
Describe the replication of HIV with schematic representation of the life cycle of HIV.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint:- In order for you to arrive at an answer, try to understand the meaning of the replication cycle. Replication in viruses begins only when it hijacks the host machinery to produce new cells. The viruses act as non-living bodies outside a host body. However, when they enter the body of the host, they start to behave as living bodies.
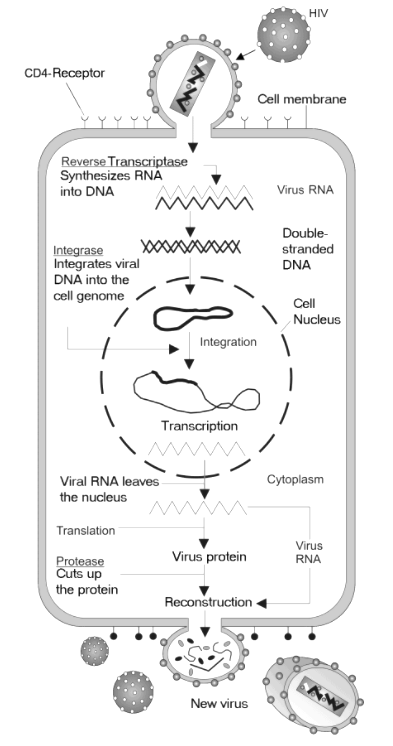
Complete Answer:-The life cycle of HIV begins when it attaches to the host cell. In the first step, the virus fuses with the host cell surface and a capsid containing the viral genome and proteins which are injected into the cell. After the viral genome and protein enter the host cell, the disintegration of the capsid takes place and reverse transcriptase enters the cell. This helps in the transcribing of the viral RNA to DNA. The viral DNA passes through the nucleus where another important HIV protein called the integrase integrates the viral DNA along with the DNA of the host. The host cell machinery is now hijacked. Now the transcription machinery of the host transcribes the HIV DNA that leads to the production of multiple copies of HIV RNA. A part of the new RNA formed becomes incorporated into the viral genome. while the cell uses other copies of the RNA to make new HIV proteins. The new viral RNA and HIV proteins combine to form a new virus.
Note:- HIV attacks the body's immune system and if not treated may read to the serious condition of AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is the last stage of HIV. It takes a long time to develop and once it is developed, it gives rise to certain types of cancer and other clinical issues due to a weakened immune system. The virus enters the body via blood or semen. It is also passed from mother to child during pregnancy.
Complete Answer:-The life cycle of HIV begins when it attaches to the host cell. In the first step, the virus fuses with the host cell surface and a capsid containing the viral genome and proteins which are injected into the cell. After the viral genome and protein enter the host cell, the disintegration of the capsid takes place and reverse transcriptase enters the cell. This helps in the transcribing of the viral RNA to DNA. The viral DNA passes through the nucleus where another important HIV protein called the integrase integrates the viral DNA along with the DNA of the host. The host cell machinery is now hijacked. Now the transcription machinery of the host transcribes the HIV DNA that leads to the production of multiple copies of HIV RNA. A part of the new RNA formed becomes incorporated into the viral genome. while the cell uses other copies of the RNA to make new HIV proteins. The new viral RNA and HIV proteins combine to form a new virus.

Note:- HIV attacks the body's immune system and if not treated may read to the serious condition of AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is the last stage of HIV. It takes a long time to develop and once it is developed, it gives rise to certain types of cancer and other clinical issues due to a weakened immune system. The virus enters the body via blood or semen. It is also passed from mother to child during pregnancy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




