
Diethylenetriamine is:
A) Chelating agent
B) Polydentate ligand
C) Tridentate ligand
D) All of these
Answer
525.6k+ views
Hint: We know that a ligand is a particle or particle, which ties to the focal metal iota to frame a coordination element or complex mixtures. Order of ligands is based on the quantity of restricting destinations with the centre metal iota, charge and size.
Complete answer:
We have to know that a ligand is a particle or particle, which gives a couple of electrons to the focal metal iota or particle to frame a coordination complex. The word ligand is from Latin, which signifies "tie or tie". Ligands can be anions, cations, and unbiased particles. Ligands go about as Lewis bases (give electron sets) and focal metal molecules saw as Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor). The idea of holding between metal to ligand changes from covalent cling to ionic bond.
We must have to remember that the chelating agents are synthetic mixtures that respond with metal particles to shape a steady, water-dissolvable complex. They are otherwise called chelants or chelators. Chelating agents have a ring-like focus which shapes in any event two bonds with the metal particle permitting it to be discharged.
We can draw the structure of Diethylenetriamine as,
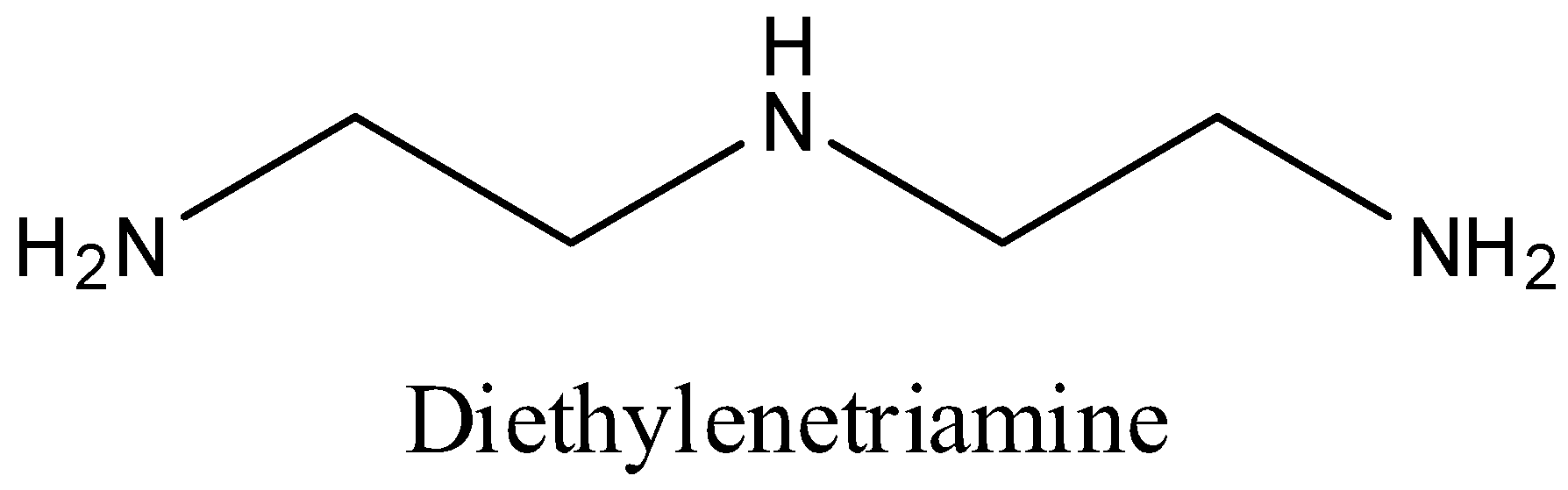
We know that Diethylenetriamine is a tridentate impartial particle with three contributor nitrogen molecules. Polydentate ligand which utilizes it’s at least two benefactor molecules to tie a solitary metal particle creating a ring is called a chelating ligand.
Hence option D is correct.
Note:
We must have to know that diethylenetriamine is the primary simple of diethylene glycol. Its compound properties look like those for ethylene diamine, and it has comparable employment. It is a frail base and its watery arrangement is antacid. DETA is a result of the creation of ethylenediamine from ethylene dichloride.
Complete answer:
We have to know that a ligand is a particle or particle, which gives a couple of electrons to the focal metal iota or particle to frame a coordination complex. The word ligand is from Latin, which signifies "tie or tie". Ligands can be anions, cations, and unbiased particles. Ligands go about as Lewis bases (give electron sets) and focal metal molecules saw as Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor). The idea of holding between metal to ligand changes from covalent cling to ionic bond.
We must have to remember that the chelating agents are synthetic mixtures that respond with metal particles to shape a steady, water-dissolvable complex. They are otherwise called chelants or chelators. Chelating agents have a ring-like focus which shapes in any event two bonds with the metal particle permitting it to be discharged.
We can draw the structure of Diethylenetriamine as,

We know that Diethylenetriamine is a tridentate impartial particle with three contributor nitrogen molecules. Polydentate ligand which utilizes it’s at least two benefactor molecules to tie a solitary metal particle creating a ring is called a chelating ligand.
Hence option D is correct.
Note:
We must have to know that diethylenetriamine is the primary simple of diethylene glycol. Its compound properties look like those for ethylene diamine, and it has comparable employment. It is a frail base and its watery arrangement is antacid. DETA is a result of the creation of ethylenediamine from ethylene dichloride.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




