
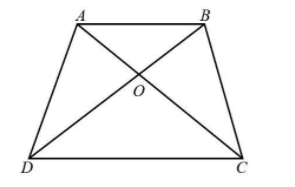
Diagonals AC and BD of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect at O in such a way that $ar(AOD) = ar(BOC)$ . Prove ABCD is a trapezium.

Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: Here, we will use the property that if two triangles lying on the same base have the same area then they both lie between a pair of parallel lines.
Complete Step-by-step Solution
The area of triangles $AOD$and $BOC$are equal that is $ar(AOD) = ar(BOC)$.
To prove that
ABCD is a trapezium.
We can observe from the diagram that in a quadrilateral ABCD the area of the triangle AOD and BOC are equal, we get,
$ar(AOD) = ar(BOC)$
Now, on adding area of triangle $ar(COD)$ on both the sides in the above expression $ar(AOD) = ar(BOC)$, we get the relation,
$ar(AOD) + ar(COD) = ar(BOC) + ar(COD)$
If we observe the diagram, then we can say that in the quadrilateral ABCD the area of triangle AOD and COD is equal to area of triangle ADC that is $ar(AOD) + ar(COD) = ar(ADC)$ and the area of triangle BOC and COD is equal to area of triangle BCD that is $ar(BOC) + ar(COD) = ar(BCD)$.
On putting $ar(AOD) + ar(COD) = ar(ADC)$ and $ar(BOC) + ar(COD) = ar(BCD)$in the above expression, we get the required relation.
$ar(ADC) = ar(BCD)$
Since, we know that ADC and BCD are two triangles of the same area and lie on the same base CD then $AB\parallel CD$.
Therefore, in quadrilateral ABCD one pair of opposite sides is parallel, that is $AB\parallel CD$. Hence, ABCD is a trapezium.
Note: The condition to obtain a trapezium from a quadrilateral is that one pair of opposite sides should be parallel to each other.
Complete Step-by-step Solution
The area of triangles $AOD$and $BOC$are equal that is $ar(AOD) = ar(BOC)$.
To prove that
ABCD is a trapezium.
We can observe from the diagram that in a quadrilateral ABCD the area of the triangle AOD and BOC are equal, we get,
$ar(AOD) = ar(BOC)$
Now, on adding area of triangle $ar(COD)$ on both the sides in the above expression $ar(AOD) = ar(BOC)$, we get the relation,
$ar(AOD) + ar(COD) = ar(BOC) + ar(COD)$
If we observe the diagram, then we can say that in the quadrilateral ABCD the area of triangle AOD and COD is equal to area of triangle ADC that is $ar(AOD) + ar(COD) = ar(ADC)$ and the area of triangle BOC and COD is equal to area of triangle BCD that is $ar(BOC) + ar(COD) = ar(BCD)$.
On putting $ar(AOD) + ar(COD) = ar(ADC)$ and $ar(BOC) + ar(COD) = ar(BCD)$in the above expression, we get the required relation.
$ar(ADC) = ar(BCD)$
Since, we know that ADC and BCD are two triangles of the same area and lie on the same base CD then $AB\parallel CD$.
Therefore, in quadrilateral ABCD one pair of opposite sides is parallel, that is $AB\parallel CD$. Hence, ABCD is a trapezium.
Note: The condition to obtain a trapezium from a quadrilateral is that one pair of opposite sides should be parallel to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




