
Describe the structure of the heart of a man. Draw a neat labeled diagram of it.
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: It is a form of self-pollination that is often different from the fertilization that may result from it. In monoecious gymnosperms, it also occurs.
Complete answer:
First we should know about the human heart to answer this question. The human heart consists of four chambers. Two atriums (auricles) and two ventricles are present. The chambers of the ventricles are larger than the auricles. Compared to the ventricles, the auricles are thin-walled. The interauricular septum divides the right auricle from the left auricle. The aperture is defined as a sinu-auricular aperture in the right ventricle. Valves guard this aperture. In the left auricle, by an oblique aperture, the pulmonary vein expands. This aperture has no ports. The two auricles are isolated by the auriculo-ventricular septum from the ventricles. Via the auriculo-ventricular aperture, the right and left auricles expand into the ventricle. The ventricular aperture of the auriculum is protected by the ventricular atrium valve. Four flaps are present in the valve. At the margin of the four flaps of such a valve, chordae tendinae are connected. Strings like chords that are connected to the muscular wall of the ventricle at their other ends are chordae tendineae.
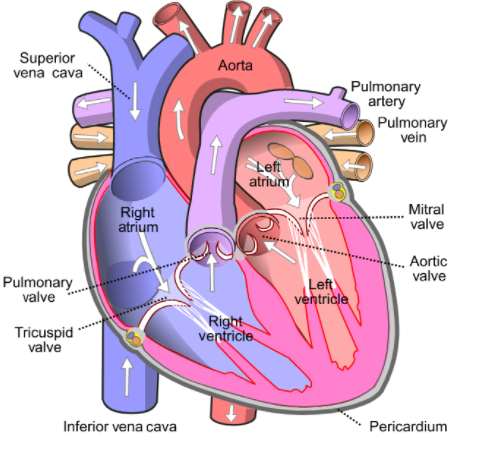
From the anterior and ventral portion of the ventricle, Truncus arteriosus emerges. On the ventral side of the right auricle, this segment runs obliquely. There have been three semilunar valves in the truncus arteriosus at the proximal end. Conus arteriosus is regarded as the basal, wide and thick-walled component of the truncus arteriosus. The ventral aorta is defined as the lateral, thin-walled and slender part of the truncus arteriosus. The conus arteriosus includes the spinal valve. Thisvalves separates the conus arteriosus lumen into a left pulmocutaneous cavum and a right aortic cavum. By pulmocutaneous arches, the blood accessing the cavum pulmocutaneous joins. Two lateral aortae separate the ventral aorta. Two arches, the carotid arch and the systemic arch, separate each lateral aorta.
Note:In a rhythm decided by a collective of pacemaking cells as in sinoatrial nodes, the heart pumps blood. This creates a current that allows the heart to contract; pass via the atrioventricular node and down the heart conduction pathway.
Complete answer:
First we should know about the human heart to answer this question. The human heart consists of four chambers. Two atriums (auricles) and two ventricles are present. The chambers of the ventricles are larger than the auricles. Compared to the ventricles, the auricles are thin-walled. The interauricular septum divides the right auricle from the left auricle. The aperture is defined as a sinu-auricular aperture in the right ventricle. Valves guard this aperture. In the left auricle, by an oblique aperture, the pulmonary vein expands. This aperture has no ports. The two auricles are isolated by the auriculo-ventricular septum from the ventricles. Via the auriculo-ventricular aperture, the right and left auricles expand into the ventricle. The ventricular aperture of the auriculum is protected by the ventricular atrium valve. Four flaps are present in the valve. At the margin of the four flaps of such a valve, chordae tendinae are connected. Strings like chords that are connected to the muscular wall of the ventricle at their other ends are chordae tendineae.

From the anterior and ventral portion of the ventricle, Truncus arteriosus emerges. On the ventral side of the right auricle, this segment runs obliquely. There have been three semilunar valves in the truncus arteriosus at the proximal end. Conus arteriosus is regarded as the basal, wide and thick-walled component of the truncus arteriosus. The ventral aorta is defined as the lateral, thin-walled and slender part of the truncus arteriosus. The conus arteriosus includes the spinal valve. Thisvalves separates the conus arteriosus lumen into a left pulmocutaneous cavum and a right aortic cavum. By pulmocutaneous arches, the blood accessing the cavum pulmocutaneous joins. Two lateral aortae separate the ventral aorta. Two arches, the carotid arch and the systemic arch, separate each lateral aorta.
Note:In a rhythm decided by a collective of pacemaking cells as in sinoatrial nodes, the heart pumps blood. This creates a current that allows the heart to contract; pass via the atrioventricular node and down the heart conduction pathway.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




