
What is dominant epistasis, give example.
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: Once the associate degree gene at one locus will mask the expression of each allele at another locus. In alternative words, the expression of 1 gene is disguised by another cistron. This can be conjointly noted as a straightforward epistasis process.
Complete answer:
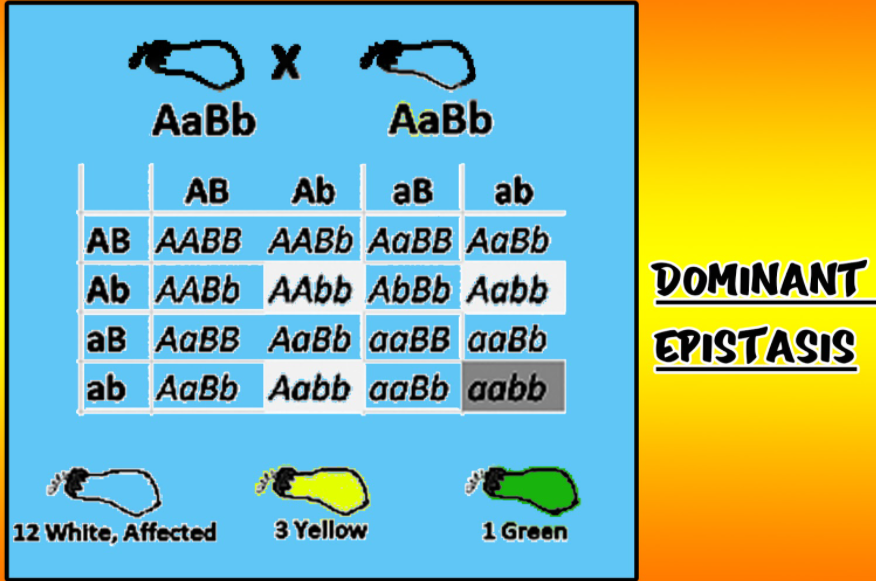
The dominant epistasis process happens once the dominant gene of 1 cistron masks the expression of all alleles of another cistron. If an associate degree organism inherits one or 2 copies of the dominant gene, it'll have the attribute. The diagram given below shows that the inheritance pattern for a trait that shows dominant epistasis when both parents are heterozygous for the trait.
Fruit and flower change plants may be a common example accustomed to illustrate the dominant epistasis process. As shown during this figure, the squash comes in three colors. Yellow (AA, Aa) is dominant over inexperienced (aa). However, since squash color is heritable, or determined by over one cistron, Gene B conjointly determines squash color. As a result of Gene B showing epistasis is a process, it's a lot more necessary than Gene A in determinative squash color.
Additional information:
In the recessive epistasis process, when recessive alleles at one locus mask the expression of each (dominant and recessive) alleles at another locus. This sort of cistron interaction is additionally called a supplementary organic process. A decent example of such cistron interaction is found for grain change maize.
So, one example of Dominant epistasis is Fruit color in squash’.
Note:
During this form of the epistasis process, a dominant gene at one locus will mask the expression of each (dominant and recessive) alleles at the second locus. This can be conjointly called inhibitory gene interaction. An associate degree example of this sort of gene interaction is found for anthocyanin pigmentation in rice.
Complete answer:
The dominant epistasis process happens once the dominant gene of 1 cistron masks the expression of all alleles of another cistron. If an associate degree organism inherits one or 2 copies of the dominant gene, it'll have the attribute. The diagram given below shows that the inheritance pattern for a trait that shows dominant epistasis when both parents are heterozygous for the trait.
Fruit and flower change plants may be a common example accustomed to illustrate the dominant epistasis process. As shown during this figure, the squash comes in three colors. Yellow (AA, Aa) is dominant over inexperienced (aa). However, since squash color is heritable, or determined by over one cistron, Gene B conjointly determines squash color. As a result of Gene B showing epistasis is a process, it's a lot more necessary than Gene A in determinative squash color.
Additional information:
In the recessive epistasis process, when recessive alleles at one locus mask the expression of each (dominant and recessive) alleles at another locus. This sort of cistron interaction is additionally called a supplementary organic process. A decent example of such cistron interaction is found for grain change maize.
So, one example of Dominant epistasis is Fruit color in squash’.
Note:
During this form of the epistasis process, a dominant gene at one locus will mask the expression of each (dominant and recessive) alleles at the second locus. This can be conjointly called inhibitory gene interaction. An associate degree example of this sort of gene interaction is found for anthocyanin pigmentation in rice.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




