
How is DNA isolated from prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Both the prokaryotic and the eukaryotic cells consist of the DNA present in them. The DNA is extracted from the cells by carrying out various steps. DNA present is double-stranded and is so long that it is compressed in such a way that it can fit in the nuclear membrane of the cell.
Complete answer:
In the DNA isolation procedure, the sample from which DNA needs to be extracted is taken and the sample is made to undergo cell lysis. In this, the cell wall is broken down and then the sample ire made to centrifuge at high speed. The cell debris is removed through this process. After these proteins are denatured using protease. Then they are made to precipitate using the organic solvents in the ratio of 1:1 of a mixture of chloroform and phenol.
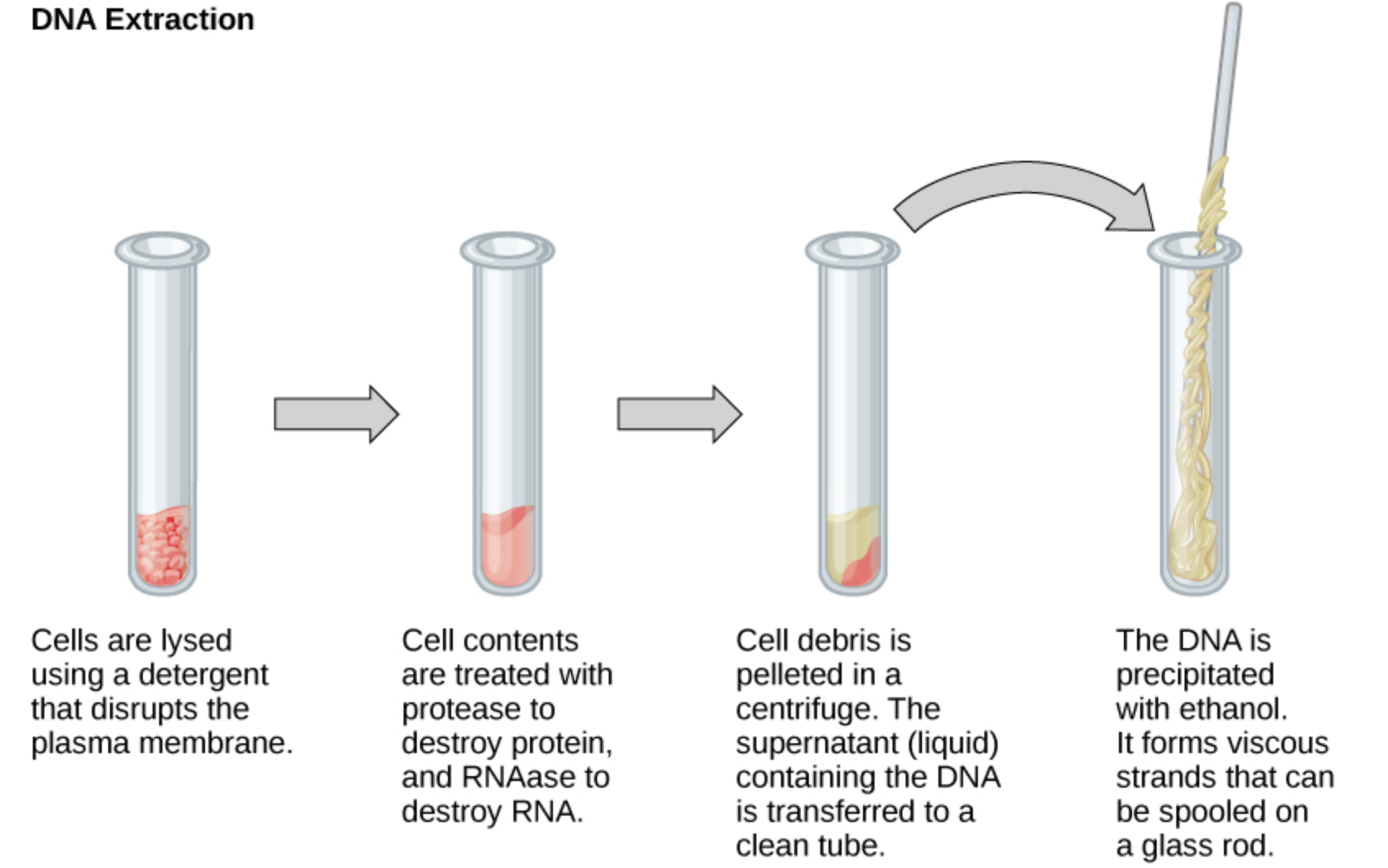
The precipitate is then removed using centrifugation. DNA can be obtained now by the precipitation of the ethanol at -20 degrees Celsius. At very low temperatures the DNA gets precipitated and then can be used for the further study. The microbes are first cultured to a level where they reach maximum density. The DNA isolation from the microbes can be done by lysing the cell using lysozyme or EDTA. Then the cell is removed by the centrifugation. The other steps are the same as done in the plant and animals’ cells.
Note: The lysis of cells using EDTA or lysozyme is necessary to help in the extraction of the DNA from the cell. The use of absolute ethanol should be only done at very low temperatures to facilitate the precipitation of the DNA.
Complete answer:
In the DNA isolation procedure, the sample from which DNA needs to be extracted is taken and the sample is made to undergo cell lysis. In this, the cell wall is broken down and then the sample ire made to centrifuge at high speed. The cell debris is removed through this process. After these proteins are denatured using protease. Then they are made to precipitate using the organic solvents in the ratio of 1:1 of a mixture of chloroform and phenol.

The precipitate is then removed using centrifugation. DNA can be obtained now by the precipitation of the ethanol at -20 degrees Celsius. At very low temperatures the DNA gets precipitated and then can be used for the further study. The microbes are first cultured to a level where they reach maximum density. The DNA isolation from the microbes can be done by lysing the cell using lysozyme or EDTA. Then the cell is removed by the centrifugation. The other steps are the same as done in the plant and animals’ cells.
Note: The lysis of cells using EDTA or lysozyme is necessary to help in the extraction of the DNA from the cell. The use of absolute ethanol should be only done at very low temperatures to facilitate the precipitation of the DNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




