a PCR. They are the copyable DNA template, primers, DNA nucleotide bases, Taq polymerase enzyme, and buffer.
Note: PCR's purpose is usually to make enough of the target DNA region that it can be analysed or otherwise used. For example, for further studies, DNA amplified by PCR may be sent for sequencing, visualised by gel electrophoresis or cloned into a plasmid. PCR has many practical applications and a lot of testing. It is used regularly in DNA cloning, medical diagnosis and DNA forensic analysis.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




