
Describe types of ovules diagrammatically.
Answer
498k+ views
Hint: The ovule is a component of flowering plants that is found inside the gynoecium, which is the flower's female portion. Ovules in the ovary are found to be connected to the placenta by a stalk-like structure. After fertilisation, ovules become seeds.
The embryo sac is present in angiosperm, and after the fusing of the male gametes, it may result in endosperm, which ultimately feeds the children.
Complete answer:
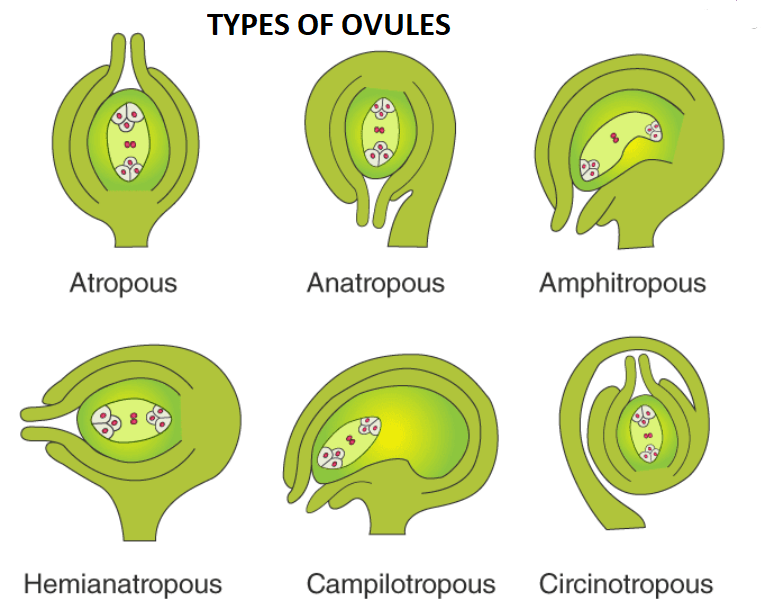
Ovules can be generated in six different ways in Angiosperms. These are the
1. Orthotropous- The micropyle, chalaza, and funicle all lie in one straight line in an orthotropous ovule. Polygonaceae, Piperaceae, and most gymnosperm ovules are examples.
2. Anatropous (Inverted)- The ovule's body is entirely inverted, bringing the micropyle and hilum very close together. This form of ovule can be found in 82 percent of angiosperm families. Plants belonging to the gamopetalae sub-class are an example.
3. Campylotropous- The micropyle is oriented towards chalaza when the ovule is bent. Chalaza is perpendicular to the funicle. Members of the Cruciferae and Leguminosae families, for example.
4. Amphitropous or transverse ovule- The ovule curvature increases, and the embryo sac takes on a horseshoe form. Alismataceae and Butomaceae, for example.
5. Hemianatropous-When the nucellus and integuments are almost perpendicular to the funicle. For instance, the Ranunculaceae and Primulaceae families.
6. Circinotropous- Except for a small section at the end of the funicle, the funicle is extraordinarily lengthy and makes a complete circle around the ovules, which are free of it.Opuntia and other members of the Cactaceae and Plumbaginaceae families are examples.
Note:
The ovules of angiosperms, which are flowering plants, are covered. This stock, which is also known as the funicle or funiculus, connects the placenta of the overview to the placenta. The hilum is the point where the funiculus connects to the ovule's structure. The outer and inner into comment, as well as an embryo sac that is covered inside it, are all present. The nucellus is the part of the embryo sac that lies between the outer and inner integuments. Except for some of the higher sections, which are known as the micropyle, the integument covers the entire nucleus.
The embryo sac is present in angiosperm, and after the fusing of the male gametes, it may result in endosperm, which ultimately feeds the children.
Complete answer:
Ovules can be generated in six different ways in Angiosperms. These are the
1. Orthotropous- The micropyle, chalaza, and funicle all lie in one straight line in an orthotropous ovule. Polygonaceae, Piperaceae, and most gymnosperm ovules are examples.
2. Anatropous (Inverted)- The ovule's body is entirely inverted, bringing the micropyle and hilum very close together. This form of ovule can be found in 82 percent of angiosperm families. Plants belonging to the gamopetalae sub-class are an example.
3. Campylotropous- The micropyle is oriented towards chalaza when the ovule is bent. Chalaza is perpendicular to the funicle. Members of the Cruciferae and Leguminosae families, for example.
4. Amphitropous or transverse ovule- The ovule curvature increases, and the embryo sac takes on a horseshoe form. Alismataceae and Butomaceae, for example.
5. Hemianatropous-When the nucellus and integuments are almost perpendicular to the funicle. For instance, the Ranunculaceae and Primulaceae families.
6. Circinotropous- Except for a small section at the end of the funicle, the funicle is extraordinarily lengthy and makes a complete circle around the ovules, which are free of it.Opuntia and other members of the Cactaceae and Plumbaginaceae families are examples.

Note:
The ovules of angiosperms, which are flowering plants, are covered. This stock, which is also known as the funicle or funiculus, connects the placenta of the overview to the placenta. The hilum is the point where the funiculus connects to the ovule's structure. The outer and inner into comment, as well as an embryo sac that is covered inside it, are all present. The nucellus is the part of the embryo sac that lies between the outer and inner integuments. Except for some of the higher sections, which are known as the micropyle, the integument covers the entire nucleus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




