
Describe the T.S. of spinal cord.
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: Spinal cord generally helps to conduct the information from brain to the effector organs by the help of spinal nerves. The Spinal cord then runs through a hollow case from the skull which is enclosed within the vertebral column.
Complete answer:
Spinal nerves then arise from the different regions of the vertebral column and are then named accordingly, the regions normally are – Neck, chest, pelvic and the abdominal.
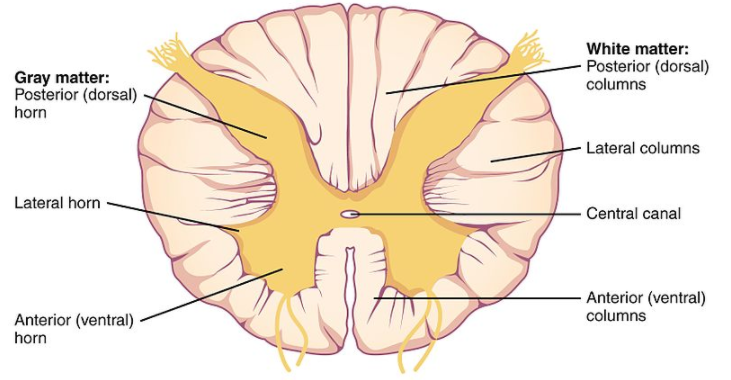
• Cross section of the-spinal cord then displays the grey matter which is shaped like a butterfly surrounded by the white matter.
• Grey matter generally consists of the central canal which is at the centre and is normally filled with a fluid which is called CSF (or Cerebrospinal fluid). It consists of the horns (four projections) and then forms the core mainly containing neurons and the cells of the CNS. There are 2 dorsal & two ventral horns.
• The white matter consists of the collection of axons which permits communication b/w different layers of the CNS. A tract is a collection of the axons and then carries specialised information. Ascending tracts and the descending tracts then send and transmit signals from the brain to the various nerve cells across the body.
• Spinal nerves then act as mediators which communicates information to & from the rest of the body & the spinal cord. We normally have 31 pairs of the spinal nerves.
• Three layers of meninges normally surround the spinal cord and the spinal nerve roots.
1. Dura mater
2. Arachnoid mater
3. Pia mater
• Dura mater normally consists of 2 layers which is the periosteal and meningeal. Epidural space is normally present between the two layers.
• Subarachnoid space generation lies b/w the arachnoid mater & the pia mater. It is filled with a cerebrospinal fluid.
Note: Important functions of The Spinal Cord are the ones mentioned below:
• Forms a connecting link between the brain and the PNS.
• Provides structural support and then builds a body posture.
• It Facilitates flexible movements.
Complete answer:
Spinal nerves then arise from the different regions of the vertebral column and are then named accordingly, the regions normally are – Neck, chest, pelvic and the abdominal.
• Cross section of the-spinal cord then displays the grey matter which is shaped like a butterfly surrounded by the white matter.
• Grey matter generally consists of the central canal which is at the centre and is normally filled with a fluid which is called CSF (or Cerebrospinal fluid). It consists of the horns (four projections) and then forms the core mainly containing neurons and the cells of the CNS. There are 2 dorsal & two ventral horns.
• The white matter consists of the collection of axons which permits communication b/w different layers of the CNS. A tract is a collection of the axons and then carries specialised information. Ascending tracts and the descending tracts then send and transmit signals from the brain to the various nerve cells across the body.
• Spinal nerves then act as mediators which communicates information to & from the rest of the body & the spinal cord. We normally have 31 pairs of the spinal nerves.
• Three layers of meninges normally surround the spinal cord and the spinal nerve roots.
1. Dura mater
2. Arachnoid mater
3. Pia mater
• Dura mater normally consists of 2 layers which is the periosteal and meningeal. Epidural space is normally present between the two layers.
• Subarachnoid space generation lies b/w the arachnoid mater & the pia mater. It is filled with a cerebrospinal fluid.

Note: Important functions of The Spinal Cord are the ones mentioned below:
• Forms a connecting link between the brain and the PNS.
• Provides structural support and then builds a body posture.
• It Facilitates flexible movements.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




