
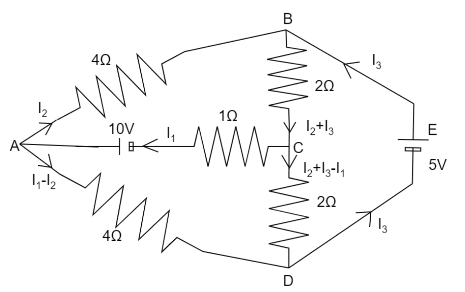
Determine the current in each branch of the network.

Answer
479.4k+ views
Hint: with the help of kirchhoff’s law we can solve this problem. Kirchhoff’s Current law states that, the total of the currents in a junction is equal to the sum of currents outside the junction. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law states that, the sum of the voltages around the closed loop is equal to null.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given network of resistors, we have been given two batteries.
The current from the battery of $ 10V $ is $ {I_1} $ at junction A the current is divided as per the current law. So, in branch AB current is $ {I_2} $ and in branch AD current is $ {I_1} - {I_2} $ . the current from second battery of $ 5V $ to the junction B is $ {I_3} $ therefore current in branch BC will be $ {I_2} + {I_3} $ . at junction C since in branch AC there is $ {I_1} $ current so for branch CD the current will be $ {I_2} + {I_3} - {I_1} $ . now from junction A current $ {I_1} - {I_2} $ is coming so at junction D after the current will combine only $ {I_3} $ will go back to the battery.
Now for loop ACDA, using Kirchhoff’s second (voltage) law which states that in a closed electric circuit the sum of the emf is equal to the sum of the product of resistance and currents flowing through them.
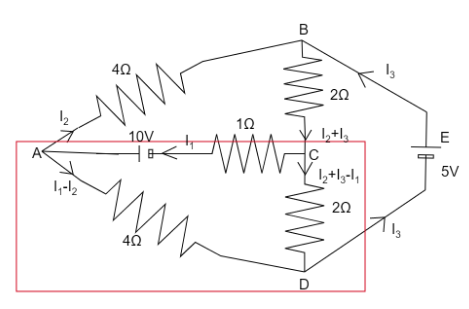
$ 10 = ({I_1} - {I_2})4 - ({I_2} + {I_3} - {I_1})2 + {I_1}(1) $
$ \Rightarrow 7{I_1} - 6{I_2} - 2{I_3} = 10 $ …………….. $ (1) $
For loop ABCA
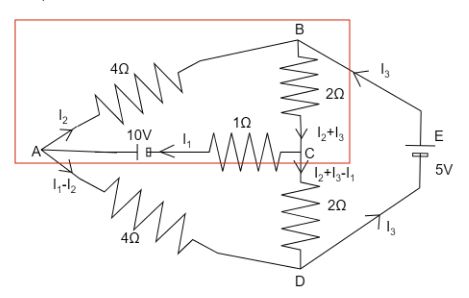
$ - 10 = - {I_2}(4) - ({I_2} + {I_3})(2) - I(1) $
$ \Rightarrow {I_1} + 6{I_2} + 2{I_3} = 10 $ ……………………. $ (2) $
In loop BCDEB
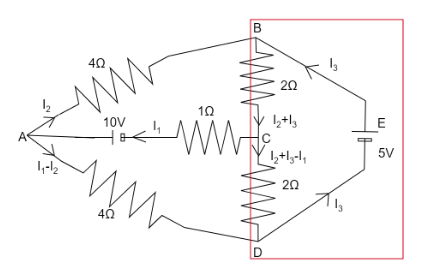
$ 5 = ({I_2} + {I_3})(2) + ({I_2} + {I_3} - {I_1})(2) $
$ - 2{I_1} + 4{I_2} + 4{I_3} = 5 $ ……………… $ (3) $
Adding equation $ (1) $ and $ (2) $ we get,
$ 8{I_1} = 20 $
$ \Rightarrow {I_1} = 2.5A $
Putting value of $ {I_1} $ in equation $ (1) $ we get
$ 7(2.5) - 6{I_2} - 2{I_3} = 10 $
$ \Rightarrow 6{I_2} + 2{I_3} = 7.5 $ ……………………. $ (4) $
Putting value of $ {I_1} $ in equation $ (3) $ we get
$ - 2(2.5) + 4{I_2} + 4{I_3} = 5 $
$ \Rightarrow 2{I_2} + 2{I_3} = 5 $ ……………………. $ (5) $
Solving equation $ (4) $ and $ (5) $
$ 4{I_2} = 2.5 $
$ \Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{5}{8}A $
Finally with this find $ {I_3} $ from equation $ (5) $
$ 2\left( {\dfrac{5}{8}} \right) + 2{I_3} = 5 $
$ \Rightarrow {I_3} = \dfrac{{15}}{8}A $ .
Note:
Because of the charging of energy at the emf source, the source of emf (E) signs positive as the current moves from low to high. Similarly, if the current changes from high to low voltage ( $ + $ to $ - $ ), the source of emf (E) signs negative due to the emf source's energy being depleted.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given network of resistors, we have been given two batteries.
The current from the battery of $ 10V $ is $ {I_1} $ at junction A the current is divided as per the current law. So, in branch AB current is $ {I_2} $ and in branch AD current is $ {I_1} - {I_2} $ . the current from second battery of $ 5V $ to the junction B is $ {I_3} $ therefore current in branch BC will be $ {I_2} + {I_3} $ . at junction C since in branch AC there is $ {I_1} $ current so for branch CD the current will be $ {I_2} + {I_3} - {I_1} $ . now from junction A current $ {I_1} - {I_2} $ is coming so at junction D after the current will combine only $ {I_3} $ will go back to the battery.
Now for loop ACDA, using Kirchhoff’s second (voltage) law which states that in a closed electric circuit the sum of the emf is equal to the sum of the product of resistance and currents flowing through them.

$ 10 = ({I_1} - {I_2})4 - ({I_2} + {I_3} - {I_1})2 + {I_1}(1) $
$ \Rightarrow 7{I_1} - 6{I_2} - 2{I_3} = 10 $ …………….. $ (1) $
For loop ABCA

$ - 10 = - {I_2}(4) - ({I_2} + {I_3})(2) - I(1) $
$ \Rightarrow {I_1} + 6{I_2} + 2{I_3} = 10 $ ……………………. $ (2) $
In loop BCDEB

$ 5 = ({I_2} + {I_3})(2) + ({I_2} + {I_3} - {I_1})(2) $
$ - 2{I_1} + 4{I_2} + 4{I_3} = 5 $ ……………… $ (3) $
Adding equation $ (1) $ and $ (2) $ we get,
$ 8{I_1} = 20 $
$ \Rightarrow {I_1} = 2.5A $
Putting value of $ {I_1} $ in equation $ (1) $ we get
$ 7(2.5) - 6{I_2} - 2{I_3} = 10 $
$ \Rightarrow 6{I_2} + 2{I_3} = 7.5 $ ……………………. $ (4) $
Putting value of $ {I_1} $ in equation $ (3) $ we get
$ - 2(2.5) + 4{I_2} + 4{I_3} = 5 $
$ \Rightarrow 2{I_2} + 2{I_3} = 5 $ ……………………. $ (5) $
Solving equation $ (4) $ and $ (5) $
$ 4{I_2} = 2.5 $
$ \Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{5}{8}A $
Finally with this find $ {I_3} $ from equation $ (5) $
$ 2\left( {\dfrac{5}{8}} \right) + 2{I_3} = 5 $
$ \Rightarrow {I_3} = \dfrac{{15}}{8}A $ .
Note:
Because of the charging of energy at the emf source, the source of emf (E) signs positive as the current moves from low to high. Similarly, if the current changes from high to low voltage ( $ + $ to $ - $ ), the source of emf (E) signs negative due to the emf source's energy being depleted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




