
When does crossing over occur in cellular reproduction?
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: Cellular reproduction is the multiplication of cells in a specific manner and cycles which are involved in making cells. Agarose gel is a medium in which DNA travels towards an electrode to show banding. This process is termed as gel electrophoresis. Cell cycles like-meiosis and mitosis are involved in rapid division.
Complete answer-
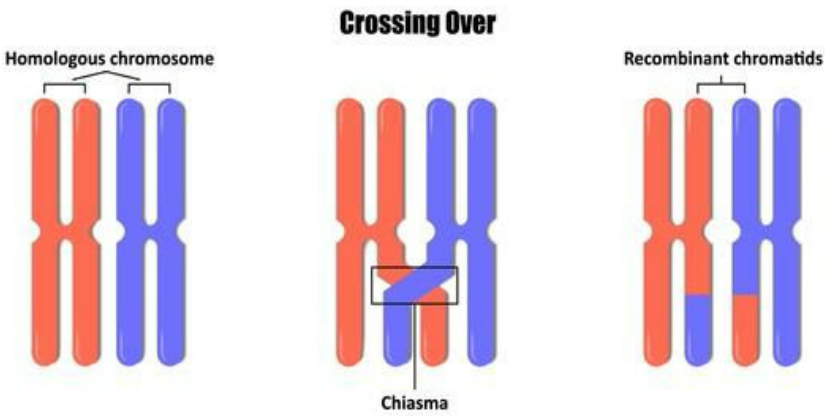
Crossing over is the transfer of genes that happens between chromosome pairs in a process. The difference between recombination and crossing over is crossing over is the sub-part of recombination.
In general, recombination can occur at any moment during a homologous pair up, whether they are tandem, lined up or at the metaphase stage of meiosis. Also, recombinant chromosomes can cross over parent strands to new strands forming new offspring. Crossing over is a subdivision of the recombination process.
While crossing over is the swapping of genetic material which occurs in the germ line. As cells divide, crossing over is common in meiosis where the formation of egg cells and sperm cells takes place while mitosis is the division of daughter cells. Hence, paired chromosomes from each parent align and the DNA sequences having similarity are paired and chromosomes cross over.
Crossing over leads to different combinations of genes from parents. They produce chimeric alleles. Crossing over happens between only homologous chromosomes. Examples-crossing over non-sister chromatids.
Note:
recombination can be performed between different sets of combinations of offspring while crossing over can only exchange the genetic material between non-sister chromatids. There are typically two types of recombination. And also, site-specific and replicative recombination.
Complete answer-
Crossing over is the transfer of genes that happens between chromosome pairs in a process. The difference between recombination and crossing over is crossing over is the sub-part of recombination.
In general, recombination can occur at any moment during a homologous pair up, whether they are tandem, lined up or at the metaphase stage of meiosis. Also, recombinant chromosomes can cross over parent strands to new strands forming new offspring. Crossing over is a subdivision of the recombination process.
While crossing over is the swapping of genetic material which occurs in the germ line. As cells divide, crossing over is common in meiosis where the formation of egg cells and sperm cells takes place while mitosis is the division of daughter cells. Hence, paired chromosomes from each parent align and the DNA sequences having similarity are paired and chromosomes cross over.
Crossing over leads to different combinations of genes from parents. They produce chimeric alleles. Crossing over happens between only homologous chromosomes. Examples-crossing over non-sister chromatids.

Note:
recombination can be performed between different sets of combinations of offspring while crossing over can only exchange the genetic material between non-sister chromatids. There are typically two types of recombination. And also, site-specific and replicative recombination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




